4 0 0 0 OA A rapid method for detection of the root-knot nematode resistance gene, Mi-1.2, in tomato cultivars
- 著者
- Chihiro Furumizu Shinichiro Sawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.1206a, (Released:2023-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 1
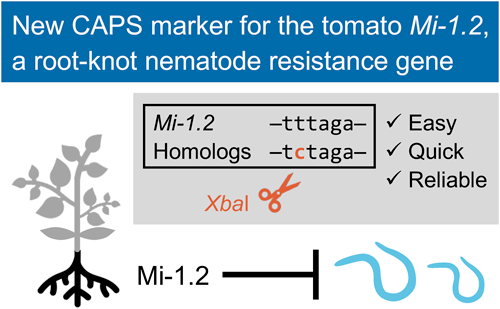
Molecular markers have been widely used in plant breeding to improve the accuracy and efficiency of trait selection. In particular, molecular markers are powerful in facilitating the introgression of resistance genes by circumventing costly and time-consuming infection assays. To achieve their practical use, it is important to ensure the tight linkage between the markers and the traits. Here we report a new cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) marker, Mi1713, for the root-knot nematode resistance gene, Mi-1.2, in cultivated tomato. The Mi1713 marker is designed in the conserved region of Mi-1.2 and its homologs in tomato and other nightshade species. Combined with a single-step procedure for preparing PCR templates, the Mi1713 marker enables rapid and reliable screening for the presence of Mi-1.2. The approach described in this study is applicable in designing CAPS markers for various genes or alleles of interest in tomato and other crops.
3 0 0 0 OA Database mining of plant peptide homologues
- 著者
- Na Yuan Chihiro Furumizu Baolong Zhang Shinichiro Sawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.1, pp.137-143, 2021-03-25 (Released:2021-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 5
In plant-pathogen interactions, pathogens employ secreted molecules, known as effectors to overcome physical barriers, modulate plant immunity, and facilitate colonization. Among these diverse effectors, some are found to mimic the plant peptides, to target host’s peptide receptors, and intervene in the peptide-regulated defense pathways and/or plant development. To better understand how pathogens have co-evolved with their plant hosts in order to improve disease management, we explored the presence of plant peptide mimics in microbes by bioinformatic analysis. In total, 36 novel peptide mimics belong to five plant peptide families were detected in bacterial and fungal kingdoms. Among them, phytosulfokine homologues were widely distributed in 22 phytopathogens and one bacterium, thereby constituted the largest proportion of the identified mimics. The putative functional peptide region is well conserved between plant and microbes, while the existence of a putative signal peptide varies between species. Our findings will increase understanding of plant-pathogen interactions, and provide new ideas for future studies of pathogenic mechanisms and disease management.
- 著者
- Ryusuke Nakai Takashi Azuma Yosuke Nakaso Shinichiro Sawa Taku Demura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.437-442, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful technique, only a few studies have investigated the dynamic behavior of small subjects using MRI owing to constraints such as experimental space and signal amount. In this study, to acquire high-resolution continuous three-dimensional gravitropism data of pea (Pisum sativum) sprouts, we developed a small-bore MRI signal receiver coil that can be used in a clinical MRI and adjusted the imaging sequence. It was expected that such an arrangement would improve signal sensitivity and improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the acquired image. All MRI experiments were performed using a 3.0-T clinical MRI scanner. An SNR comparison using an agarose gel phantom to confirm the improved performance of the small-bore receiver coil and an imaging experiment of pea sprouts exhibiting gravitropism were performed. The SNRs of the images acquired with a standard 32-channel head coil and the new small-bore receiver coil were 5.23±0.90 and 57.75±12.53, respectively. The SNR of the images recorded using the new coil was approximately 11-fold higher than that of the standard coil. In addition, when the accuracy of MR imaging that captures the movement of pea sprout was verified, the difference in position information from the optical image was found to be small and could be used for measurements. These results of this study enable the application of a clinical MRI system for dynamic plant MRI. We believe that this study is a significant first step in the development of plant MRI technique.
- 著者
- Syuuto Toyoda Morihiro Oota Hayato Ishikawa Shinichiro Sawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.1, pp.157-159, 2021-03-25 (Released:2021-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 18
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs, genus Meloidogyne) are a class of plant parasites that seek out and infect the roots of many plant species. The identification of RKN attractants can be used in agriculture in conjunction with nematode-trapping technology to redirect RKN movements and eventually reduce their prevalence in the field. Here, we discovered that some commercial silica gels can attract nematodes. Silica gels that attract nematodes contain calcium sulfate. Calcium sulfate and calcium carbonate showed strong nematode attraction properties. When plant seeds were surrounded by calcium sulfate or calcium carbonate, nematodes were not attracted to the plant seeds. We propose that calcium sulfate and calcium carbonate can be used in agriculture as a novel material to trap RKN.
- 著者
- Reira Suzuki Takashi Ueda Takuji Wada Masaki Ito Takashi Ishida Shinichiro Sawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.1, pp.1-8, 2021-03-25 (Released:2021-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Root-knot nematodes (RKN; Meloidogyne incognita) are phytoparasitic nematodes that cause significant damage to crop plants worldwide. Recent studies have revealed that RKNs disrupt various physiological processes in host plant cells to induce gall formation. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of gall formation induced by nematodes. We have previously found that RNA expression levels of some of genes related to micro-RNA, cell division, membrane traffic, vascular formation, and meristem maintenance system were modified by nematode infection. Here we evaluated these genes importance during nematode infection by using Arabidopsis mutants and/or β-glucronidase (GUS) marker genes, particularly after inoculation with nematodes, to identify the genes involved in successful nematode infection. Our results provide new insights not only for the basic biology of plant–nematode interactions but also to improve nematode control in an agricultural setting.
- 著者
- Kenji Suetsugu Shingo Kaida Hirokazu Fukunaga Shinichiro Sawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Plant Systematics
- 雑誌
- Acta Phytotaxonomica et Geobotanica (ISSN:13467565)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.3, pp.243-248, 2020-10-31 (Released:2020-11-29)
A new color variant of Lecanorchis japonica Blume, L. japonica f. lutea (Orchidaceae), is described from Kagoshima and Chiba prefectures, Japan. Lecanorchis japonica f. lutea differs from L. japonica f. japonica only by its brilliant yellow coloration. Additionally, L. japonica f. lutea is superficially similar to L. hokurikuensis f. kiiensis but differs in having widely open flowers (vs. barely open flowers) and a nearly entire column wing (vs. apparent projections below column wing).