- 著者
- Chiharu Aizawa Masahiro Okabe Daisuke Takahashi Makoto Sagasaki Mao Watanabe Toshinari Fujimoto Yuuki Yoshioka Ai Katsuma Ai Kimura Daisuke Miyamoto Nana Sato Ken Okamoto Kimiyoshi Ichida Yoichi Miyazaki Takashi Yokoo
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.0678-22, (Released:2023-02-08)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Exercise-induced acute kidney injury (EIAKI) is frequently complicated with renal hypouricemia (RHUC). In patients with RHUC, limiting anaerobic exercise can prevent EIAKI. However, it is challenging to reduce exercise intensity in athletes. We herein report a 16-year-old Japanese football player with familial RHUC with compound heterozygous mutations in urate transporter 1 (URAT1) who presented with recurrent EIAKI. As prophylaxis (hydration during exercise) could not prevent EIAKI, febuxostat was initiated. EIAKI was not observed for 16 months despite exercising intensively. Hence, non-purine-selective xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitors may decrease the incidence of EIAKI in athletes with RHUC.
- 著者
- Norihiko Shiiya Naoki Washiyama Daisuke Takahashi Kazumasa Tsuda Yuko Ohashi Kayoko Natsume Masahiro Hirano
- 出版者
- The Editorial Committee of Annals of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
- 雑誌
- Annals of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (ISSN:13411098)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ra.22-00148, (Released:2022-09-15)
- 参考文献数
- 52
Single-stage extended replacement from the ascending to the distal descending aorta or beyond is a formidable operation that should be preserved for those who have no other option or those who are physically fit, and should be performed in the experienced centers. Hybrid operations combining open surgical repair with thoracic endovascular aortic repair through a median sternotomy incision are preferable because these operations are less invasive than the extended open aortic repair and the risk of spinal cord ischemia is lower compared with the frozen elephant trunk operation. However, these operations are associated with the inherent demerits of endovascular aneurysm exclusion. When the underlying aortic pathology necessitates extended open aortic repair in a single stage, approaches such as the anterolateral partial sternotomy, straight incision with rib cross, and extended thoracotomy with sternal transection may be useful to provide sufficient exposure for both aortic reconstruction and organ protection, with less surgical stress to the patients.
- 著者
- Wei Zhe Naomi Hoshina Yukihiro Itoh Toshifumi Tojo Takayoshi Suzuki Koji Hase Daisuke Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1364-1372, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
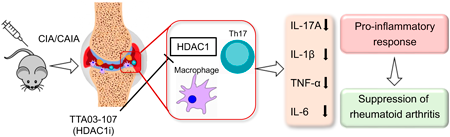
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is systemic autoimmune arthritis that causes joint inflammation and destruction. Accumulating evidence has shown that inhibitors of class I histone deacetylases (HDACs) (i.e., HDAC1, 2, 3, and 8) are potential therapeutic candidates as targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs). Nevertheless, the inhibition of class I HDACs has severe adverse effects because of their broad spectrum. We evaluated the therapeutic effect of a novel selective HDAC1 inhibitor TTA03-107 for collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) models in mice. We also examined the effect of TTA03-107 in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells in vitro. Here, we delineate that TTA03-107 reduced the severity of autoimmune arthritis without obvious adverse effects in CIA and CAIA models. Moreover, TTA03-107 suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-17A, in serum and joint tissue. In vitro treatment of BMDMs with TTA03-107 dampened the M1 differentiation and inflammatory cytokine production. TTA03-107 also suppressed the differentiation of Th17 cells. These results demonstrate that TTA03-107 can attenuate the development of arthritis in experimental RA models by inhibiting the differentiation and activation of macrophages and Th17 cells. Therefore, TTA03-107 is a potential tsDMARD candidate.
1 0 0 0 OA Intestinal epithelial cell-specific deletion of α-mannosidase II ameliorates experimental colitis
- 著者
- Koichiro Suzuki Takahiro Yamada Keiko Yamazaki Masato Hirota Narumi Ishihara Mizuki Sakamoto Daisuke Takahashi Hideki Iijima Koji Hase
- 出版者
- Japan Society for Cell Biology
- 雑誌
- Cell Structure and Function (ISSN:03867196)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.17022, (Released:2018-01-18)
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a refractory disease of the gastrointestinal tract that is believed to develop in genetically susceptible individuals. Glycosylation, a type of post-translational modification, is involved in the development of a wide range of diseases, including IBD, by modulating the function of various glycoproteins. To identify novel genes contributing to the development of IBD, we analyzed single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of glycosylation-related genes in IBD patients and identified MAN2A1, encoding alpha-mannosidase II (α-MII), as a candidate gene. α-MII plays a crucial, but not exclusive, role in the maturation of N-glycans. We also observed that intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), which establish the first-line barrier and regulate gut immunity, selectively expressed α-MII with minimal expression of its isozyme, alpha-mannosidase IIx (α-MIIx). This led us to hypothesize that IEC-intrinsic α-MII is implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD. To test this hypothesis, we generated IEC-specific α-MII-deficient (α-MIIΔIEC) mice. Although α-MII deficiency has been shown to have a minimal effect on N-glycan maturation in most cell types due to the compensation by α-MIIx, ablation of α-MII impaired the maturation of N-glycans in IECs. α-MIIΔIEC mice were less susceptible to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis compared with control littermates. In accordance with this, neutrophil infiltration in the colonic mucosa was attenuated in α-MIIΔIEC mice. Furthermore, gene expression levels of neutrophil-attracting chemokines were downregulated in the colonic tissue. These results suggest that IEC-intrinsic α-MII promotes intestinal inflammation by facilitating chemokine expression. We propose SNPs in MAN2A1 as a novel genetic factor for IBD. Key words: inflammatory bowel disease, alpha-mannosidase II, intestinal epithelial cell, N-glycosylation