- 著者
- Takehiro Suzuki Hiroaki Yamaguchi Motoi Kikusato Tetsuro Matsuhashi Akihiro Matsuo Takeya Sato Yuki Oba Shun Watanabe Daichi Minaki Daisuke Saigusa Hiroko Shimbo Nobuyoshi Mori Eikan Mishima Hisato Shima Yasutoshi Akiyama Yoichi Takeuchi Akinori Yuri Koichi Kikuchi Takafumi Toyohara Chitose Suzuki Masahiro Kohzuki Jun-ichi Anzai Nariyasu Mano Shigeo Kure Teruyuki Yanagisawa Yoshihisa Tomioka Masaaki Toyomizu Sadayoshi Ito Hitoshi Osaka Ken-ichiro Hayashi Takaaki Abe
- 出版者
- 東北ジャーナル刊行会
- 雑誌
- The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine (ISSN:00408727)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.236, no.3, pp.225-232, 2015 (Released:2015-06-26)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 2 34
Mitochondria are key organelles implicated in a variety of processes related to energy and free radical generation, the regulation of apoptosis, and various signaling pathways. Mitochondrial dysfunction increases cellular oxidative stress and depletes ATP in a variety of inherited mitochondrial diseases and also in many other metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Mitochondrial diseases are characterized by the dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, caused by mutations in the genes encoded by either nuclear DNA or mitochondrial DNA. We have hypothesized that chemicals that increase the cellular ATP levels may ameliorate the mitochondrial dysfunction seen in mitochondrial diseases. To search for the potential drugs for mitochondrial diseases, we screened an in-house chemical library of indole-3-acetic-acid analogs by measuring the cellular ATP levels in Hep3B human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. We have thus identified mitochonic acid 5 (MA-5), 4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-4-oxobutanoic acid, as a potential drug for enhancing ATP production. MA-5 is a newly synthesized derivative of the plant hormone, indole-3-acetic acid. Importantly, MA-5 improved the survival of fibroblasts established from patients with mitochondrial diseases under the stress-induced condition, including Leigh syndrome, MELAS (myopathy encephalopathy lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes), Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy, and Kearns-Sayre syndrome. The improved survival was associated with the increased cellular ATP levels. Moreover, MA-5 increased the survival of mitochondrial disease fibroblasts even under the inhibition of the oxidative phosphorylation or the electron transport chain. These data suggest that MA-5 could be a therapeutic drug for mitochondrial diseases that exerts its effect in a manner different from anti-oxidant therapy.
- 著者
- Masamitsu Maekawa Keitaro Miyoshi Aya Narita Toshihiro Sato Yu Sato Masaki Kumondai Masafumi Kikuchi Katsumi Higaki Torayuki Okuyama Yoshikatsu Eto Hiroshi Sakamaki Nariyasu Mano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1259-1268, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 65
- 被引用文献数
- 3
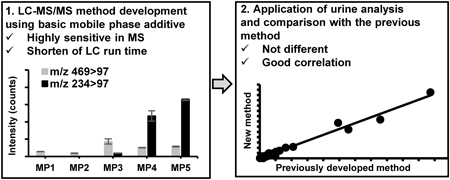
As Niemann–Pick disease type C (NPC) is difficult to diagnose owing to its various clinical symptoms; biomarker tests have been developed. Previously, we revealed urinary sulfated cholesterol metabolites as noninvasive biomarkers for NPC. However, LC/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) requires long separation time and large urine volumes. Recently, a basic mobile phase was reported to increase the MS intensity. Thus, we developed a highly sensitive and rapid LC/MS/MS method for analyzing urinary cholesterol metabolites using a basic mobile phase additive. 3β-Sulfooxy-7β-N-acetylglucosaminyl-5-cholenic acid, its glycine and taurine conjugates, 3β-sulfooxy-7β-hydroxy-5-cholenic acid, and 7-oxo form were measured, with selected reaction monitoring in negative ion mode. Oasis HLB and L-column 3 were used for column-switching LC/MS/MS and urine diluted 10-fold was employed as the sample. After trapping, gradient separation was performed using solutions containing 1% (v/v) ammonium solution. On average, a 16-fold increase in peak areas was observed compared to that obtained at pH 5.5 with the mobile phases. Although the previous method needed 60 min for separation from interference peaks, we succeeded to separate them in 7 min with optimized LC condition. Further, all compounds showed good linearity from 0.3–1000 ng/mL, with satisfactory intra- and inter-day reproducibility. The developed method was applied to the urinalysis of healthy participants and NPC patients. Overall, the concentrations of metabolites correlated with those obtained using the previous method. Therefore, we succeeded to increasing MS intensity and shorten LC running time; and the method is useful for the noninvasive diagnostic screening of patients with NPC.
- 著者
- Masaki Kumondai Masamitsu Maekawa Eiji Hishinuma Yu Sato Toshihiro Sato Masafumi Kikuchi Masahiro Hiratsuka Nariyasu Mano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.455-463, 2023-03-01 (Released:2023-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 52
CYP3A4, which contributes to the metabolism of more than 30% of clinically used drugs, exhibits high variation in its activity; therefore, predicting CYP3A4 activity before drug treatment is vital for determining the optimal dosage for each patient. We aimed to develop and validate an LC-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method that simultaneously measures the levels of CYP3A4 activity-related predictive biomarkers (6β-hydroxycortisol (6β-OHC), cortisol (C), 1β-hydroxydeoxycholic acid (1β-OHDCA), and deoxycholic acid (DCA)). Chromatographic separation was achieved using a YMC-Triart C18 column and a gradient flow of the mobile phase comprising deionized water/25% ammonia solution (100 : 0.1, v/v) and methanol/acetonitrile/25% ammonia solution (50 : 50 : 0.1, v/v/v). Selective reaction monitoring in the negative-ion mode was used for MS/MS, and run times of 33 min were used. All analytes showed high linearity in the range of 3–3000 ng/mL. Additionally, their concentrations in urine samples derived from volunteers were analyzed via treatment with deconjugation enzymes, ignoring inter-individual differences in the variation of other enzymatic activities. Our method satisfied the analytical validation criteria under clinical conditions. Moreover, the concentrations of each analyte were quantified within the range of calibration curves for all urine samples. The conjugated forms of each analyte were hydrolyzed to accurately examine CYP3A4 activity. Non-invasive urine sampling employed herein is an effective alternative to invasive plasma sampling. The analytically validated simultaneous quantification method developed in this study can be used to predict CYP3A4 activity in precision medicine and investigate the potential clinical applications of CYP3A4 biomarkers (6β-OHC/C and 1β-OHDCA/DCA ratios).
- 著者
- Anna Iwahori Masamitsu Maekawa Aya Narita Akie Kato Toshihiro Sato Jiro Ogura Yu Sato Masafumi Kikuchi Atsuko Noguchi Katsumi Higaki Torayuki Okuyama Tsutomu Takahashi Yoshikatsu Eto Nariyasu Mano
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b20-00400, (Released:2020-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Early diagnosis of Niemann-Pick diseases (NPDs) is important for better prognosis of such diseases. N-Palmitoyl-O-phosphocholine-serine (PPCS) is a new NPD biomarker possessing high sensitivity, and with its combination with sphingosylphosphocholine (SPC) it may be possible to distinguish NPD-C from NPD-A/B. In this study, a rapid liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) method (method 1) and a validated LC/MS/MS analysis (method 2) of PPCS and SPC were developed, and we have proposed a diagnostic screening strategy for NPDs using a combination of serum PPCS and SPC concentrations.Nexera and API 5000 were used as LC/MS/MS systems. C18 columns with lengths of 10 mm and 50 mm were used for method 1 and 2, respectively. 2H3-labeled PPCS (PPCS-2H3_ and nor-SPC were used as internal standards. Selective reaction monitoring in positive-ion mode was used for MS/MS. Run times of 1.2 min and 8 min were set for methods 1 and 2, respectively.In both methods 1 and 2, two analytes showed high linearity in the range of 1–4000 ng/mL. Method 2 provided high accuracy and precision in method validation. Serum concentrations of both analytes were significantly higher in NPD-C patients than those of healthy subjects in both methods. Serum PPCS correlated between methods 1 and 2; however, it was different in the case of SPC. The serum PPCS/SPC ratio was different in healthy subjects, NPD-C, and NPD-A/B. These results suggest that using a combination of the two LC/MS/MS analytical methods for PPCS and SPC is useful for diagnostic screening of NPDs.