- 著者
- Xue Feng Yishuo Xu Ming Zeng Yuhan Qin Ziqian Weng Yanli Sun Zhanqun Gao Luping He Chen Zhao Ning Wang Dirui Zhang Chao Wang Yini Wang Lulu Li Chao Fang Jiannan Dai Haibo Jia Bo Yu
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0200, (Released:2023-07-04)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: Microvascular reperfusion following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is associated with the prognosis of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). We investigated how plaque characteristics detected by optical coherence tomography (OCT) in STEMI patients affect the status of the microcirculation during PCI.Methods and Results: This retrospective, single-center study was a post hoc analysis basedon the multicenter SALVAGE randomized control trial (NCT03581513) that enrolled 629 STEMI patients, and finally we enrolled 235 patients who underwent PCI and pre-intervention OCT. Microvascular perfusion was evaluated using the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) myocardial perfusion frame count (TMPFC). Patients were divided into 3 groups based on the change in TMPFC from before to after PCI: improving TMPFC (n=11; 4.7%), stable TMPFC (n=182; 77.4%), and worsening TMPFC group (n=42; 17.9%). The proportion of patients with a microcirculation dysfunction before reperfusion was 11.9%, which increased significantly by (P=0.079) 8.5% to 20.4% after reperfusion. Compared with plaque characteristics in the stable and worsening TMPFC groups, the improving TMPFC group had fewer thrombi (90.7% and 90.5% vs. 89.4%, respectively; P=0.018), a lower proportion of plaque rupture (66.5% and 66.3% vs. 54.5%, respectively; P=0.029), and a lower proportion of lipid-rich plaques (89.6% and 88.1% vs. 63.6%, respectively; P=0.036).Conclusions: PCI may not always achieve complete myocardial reperfusion. Thrombi, plaque rupture, and lipid-rich plaques detected by OCT can indicate microcirculation dysfunction during the reperfusion period.
- 著者
- Lili Li Ning Wang Qizhong Jin Qian Wu Yafang Liu Yan Wang
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.11, pp.1004-1010, 2017-11-01 (Released:2017-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 17 20
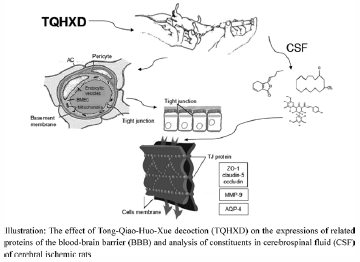
Tong-Qiao-Huo-Xue Decoction (TQHXD) is a classical prescription in traditional Chinese medicine treating blood stagnation in the head and facial channels, especially cerebral ischemia. We investigate the effect of TQHXD on the expressions of related proteins of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and analysis of constituents in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) on cerebral ischemic model rats. Here, we demonstrate that TQHXD protected the hippocampus neurons, reduced the opening of tight junction (TJ) and decreased the permeability of BBB by up-regulating ZO-1, occludin, claudin-5 expressions, down-regulating aquaporin-4 (AQP-4) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expressions. Meanwhile, we detected Muscone, ligustilide and hydroxysafflor yellow A in CSF on cerebral ischemic model rats. These compounds could be identified as the main active ingredients of TQHXD on protecting the damaged BBB. These results suggest that TQHXD could act as a potential neuroprotective agent against BBB damage for cerebral ischemia.
- 著者
- Qing-hai Hu Jun-jie Xu Zhen-xing Chu Jing Zhang Yan-qiu Yu Huan Yu Hai-bo Ding Yong-jun Jiang Wen-qing Geng Ning Wang Hong Shang
- 出版者
- 国立感染症研究所 Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases 編集委員会
- 雑誌
- Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases (ISSN:13446304)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.JJID.2016.177, (Released:2016-10-31)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 8
We aimed to assess the prevalence and determinants of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) mono-infection and HSV-2/syphilis co-infection in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive men who have sex with men (MSM) in China. A cross-sectional study was conducted on 545 HIV-positive MSM in Shenyang between February 2009 and October 2014. Participants received physical examinations and serological tests for HSV-2 and syphilis. A multinomial logistic regression was used to identify risk factors associated with HSV-2/syphilis co-infection and HSV-2 mono-infection. The HSV-2 mono-infection, syphilis mono-infection, and HSV-2/syphilis co-infection prevalence (95% confidence interval) was 48.6% (44.4–52.8%), 34.3% (30.3–38.3%), and 22.9% (19.4–26.5%), respectively. In regression analysis, after controlling within HSV-2/syphilis-seronegative cases, related factors for HSV-2/syphilis co-infection were age (25–50 years vs. ≤24 years, aOR: 4.55; >50 years vs. ≤24 years, aOR: 43.02), having regular female sexual partner(s) in the past 6 months (aOR: 0.43) and age at first MSM experience (>18 years vs ⩽18 years, aOR: 2.59) (all P < 0.05).The high prevalence of HSV-2 infection and HSV-2/syphilis co-infection in HIV-positive MSM indicates high HIV secondary transmission risk. A campaign for detection and treatment of HSV-2 and syphilis is urgently required for HIV-positive MSM in China.
1 0 0 0 黄河流域の主要地域における地下水収支・循環
- 著者
- ハン チャンタオ チャン アルヨン ホウ シンウェイ Lijun Shan Zhongdao Zhu Ning Wang Eryong Zhang Xinwei Hou Cunrong Gao Yingchun Shi Hongmei Zhao Jianqing Ding Xingchun Liu Baogui Li
- 出版者
- 国立研究開発法人 産業技術総合研究所 地質調査総合センター
- 雑誌
- 地質調査研究報告 (ISSN:13464272)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.1, pp.59-86, 2009
- 被引用文献数
- 1
黄河流域の主要な平野や盆地は中国の社会・経済開発にとって極めて重要な地域であるので,その地域の地下水の収支と循環を明らかにすることもまた重要である.本研究では,黄河源流域,銀川平野,呼和浩特・包頭平野,太原平野,関中平野および黄河下流域を地下水の収支と循環に関する研究対象地域として選定し,地下水の水素・酸素の安定同位体比,水質などの特徴を明らかにする.また,地下水の流動系や水収支について考察する.
- 著者
- Ning Wang Naoko Kitamoto Ryo Ohsawa Tatsuhito Fujimura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Breeding
- 雑誌
- Breeding Science (ISSN:13447610)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.107-112, 2008 (Released:2008-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 9 15
Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is a useful vegetable with diverse features and worldwide distribution; however, the diversification and domestication history of cultivated radish has not been well documented. In order to understand genetic relationships among radishes around the world and the resulting diversity, we analyzed 65 accessions of cultivated radish collected from 21 Eurasian and North African countries using 221 amplified fragment-length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. These accessions formed four groups according to their provenance (Europe, Middle East, South Asia, and East Asia) in a neighbor-joining (NJ) tree. Despite geographical barriers, there might thus be a frequent exchange of germplasms within each region. The average genetic diversity did not differ significantly among the groups, ranging from 0.267 (Middle East) to 0.297 (East Asia), indicating that no obvious bottleneck effect in each region has occurred during the spread of this species.
- 著者
- Hui Zhu Dong Zeng Qiang Wang Ning Wang Bo Zeng Lili Niu Xueqin Ni
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Microbial Ecology · The Japanese Society of Soil Microbiology
- 雑誌
- Microbes and Environments (ISSN:13426311)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ME17163, (Released:2018-07-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 14
Diarrhea is often associated with marked alterations in the intestinal microbiota, termed dysbiosis; however, limited information is currently available on the intestinal microbiota in captive golden snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) with diarrhea. We herein characterized the fecal microbiota in diarrhea and healthy monkeys using the Illumina MiSeq platform. The concentrations of fecal short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and copy numbers of virulence factor genes were also assessed using gas chromatography and quantitative PCR (qPCR), respectively. The results obtained showed that diarrhea monkeys harbored a distinctive microbiota from that of healthy monkeys and had 45% fewer Bacteroidetes. Among healthy subjects, old monkeys had the lowest relative abundance of Bacteroidetes. Linear discriminant analysis coupled with the effect size (LEfSe) and canonical correlation analysis (CCA) identified significant differences in microbial taxa between diarrhea and healthy monkeys. A PICRUSt analysis revealed that several pathogenic genes were enriched in diarrhea monkeys, while glycan metabolism genes were overrepresented in healthy monkeys. A positive correlation was observed between the abundance of nutrition metabolism-related genes and the individual digestive capacities of healthy monkeys. Consequently, the abundance of genes encoding heat stable enterotoxin was significantly higher in diarrhea monkeys than in healthy monkeys (P<0.05). In healthy subjects, adult monkeys had significant higher concentrations of butyrate and total SCFAs than old monkeys (P<0.05). In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that diarrhea had a microbial component and changes in the microbial structure were accompanied by altered systemic metabolic states. These results suggest that pathogens and malabsorption are the two main causes of diarrhea, which are closely related to the microbial structure and functions.