- 著者
- Satoshi Katano Toshiyuki Yano Katsuhiko Ohori Hidemichi Kouzu Ryohei Nagaoka Suguru Honma Kanako Shimomura Takuya Inoue Yuhei Takamura Tomoyuki Ishigo Ayako Watanabe Masayuki Koyama Nobutaka Nagano Takefumi Fujito Ryo Nishikawa Wataru Ohwada Akiyoshi Hashimoto Masaki Katayose Sumio Ishiai Tetsuji Miura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0584, (Released:2021-09-17)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 25
Background:A strategy to predict mortality in elderly heart failure (HF) patients has not been established.Methods and Results:We retrospectively enrolled 413 HF patients aged ≥65 years (mean age 78 years) who had received comprehensive cardiac rehabilitation (CR) during hospitalization. Basic activities of daily life were assessed before discharge using the Barthel index (BI). Of 413 HF patients, 116 (28%) died during a median follow-up period of 1.90 years (interquartile range 1.20–3.23 years). An adjusted dose-dependent association analysis showed that the hazard ratio (HR) of mortality increased in an almost linear manner as the BI score decreased, and that a BI score of 85 corresponded to an HR of 1.0. Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that the survival rate was lower for patients with a low BI (<85) than for those with a high BI (≥85; 65% vs. 74%, respectively; P=0.007). In multivariate Cox regression analyses, low BI was independently associated with higher mortality after adjusting for predictors, including B-type natriuretic peptide. Inclusion of the BI into the adjusted model improved the accuracy of the prediction of mortality.Conclusions:A BI score <85 at the time of discharge is associated with increased mortality independent of known prognostic markers, and achieving functional status with a BI score ≥85 by comprehensive CR during hospitalization may contribute to favorable outcomes in elderly HF patients.
- 著者
- Satoshi Katano Akiyoshi Hashimoto Katsuhiko Ohori Ayako Watanabe Remi Honma Rimi Yanase Tomoyuki Ishigo Takefumi Fujito Hirofumi Ohnishi Kazufumi Tsuchihashi Sumio Ishiai Tetsuji Miura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-17-1202, (Released:2018-04-07)
- 参考文献数
- 39
- 被引用文献数
- 28
Background:Whether the short-term effect of cardiac rehabilitation (CR) in elderly patients with heart failure (HF) is influenced by nutritional status is uncertain, so the present study investigated the effect of nutritional status on functional recovery after CR in elderly HF inpatients.Methods and Results:We enrolled 145 patients admitted for treatment of HF who were aged ≥65 years and had a low functional status defined as a Barthel index (BI) score ≤85 points at the commencement of CR. Nutritional status was assessed by the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form (MNA-SF) and total energy intake per day. The primary endpoint was functional status determined by the BI score at discharge. The median CR period was 20 days (interquartile range: 14–34 days), and 87 patients (60%) were functionally dependent (BI score ≤85) at discharge. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that MNA-SF score (odds ratio [OR]: 0.76, P=0.02) and total energy intake at the commencement of CR (OR: 0.91, P=0.02) were independent predictors of functional dependence after CR. MNA-SF score ≤7 and total energy intake ≤24.5 kcal/kg/day predicted functional dependence at discharge with moderate sensitivity and specificity.Conclusions:MNA-SF score and total energy intake at the commencement of CR are novel predictors of the extent of functional recovery of elderly HF inpatients after in-hospital CR.
- 著者
- Kazuhiro WAKAMATSU Sumio ISHIAI Nobuko AIHARA Sho KUROKAWA Yusuke KIMURA Nobuhiro MIKUNI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0319, (Released:2023-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
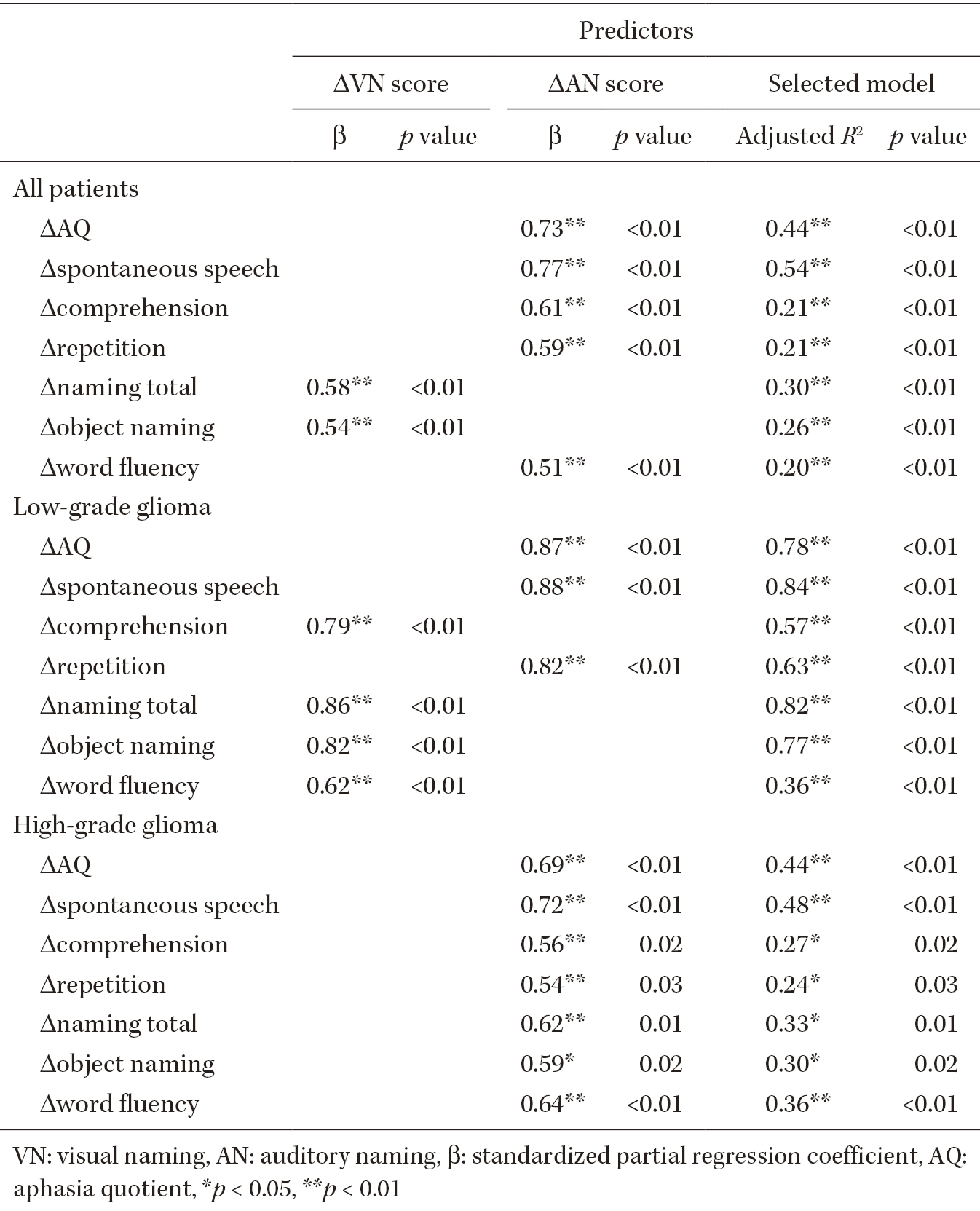
Language tasks for monitoring intraoperative language symptoms have not yet been established. This study aimed to examine whether the quantitative evaluation of language function with visual and auditory naming during awake craniotomy predicts early postoperative language function in patients. Thirty-seven patients with brain tumors in the language-dominant hemisphere were included. They underwent visual and auditory naming preoperatively and at the end of tumor resection for intraoperative evaluation. Using the Western Aphasia Battery, their overall language functions were evaluated preoperatively, early postoperatively (within 1 week), and late postoperatively (after 1 month). The preoperative and intraoperative changes in the visual and auditory naming scores were significantly correlated with most of the Western Aphasia Battery score changes between the preoperative and early postoperative evaluations, which was more remarkable for auditory naming. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that changes in the auditory naming score predicted the preoperative to early postoperative changes in the aphasia quotient of the Western Aphasia Battery. Receiver operating characteristics analysis showed a higher area under the curve or discriminative power for auditory than visual naming in predicting the development or exacerbation of aphasia in the early postoperative period. Considering the analyses applied separately for low- and high-grade glioma, auditory naming, which taps into a wider range of linguistic functions, may be more informative than visual naming as language evaluation in awake craniotomy for the early postoperative development of aphasia, especially for patients with high-grade glioma.
- 著者
- Masazumi FUJII Satoshi MAESAWA Sumio ISHIAI Kenichiro IWAMI Miyako FUTAMURA Kiyoshi SAITO
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.7, pp.379-386, 2016 (Released:2016-07-15)
- 参考文献数
- 57
- 被引用文献数
- 24 41
The neural basis of language had been considered as a simple model consisting of the Broca’s area, the Wernicke’s area, and the arcuate fasciculus (AF) connecting the above two cortical areas. However, it has grown to a larger and more complex model based upon recent advancements in neuroscience such as precise imaging studies of aphasic patients, diffusion tensor imaging studies, functional magnetic resonance imaging studies, and electrophysiological studies with cortical and subcortical stimulation during awake surgery. In the present model, language is considered to be processed through two distinct pathways, the dorsal stream and the ventral stream. The core of the dorsal stream is the superior longitudinal fasciculus/AF, which is mainly associated with phonological processing. On the other hand, semantic processing is done mainly with the ventral stream consisting of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and the intratemporal networks. The frontal aslant tract has recently been named the deep frontal tract connecting the supplementary motor area and the Broca’s area and it plays an important role in driving and initiating speech. It is necessary for every neurosurgeon to have basic knowledge of the neural basis of language. This knowledge is essential to plan safer surgery and preserve the above neural structures during surgery.