- 著者
- Etsuro Ito Rei Shima Tohru Yoshioka
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.132-139, 2019 (Released:2019-08-24)
- 参考文献数
- 79
- 被引用文献数
- 26
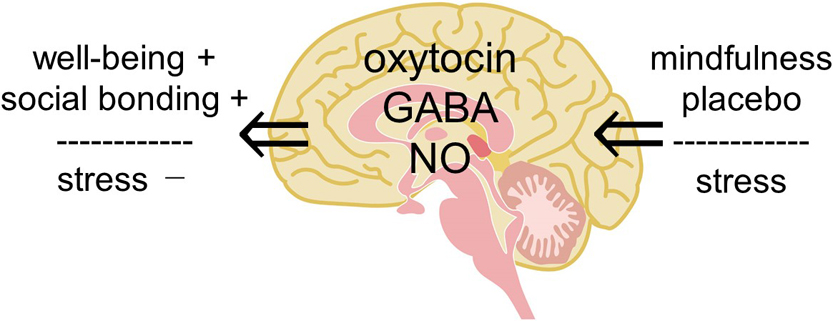
We review the involvement of a small molecule, oxytocin, in various effects of physical stimulation of somatosensory organs, mindfulness meditation, emotion and fragrance on humans, and then propose a hypothesis that complex human states and behaviors, such as well-being, social bonding, and emotional behavior, are explained by oxytocin. We previously reported that oxytocin can induce pain relief and described the possibility how oxytocin in the dorsal horn and/or the dorsal root ganglion relieves joint and muscle pain. In the present article, we expand our research target from the physical analgesic effects of oxytocin to its psychologic effects to upregulate well-being and downregulate stress and anxiety. For this purpose, we propose a “hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis-oxytocin model” to explain why mindfulness meditation, placebo, and fragrance can reduce stress and anxiety, resulting in contentment. This new proposed model of HPA axis-oxytocin in the brain also provides a target to address other questions regarding emotional behaviors, learning and memory, and excess food intake leading to obesity, aimed at promoting a healthy life.
2 0 0 0 OA Subattomole detection of adiponectin in urine by ultrasensitive ELISA coupled with thio-NAD cycling
- 著者
- Mika Morikawa Rina Naito Koichi Mita Satoshi Watabe Kazunari Nakaishi Teruki Yoshimura Toshiaki Miura Seiichi Hashida Etsuro Ito
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, pp.79-86, 2015 (Released:2015-11-12)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1 16
Adiponectin is a hormone secreted from adipocytes, and it demonstrates antidiabetic, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects. However, the patterns of change in urinary adiponectin levels in various diseases remain unknown, because only trace amounts of the hormone are present in urine. In the present study, we applied an ultrasensitive ELISA coupled with thio-NAD cycling to measure urinary adiponectin levels. Spike-and-recovery tests using urine confirmed the reliability of our ultrasensitive ELISA. The limit of detection for adiponectin in urine was 2.3×10–19 moles/assay (1.4 pg/mL). The urinary adiponectin concentration ranged between 0.04 and 5.82 ng/mL in healthy subjects. The pilot study showed that the urinary adiponectin levels, which were corrected by the creatinine concentration, were 0.73±0.50 (ng/mg creatinine, N=6) for healthy subjects, versus 12.02±3.85 (ng/mg creatinine, N=3) for patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). That is, the urinary adiponectin levels were higher (P<0.05) in DM patients than in healthy subjects. Further, these urinary adiponectin levels tended to increase with the progression of DM accompanied with nephropathy. Our method is thus expected to provide a simple, rapid and reasonably priced test for noninvasive monitoring of the progression of DM without the requirement of special tools.