- 著者
- Ning Luo Gui-bing Chen Teng Zhang Jie Zhao Jing-nan Fu Ning Lu Tao Ma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.187-193, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
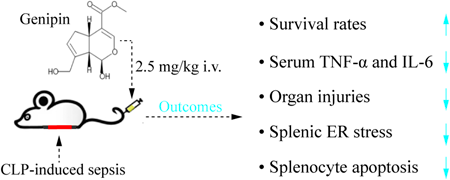
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) dysfunction is characterized by ER stress, which can be triggered by sepsis. Recent studies have reported that lessening ER stress is a promising therapeutic approach to improving the outcome of sepsis. Genipin is derived from gardenia fruit, which is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb for anti-inflammation. Here, mice were treated with genipin (2.5 mg/kg) intravenously to assess its biological effects and underlying mechanism against polymicrobial sepsis. Furthermore, the present study focused on detecting the levels of ER stress-related proteins, including protein kinase R-like ER kinase (PERK), glucose-regulated protein of 78 kDa (GRP78), phosphorylated-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (p-eIF2α), and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein (CHOP). The results demonstrated that genipin significantly decreased the serum concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6, alleviated histopathological damage to the lungs, livers and spleens, and even improved the survival rates of septic mice. Moreover, sepsis significantly upregulated the protein expression levels of splenic GRP78, PERK, p-eIF2α and CHOP, but their levels were significantly suppressed by genipin. Furthermore, genipin also significantly downregulated cleaved caspase-3 expression levels and reduced sepsis-induced splenocyte apoptosis. In conclusion, genipin potentially improved the survival rate of sepsis and attenuated sepsis-induced organ injury and an excessive inflammatory response in mice. The effects of genipin against sepsis were potentially associated with decreased splenocyte apoptosis via the attenuation of sepsis-induced ER stress to further inhibit ER stress-induced apoptosis.
- 著者
- Xuelong Jin Zhaoqiang Zhang Wenli Jing Jie Zhao
- 出版者
- Japan Brain Science society
- 雑誌
- 脳科学誌 (ISSN:13415301)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, pp.5-16, 2013-09-30 (Released:2017-06-01)
Objective: To study and evaluate a new internal capsule hemorrhage animal model. Methods: We established an internal capsule hemorrhage animal model using Horseley-Clarke technique. Internal capsule was orientated referring to Sawyer rabbit brain stereotaxic atlas. The model was duplicated by injecting 0.5 ml autologous arterial blood into hind limb of internal capsule. We used HE stain to observe the changes of brain tissues. Then somatosensory evoked potential, and intracranial pressure were measured. Results: Obvious hematoma was detected in brain tissues under light microscopes. The latency of N1 and P1 in somatosensory evoked potential prolonged and the peak-to-peak value of N2-P1 decreased. Meantime intracranial pressure increased. Conclusion: We established an internal capsule hemorrhage animal model successfully. Histopathologic changes of the brain tissues and abnormal somatosensory evoked potential were found. We observed an increase in intracrnial pressure. These can provide the reference for the study of intracerebral hemorrhage.
- 著者
- Jie Zhao Xuelong Jin
- 出版者
- Japan Brain Science society
- 雑誌
- 脳科学誌 (ISSN:13415301)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, pp.47-59, 2011 (Released:2017-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Traditionally, we use CT and MRI to observe brain's structure, but there are many new ways to get the images of brain activity. Currently Smart MR imaging agent, Two- photon microscope, Neuro Trace, Fluorescent Protein, Photostable quantum dots, Connexin 29, NUTMEG and Statistical parametric mapping (SPM), The Short-Term Maxi- mum Lyapunov Exponent (STLmax) Topographic Brain Activity Maps have been used to observe the brain. Next, make a summary about new technologies for the visualization of the brain function.
1 0 0 0 OA Anticancer and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Diosmin against Dalton Ascitic Lymphoma Induced Leukemia
- 著者
- Xiangmei Yao Xuezhong Gu Song Jin Keqian Shi Xiaoli Gao Qi Wang Jie Zhao Haixi Zhang Xun Lai
- 出版者
- Japan Oil Chemists' Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Oleo Science (ISSN:13458957)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.5, pp.665-673, 2021 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Cancer is the world’s biggest health problem and cancer-induced mortality happened all over the planet after the heart disease. The present study was to scrutinize the anti-leukemia effect of diosmin against Dalton Ascitic Lymphoma (DAL) induced leukemia in mice. DAL cell was used for induction the solid tumor. Body weight, life spans, tumor volume and mean survival time was estimated. Antioxidant, biochemical and pro-inflammatory cytokines were estimated. Diosmin showed the cell viability effect at dose dependent manner against the both cell lines. DAL induced solid tumor mice showed the decreased body weight, mean survival days, non viable cell count and increased the tumor volume, viable cell count and diosmin significantly (p < 0.001) reverse the effect of DAL. Diosmin significantly (p < 0.001) altered the hematological, differential leukocytes, antioxidant, biochemical, pro-inflammatory cytokines at dose dependently. Collectively, we can say that diosmin might alter the DAL induced abnormality via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.