- 著者
- María del Carmen Marín Alexander L. Jaffe Patrick T. West Masae Konno Jillian F. Banfield Keiichi Inoue
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.e201023, (Released:2023-03-08)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
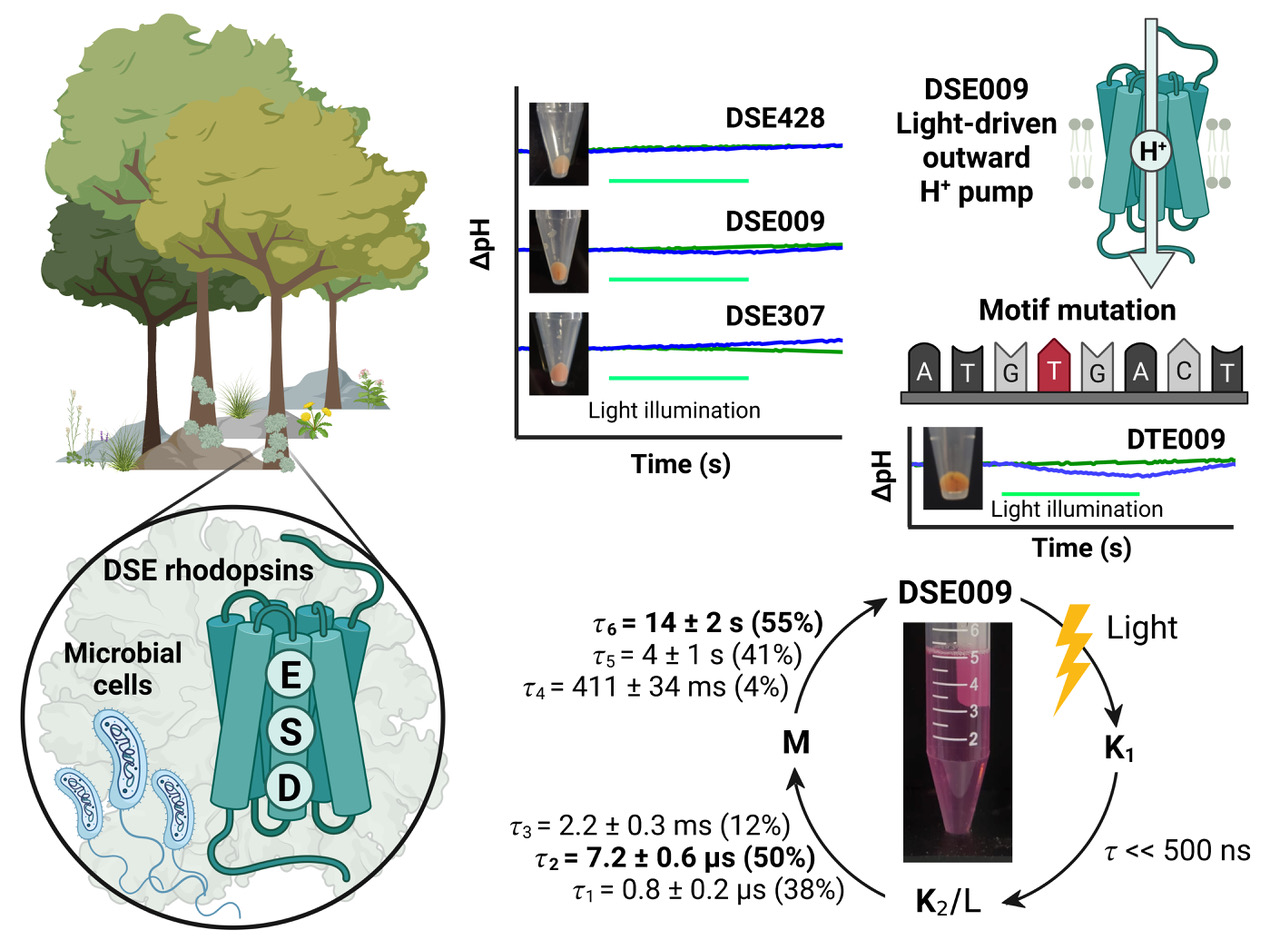
Microbial rhodopsins are photoreceptive transmembrane proteins that transport ions or regulate other intracellular biological processes. Recent genomic and metagenomic analyses found many microbial rhodopsins with unique sequences distinct from known ones. Functional characterization of these new types of microbial rhodopsins is expected to expand our understanding of their physiological roles. Here, we found microbial rhodopsins having a DSE motif in the third transmembrane helix from members of the Actinobacteria. Although the expressed proteins exhibited blue–green light absorption, either no or extremely small outward H+ pump activity was observed. The turnover rate of the photocycle reaction of the purified proteins was extremely slow compared to typical H+ pumps, suggesting these rhodopsins would work as photosensors or H+ pumps whose activities are enhanced by an unknown regulatory system in the hosts. The discovery of this rhodopsin group with the unique motif and functionality expands our understanding of the biological role of microbial rhodopsins.
- 著者
- Yumeka Yamauchi Masae Konno Shota Ito Satoshi P. Tsunoda Keiichi Inoue Hideki Kandori
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.14, pp.57-66, 2017 (Released:2017-05-20)
- 参考文献数
- 58
- 被引用文献数
- 35
Microbial rhodopsins are membrane proteins found widely in archaea, eubacteria and eukaryotes (fungal and algal species). They have various functions, such as light-driven ion pumps, light-gated ion channels, light sensors and light-activated enzymes. A light-driven proton pump bacteriorhodopsin (BR) contains a DTD motif at positions 85, 89, and 96, which is unique to archaeal proton pumps. Recently, channelrhodopsins (ChRs) containing the DTD motif, whose sequential identity is ~20% similar to BR and to cation ChRs in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (CrCCRs), were found. While extensive studies on ChRs have been performed with CrCCR2, the molecular properties of DTD ChRs remain an intrigue. In this paper, we studied a DTD rhodopsin from G. theta (GtCCR4) using electrophysiological measurements, flash photolysis, and low-temperature difference FTIR spectroscopy. Electrophysiological measurements clearly showed that GtCCR4 functions as a light-gated cation channel, similar to other G. theta DTD ChRs (GtCCR1-3). Light-driven proton pump activity was also suggested for GtCCR4. Both electrophysiological and flash photolysis experiments showed that channel closing occurs upon reprotonation of the Schiff base, suggesting that the dynamics of retinal and channels are tightly coupled in GtCCR4. From Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy at 77 K, we found that the primary reaction is an all-trans to a 13-cis photoisomerization, like other microbial rhodopsins, although perturbations in the secondary structure were much smaller in GtCCR4 than in CrCCR2.