- 著者
- Eri Kamon Chihiro Noda Takumi Higaki Taku Demura Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21.0519a, (Released:2021-09-18)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Secondary cell walls (SCWs) accumulate in specific cell types of vascular plants, notably xylem vessel cells. Previous work has shown that calcium ions (Ca2+) participate in xylem vessel cell differentiation, but whether they function in SCW deposition remains unclear. In this study, we examined the role of Ca2+ in SCW deposition during xylem vessel cell differentiation using Arabidopsis thaliana suspension-cultured cells carrying the VND7-inducible system, in which VND7 activity can be post-translationally upregulated to induce transdifferentiation into protoxylem-type vessel cells. We observed that extracellular Ca2+ concentration was a crucial determinant of differentiation, although it did not have consistent effects on the transcription of VND7-downstream genes as a whole. Increasing the Ca2+ concentration reduced differentiation but the cells could generate the spiral patterning of SCWs. Exposure to a calcium-channel inhibitor partly restored differentiation but resulted in abnormal branched and net-like SCW patterning. These data suggest that Ca2+ signaling participates in xylem vessel cell differentiation via post-transcriptional regulation of VND7-downstream events, such as patterning of SCW deposition.
- 著者
- Tian Tian Tan Taku Demura Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Cell and Molecular Biology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.1-6, 2019-03-25 (Released:2019-03-31)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Xylem is an essential conductive tissue in vascular plants, and secondary cell wall polymers found in xylem vessel elements, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, are promising sustainable bioresources. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying xylem vessel element differentiation is an important step towards increasing woody biomass and crop yields. Establishing in vitro induction systems, in which vessel element differentiation is induced by phytohormonal stimuli or by overexpression of specific transcription factors, has been vital to this research. In this review, we present an overview of these in vitro induction systems, and describe two recently developed in vitro induction systems, VISUAL (Vascular cell Induction culture System Using Arabidopsis Leaves) and the KDB system. Furthermore, we discuss the potentials and limitations of each of these new in vitro induction systems for advancing our understanding of the molecular mechanisms driving xylem vessel element differentiation.
- 著者
- Chikage Umeda-Hara Hidekazu Iwakawa Misato Ohtani Taku Demura Tomoko Matsumoto Jun Kikuchi Koji Murata Masaaki Umeda
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.215-220, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
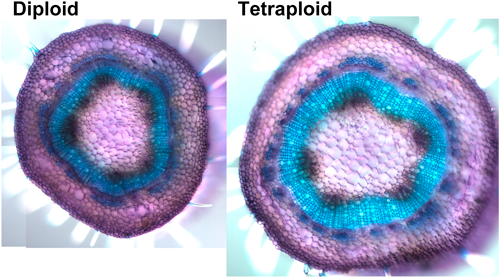
Somatic polyploidization often increases cell and organ size, thereby contributing to plant biomass production. However, as most woody plants do not undergo polyploidization, explaining the polyploidization effect on organ growth in trees remains difficult. Here we developed a new method to generate tetraploid lines in poplars through colchicine treatment of lateral buds. We found that tetraploidization induced cell enlargement in the stem, suggesting that polyploidization can increase cell size in woody plants that cannot induce polyploidization in normal development. Greenhouse growth analysis revealed that radial growth was enhanced in the basal stem of tetraploids, whereas longitudinal growth was retarded, producing the same amount of stem biomass as diploids. Woody biomass characteristics were also comparable in terms of wood substance density, saccharification efficiency, and cell wall profiling. Our results reveal tetraploidization as an effective strategy for improving woody biomass production when combined with technologies that promote longitudinal stem growth by enhancing metabolite production and/or transport.
- 著者
- Eri Kamon Chihiro Noda Takumi Higaki Taku Demura Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.331-337, 2021-09-25 (Released:2021-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Secondary cell walls (SCWs) accumulate in specific cell types of vascular plants, notably xylem vessel cells. Previous work has shown that calcium ions (Ca2+) participate in xylem vessel cell differentiation, but whether they function in SCW deposition remains unclear. In this study, we examined the role of Ca2+ in SCW deposition during xylem vessel cell differentiation using Arabidopsis thaliana suspension-cultured cells carrying the VND7-inducible system, in which VND7 activity can be post-translationally upregulated to induce transdifferentiation into protoxylem-type vessel cells. We observed that extracellular Ca2+ concentration was a crucial determinant of differentiation, although it did not have consistent effects on the transcription of VND7-downstream genes as a whole. Increasing the Ca2+ concentration reduced differentiation but the cells could generate the spiral patterning of SCWs. Exposure to a calcium-channel inhibitor partly restored differentiation but resulted in abnormal branched and net-like SCW patterning. These data suggest that Ca2+ signaling participates in xylem vessel cell differentiation via post-transcriptional regulation of VND7-downstream events, such as patterning of SCW deposition.
- 著者
- Chikage Umeda-Hara Hidekazu Iwakawa Misato Ohtani Taku Demura Tomoko Matsumoto Jun Kikuchi Koji Murata Masaaki Umeda
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.0716a, (Released:2022-09-17)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Somatic polyploidization often increases cell and organ size, thereby contributing to plant biomass production. However, as most woody plants do not undergo polyploidization, explaining the polyploidization effect on organ growth in trees remains difficult. Here we developed a new method to generate tetraploid lines in poplars through colchicine treatment of lateral buds. We found that tetraploidization induced cell enlargement in the stem, suggesting that polyploidization can increase cell size in woody plants that cannot induce polyploidization in normal development. Greenhouse growth analysis revealed that radial growth was enhanced in the basal stem of tetraploids, whereas longitudinal growth was retarded, producing the same amount of stem biomass as diploids. Woody biomass characteristics were also comparable in terms of wood substance density, saccharification efficiency, and cell wall profiling. Our results reveal tetraploidization as an effective strategy for improving woody biomass production when combined with technologies that promote longitudinal stem growth by enhancing metabolite production and/or transport.
- 著者
- Aili Ailizati Isura Sumeda Priyadarshana Nagahage Atsuko Miyagi Toshiki Ishikawa Maki Kawai-Yamada Taku Demura Masatoshi Yamaguchi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.147-153, 2022-06-25 (Released:2022-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 1
An Arabidopsis NAC domain transcription factor VND-INTERACTING2 (VNI2) was originally isolated as an interacting protein with another NAC domain transcription factor, VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 (VND7), a master regulator of xylem vessel element differentiation. VNI2 inhibits transcriptional activation activity of VND7 by forming a protein complex. Here, to obtain insights into how VNI2 regulates VND7, we tried to identify the amino acid region of VNI2 required for inhibition of VND7. VNI2 has an amino acid sequence similar to the ETHYLENE-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTOR (ERF)-associated amphiphilic repression (EAR) motif, conserved in transcriptional repressors, at the C-terminus. A transient expression assay showed that the EAR-like motif of VNI2 was not required for inhibition of VND7. The C-terminal deletion series of VNI2 revealed that 10 amino acid residues, highly conserved in the VNI2 orthologs contributed to effective repression of the transcriptional activation activity of VND7. Observation of transgenic plants ectopically expressing VNI2 showed that the identified 10 amino acid sequence strongly affected xylem vessel formation and plant growth. These data indicated that the 10 amino acid sequence of VNI2 has an important role in its transcriptional repression activity and negative regulation of xylem vessel formation.
1 0 0 0 OA An Arabidopsis NAC domain transcriptional activator VND7 negatively regulates VNI2 expression
- 著者
- Aili Ailizati Isura Sumeda Priyadarshana Nagahage Atsuko Miyagi Toshiki Ishikawa Maki Kawai-Yamada Taku Demura Masatoshi Yamaguchi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.4, pp.415-420, 2021-12-25 (Released:2021-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 4
A NAC domain transcription factor, VND-INTERACTING2 (VNI2) is originally isolated as an interacting protein with another NAC domain transcription factor, VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 (VND7), a master regulator of xylem vessel element differentiation. VND7 directly or indirectly induces expression of a number of genes associated with xylem vessel element differentiation, while VNI2 inhibits the transcriptional activation activities of VND7 by forming a protein complex. VNI2 is expressed at an earlier stage of xylem vessel element differentiation than VND7. Here, to investigate whether VND7 also affects VNI2, a transient expression assay was performed. We demonstrated that VND7 downregulated VNI2 expression. Other transcription factors involved in xylem vessel formation did not show the negative regulation of VNI2 expression. Rather, MYB83, a downstream target of VND7, upregulated VNI2 expression. By using the deletion series of the VNI2 promoter, a 400 bp region was identified as being responsible for downregulation by VND7. These data suggested that VND7 and VNI2 mutually regulate each other, and VNI2 expression is both positively and negatively regulated in the transcriptional cascade.
- 著者
- Satoru Tsugawa Norihiro Kanda Moritaka Nakamura Tatsuaki Goh Misato Ohtani Taku Demura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.443-450, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 2 4
Plant shoots can bend upward against gravity, a behavior known as shoot gravitropism. The conventional quantification of shoot bending has been restricted to measurements of shoot tip angle, which cannot fully describe the spatio-temporal bending process. Recently, however, advanced imaging analyses have been developed to quantify in detail the spatio-temporal changes in inclination angle and curvature of the shoot. We used one such method (KymoRod) to analyze the gravitropism of the Arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stem, and successfully extracted characteristics that capture when and where bending occurs. Furthermore, we implemented an elastic spring theoretical model and successfully determined best fitted parameters that may explain typical bending behaviors of the inflorescence stem. Overall, we propose a data-model combined framework to quantitatively investigate shoot gravitropism in plants.
- 著者
- Ryusuke Nakai Takashi Azuma Yosuke Nakaso Shinichiro Sawa Taku Demura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.437-442, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful technique, only a few studies have investigated the dynamic behavior of small subjects using MRI owing to constraints such as experimental space and signal amount. In this study, to acquire high-resolution continuous three-dimensional gravitropism data of pea (Pisum sativum) sprouts, we developed a small-bore MRI signal receiver coil that can be used in a clinical MRI and adjusted the imaging sequence. It was expected that such an arrangement would improve signal sensitivity and improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the acquired image. All MRI experiments were performed using a 3.0-T clinical MRI scanner. An SNR comparison using an agarose gel phantom to confirm the improved performance of the small-bore receiver coil and an imaging experiment of pea sprouts exhibiting gravitropism were performed. The SNRs of the images acquired with a standard 32-channel head coil and the new small-bore receiver coil were 5.23±0.90 and 57.75±12.53, respectively. The SNR of the images recorded using the new coil was approximately 11-fold higher than that of the standard coil. In addition, when the accuracy of MR imaging that captures the movement of pea sprout was verified, the difference in position information from the optical image was found to be small and could be used for measurements. These results of this study enable the application of a clinical MRI system for dynamic plant MRI. We believe that this study is a significant first step in the development of plant MRI technique.
1 0 0 0 OA Root shape adaptation to mechanical stress derived from unidirectional vibrations in Populus nigra
- 著者
- Marcel Pascal Beier Satoru Tsugawa Taku Demura Toru Fujiwara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.423-428, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1 4
While it is known that plant roots can change their shapes to the stress direction, it remains unclear if the root orientation can change as a means for mechanical reinforcement. When stress in form of a unidirectional vibration is applied to cuttings of Populus nigra for 5 min a day over a period of 20 days, the root system architecture changes. The contribution of roots with a diameter larger than 0.04 cm increases, while the allocation to roots smaller than 0.03 cm decreases. In addition to the root diameter allocation, the root orientation in the stem proximity was analyzed by appearance and with a nematic tensor analysis in an attempt to calculate the average root orientation. The significant different allocation to roots with a larger diameter, and the tendency of roots to align in the vicinity of the stress axis (not significantly different), are indicating a mechanical reinforcement to cope with the received strain. This work indicates an adaptive root system architecture and a possible adaptive root orientation for mechanical reinforcement.
- 著者
- Eri Akita Yaxiaer Yalikun Kazunori Okano Yuki Yamasaki Misato Ohtani Yo Tanaka Taku Demura Yoichiroh Hosokawa
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.417-422, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1 4
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) can measure the mechanical properties of plant tissue at the cellular level, but for in situ observations, the sample must be held in place on a rigid support and it is difficult to obtain accurate data for living plants without inhibiting their growth. To investigate the dynamics of root cell stiffness during seedling growth, we circumvented these problems by using an array of glass micropillars as a support to hold an Arabidopsis thaliana root for AFM measurements without inhibiting root growth. The root elongated in the gaps between the pillars and was supported by the pillars. The AFM cantilever could contact the root for repeated measurements over the course of root growth. The elasticity of the root epidermal cells was used as an index of the stiffness. By contrast, we were not able to reliably observe roots on a smooth glass substrate because it was difficult to retain contact between the root and the cantilever without the support of the pillars. Using adhesive to fix the root on the smooth glass plane overcame this issue, but prevented root growth. The glass micropillar support allowed reproducible measurement of the spatial and temporal changes in root cell elasticity, making it possible to perform detailed AFM observations of the dynamics of root cell stiffness.
1 0 0 0 OA Preface to the special issue “Approaches for strategies of mechanical optimization in plants”
- 著者
- Taku Demura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.37, no.4, pp.393-395, 2020-12-25 (Released:2020-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 1