- 著者
- Yuta Fujii Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.1, pp.81-87, 2015-03-25 (Released:2015-04-04)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3 22
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was discovered from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria, and several improvements have been carried out to change its physicochemical properties. The resulting improved GFP variants have been used as reporter proteins for bioimaging techniques in various research fields including plant science. Almost all GFP variants were developed using Escherichia coli to improve fluorescence properties in mammalian cells, but the impact in other organisms such as plant cells remains to be determined. In this study, we performed comparative analysis of four improved GFP variants, GFP-S65T, eGFP, frGFP and sfGFP, with reference to the fluorescence intensity in Arabidopsis protoplasts, and found that sfGFP is the brightest. Using non-fluorescent fragments from the GFP variants, we also conducted bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays to find appropriate fragment pairs of GFP-based BiFC for visualization of protein–protein interactions in living plant cells. Our observations revealed that the brightest is the sfGFP-based BiFC. Further, as an evaluation method for the sfGFP-based BiFC, a BiFC competition assay was successfully completed for the first time in planta. The present study provides useful information for selection and improvement of the GFP molecule and its application to BiFC technology in plants.
- 著者
- Sara Jonasson Johan Eriksson Lotta Berntzon Ulla Rasmussen Birgitta Bergman
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.3, pp.227-232, 2008-06-01 (Released:2008-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 53
- 被引用文献数
- 5 13
The non-protein amino acid β-N-methyl-amino-L-alanine (BMAA) is a neurotoxin that was recently found to be produced by most cyanobacteria. The neurotoxin was discovered in 1967 in the seeds of the cycad Cycas micronesica, but this BMAA may originate from the symbiotic cyanobacterium Nostoc, which inhabits the roots of cycads. BMAA is thought to be the cause of the deadly neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism dementia complex (ALS/PDC), common among the Chamorro people of Guam. It was demonstrated that the Chamorros, in all probability, have been exposed to high levels of BMAA through dietary consumption of flying foxes which fed mainly on cycads seeds. BMAA production may be a common conserved evolutionary feature among cyanobacteria and due to their wide global distribution, the toxin may be a common concern and potentially involved in provoking degenerative diseases worldwide. BMAA may likewise be bioaccumulated in other cyanobacterial based food webs within ecosystems outside Guam, and it is proposed that such webs may exist in the Baltic Sea, with its massive occurrence of cyanobacteria (blooms).
2 0 0 0 OA Perspective: Plant biology—A quiet pioneer
- 著者
- Machi F. Dilworth
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, no.2, pp.183-187, 2009-03-25 (Released:2009-03-27)
- 参考文献数
- 16
The study of plants contributed to establishment of the foundation for modern biology. For example, it was observations first made in plants that led to two fundamental theories of biology—cell theory and genetics. Throughout the 20th century, plant biology continued to make contributions to the conceptual and technological advances in basic biology and biotechnology, although plant biology's contributions were not always recognized by the field of biology at large. Plants have direct applications to today's major societal challenges including food security, climate change, energy, and sustainability. Solutions to these challenges require innovative technologies that are solidly based on science.
- 著者
- Yasumoto Shuhei Umemoto Naoyuki Lee Hyoung Jae Nakayasu Masaru Sawai Satoru Sakuma Tetsushi Yamamoto Takashi Mizutani Masaharu Saito Kazuki Muranaka Toshiya
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.167-173, 2019
- 被引用文献数
- 32
<p>Potato (<i>Solanum tuberosum</i>) is one of the most important crops in the world. However, it is generally difficult to breed a new variety of potato crops because they are highly heterozygous tetraploid. Steroidal glycoalkaloids (SGAs) such as α-solanine and α-chaconine found in potato are antinutritional specialized metabolites. Because of their toxicity following intake, controlling the SGA levels in potato varieties is critical in breeding programs. Recently, genome-editing technologies using artificial site-specific nucleases such as TALEN and CRISPR-Cas9 have been developed and used in plant sciences. In the present study, we developed a highly active Platinum TALEN expression vector construction system, and applied to reduce the SGA contents in potato. Using <i>Agrobacterium-</i>mediated transformation, we obtained three independent transgenic potatoes harboring the TALEN expression cassette targeting SSR2 gene, which encodes a key enzyme for SGA biosynthesis. Sequencing analysis of the target sequence indicated that all the transformants could be <i>SSR2</i>-knockout mutants. Reduced SGA phenotype in the mutants was confirmed by metabolic analysis using LC-MS. In vitro grown <i>SSR2</i>-knockout mutants exhibited no differences in morphological phenotype or yields when compared with control plants, indicating that the genome editing of SGA biosynthetic genes such as <i>SSR2</i> could be a suitable strategy for controlling the levels of toxic metabolites in potato. Our simple and powerful plant genome-editing system, developed in the present study, provides an important step for future study in plant science.</p>
- 著者
- Yamauchi Daisuke
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.3, pp.263-267, 2000-09-01
- 参考文献数
- 20
A gene for Brazil nut 2S albumin, a methionine-rich protein, was fused to a promoter region of the canavalin gene. This chimeric gene was introduced into shoot apices of embryonic axes of French bean by particle bombardment and seeds were obtained from plants regenerated from the bombarded axes. Protein in the transgenic seeds was analyzed by immunoblotting with an antiserum against Brazil nut 2S albumin. A 12-kDa immunoreactive polypeptide was detected and its amount in the seed was estimated to comprise less than 1% of the soluble protein.
- 著者
- 石丸 幹二 荒川 裕子 佐土嶋 信二 山口 義昭
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- 植物組織培養 (ISSN:02895773)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, no.2, pp.191-193, 1993
- 被引用文献数
- 4 15
- 著者
- 田澤 一二 阿部 利徳 笹原 健夫
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- 植物組織培養 = Plant tissue culture letters (ISSN:02895773)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.1, pp.7-14, 1996-04-01
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
本研究では, シオデの節間由来のプロトコーム様体 (PLB) を液体培養することによって大量に形成させ, シオデの大量増殖を可能にした. すなわち, NAAを含む液体培地でシオデのPLBを液体振盈培養することによって, 1個のPLBから大量のPLB (クラスター) を形成させ, これらが幼芽に生長したのち, 一定期間の前培養を行い, ホルモン・フリーの固体培地に移植して発根させ, 大量の植物体を順化させた.<br>さらに, 液体培養したPLB-クラスターから人為的に切り取ったPLBを再度液体培地に移植した. この二次増殖系では, ホルモン・フリーの固体培地に移植することによってより多くのPLB-クラスターおよび幼芽・幼根が形成された. この手法によって, 多循環的にPLB-クラスターおよび植物体の再生・増殖が可能となった.<br>なお, 固体培地と異なり, 液体培地は褐変し, PLBおよびクラスターも褐変し枯死する結果となった. また, 褐変とともに液体培地のpHが低下した. この褐変とpHの低下は, 液体培地を2ないし3日間隔で新鮮培地で交換することによって緩和することができた.
1 0 0 0 アサガオのラクトース耐性および非耐性株における生理的差異
- 著者
- 久島 繁 渡辺 恒夫 新井 勇治 THORPE Trevor A.
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- 植物組織培養 (ISSN:02895773)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.2, pp.52-58, 1985
ラクトース適応のメカニズムを検討するため, アサガオの非耐性および耐性培養株を用いて, いくつかの検討を行った. 両接細胞にラクターゼ, UDP-ガラクトースピロフォスフォリラーゼ, UDP-グルコースピロフォスフォリラーゼおよびUDP-ガラクトースエピメラーゼ活性は存在した. それゆえ, 非適応細胞も潜在的にはラクトース代謝能を持つものと思われた. しかし, この細胞ではUDP-ガラクトースエピメラーゼ活性は極めて弱く, 細胞壁結合型ラクターゼ活性は適応細胞のそれの約30%であった. ラクトース適応細胞をラクトース培地で培養した場合, 培養期間を通じて細胞内グルコース含量は低く, ガラクトース含量は高かった. それゆえ, これらの細胞はガラクトースよりグルコースをプレファレンシャルに利用するものと思われる. ガラクトースに培養した非適応細胞のG-6-P, G-1-PおよびGal-1-Pの含量はショ糖で培養したそれの約3倍であった. また, UDPGおよびUDP galの含量はショ糖で培養した場合のそれぞれ約1.5倍, 僅増であった. それに比して, ガラクトース培養非適応細胞のG-6-P, G-1-P, Gal-1-Pの含量はショ糖培養のそれの約2倍となっており, ガラクトース培養適応細胞のそれより約20%低かった. この事は適応細胞が非適応細胞に比して大きなガラクトースおよびラクトース代謝能を持っている事を示唆している. これらの結果に基づきラクトースおよびガラクトースの阻害とそれに対する適応について論議した.
1 0 0 0 OA Flower color modification of Petunia hybrida commercial varieties by metabolic engineering
- 著者
- Shinzo Tsuda Yuko Fukui Noriko Nakamura Yukihisa Katsumoto Keiko Yonekura-Sakakibara Masako Fukuchi-Mizutani Kazuyuki Ohira Yukiko Ueyama Hideo Ohkawa Timothy A. Holton Takaaki Kusumi Yoshikazu Tanaka
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.21, no.5, pp.377-386, 2004 (Released:2005-06-03)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 35 76
Petunia flower colors are mainly due to flavonoids. The flower color of commercial varieties of Petunia hybrida was successfully modified by the suppression of endogenous flavonoid biosynthetic genes, the expression of a hetelorogous flavonoid biosynthetic gene, and the combination of both. Flower color changed from purple to almost white or from purple to red by the suppression of the endogenous gene expression, from red to orange by the down-regulation of the flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene and the expression of the rose dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene, and from violet to pale violet by the expression of the flavonol synthase or flavone synthase gene. These results clearly indicate the usefulness of metabolic engineering of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway to modify flower color. Only a few of the transgenic petunia exhibited phenotypic stability. For commercialisation, it is necessary to generate many independent transgenic lines, select elite lines with stable phenotypes and maintain them in tissue culture.
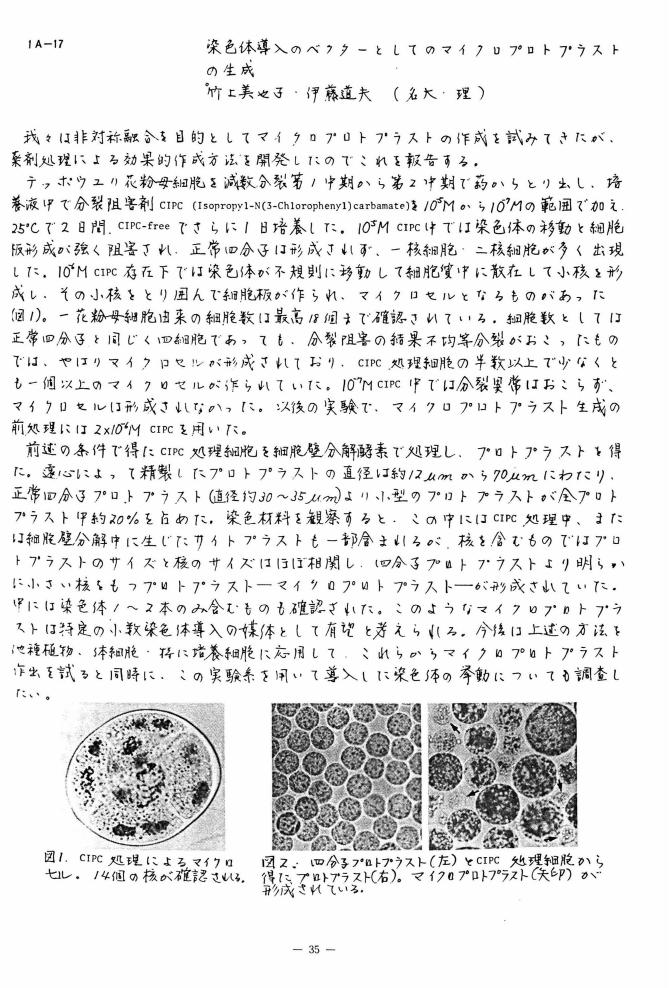
1 0 0 0 OA 染色体導入のベクターとしてのマイクロプロトプラストの生成
- 著者
- 竹上 美也子 伊藤 道夫
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- 植物組織培養 (ISSN:02895773)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.Supplement, pp.35-35, 1985 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 OA Datuia innoxia 培養細胞のアデニン要求株の生理特性
- 著者
- 古橋 勝久 古山 幸弘 保坂 義隆
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- 植物組織培養 (ISSN:02895773)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.Supplement, pp.65-65, 1985 (Released:2010-04-30)
1 0 0 0 OA 有用物質の生産
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.Supplement, pp.29-42, 2000 (Released:2010-04-30)
- 著者
- Emi Ito Tomohiro Uemura Takashi Ueda Akihiko Nakano
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.16.0218a, (Released:2016-04-09)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 9
In plant cells, the trans-Golgi network (TGN) is known to act as the early endocytic compartment, whereas RAB5-localizing multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) act as the later compartment. Land plants and certain green algal species possess plant-unique RAB5 homologs (ARA6/RABF1 in Arabidopsis thaliana) in addition to the orthologs of animal RAB5 (RHA1/RABF2a and ARA7/RABF2b in A. thaliana), and these two RAB5 members reside in substantially overlapping but different subpopulations of MVEs. Several studies indicate that the TGN and MVEs are closely related; however, the distribution of the two RAB5 groups in relation to the TGN remains elusive. Here, we quantitatively showed that ARA6 and ARA7 are closely associated with the TGN, and the subpopulation of ARA6 and ARA7 overlaps with the TGN in the root epidermal cells of A. thaliana.
- 著者
- Tomonao Matsushita
- 出版者
- 日本植物細胞分子生物学会
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.5, pp.515-519, 2011-12-25 (Released:2012-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is a phenomenon by which transgenes that share homology in their promoter regions are inactivated. TGS is known to be reduced by using different promoters to drive the expression of each transgene. However, in order to perform a large-scale genetic screen in which overexpression lines are mutagenized by T-DNA tagging and therefore harbor two types of transgene, it is critical to develop a technique that consistently blocks TGS. Here, I report a versatile method that completely prevents TGS in transgenic Arabidopsis. A seedling morphology-based assay demonstrated that TGS could be significantly diminished by using different terminator sequences for each transgene. Furthermore, it was suggested that TGS might be reduced if the orientations of the two T-DNA sequences were reversed relative to each other. By combining these strategies, I showed that TGS was completely blocked in over 50,000 T1 plants. These findings present a thorough and versatile method to prevent TGS that is potentially applicable to various plant species and is expected to be used in diverse situations, from basic to applied research fields.