- 著者
- Masaki Hirabatake Hiroaki Ikesue Shintaro Yoshino Mayu Morimoto Toshinari Yamasaki Tohru Hashida Mutsushi Kawakita Nobuyuki Muroi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.8, pp.1065-1071, 2023-08-01 (Released:2023-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Pazopanib is one of recommended treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Despite its effectiveness, patients often difficult to continue pazopanib treatment due to adverse events (AEs). We established an ambulatory care pharmacy practice that enables pharmacist–urologist collaboration to manage patients with RCC. This study evaluated the usefulness of this collaborative management. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 51 consecutive patients with metastatic RCC receiving pazopanib at the Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital between April 2014 and December 2020. Our collaborative management was implemented in October 2016. The time to pazopanib discontinuation was compared between patients who started pazopanib before (n = 30) and after (n = 21) the implementation of the collaborative management. A multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to analyze the factors associated with pazopanib discontinuation. In the collaborative management, the oncology pharmacists had a total of 245 face-to-face patient consultations, and provided 286 suggestions [according to supportive care in pazopanib treatment (214 suggestions) were most frequent], and 236 (82.5%) were accepted by urologists. The median time to discontinuation (6.1 months vs. 2.4 months, p = 0.024) was significantly longer in the after group. Multivariate analysis showed that collaborative management (hazard ratio (HR) 0.49, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.26–0.88, p = 0.017), and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) ≥2 at pazopanib initiation (HR 3.87, 95% CI 1.47–9.13, p = 0.008) were significantly associated with pazopanib discontinuation. These results suggested that, compared to conventional management, collaborative management is effective at prolonging the time to pazopanib discontinuation.
1 0 0 0 OA Risk Factors of Proteinuria in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Lenvatinib
- 著者
- Hiroaki Ikesue Haruna Yamamoto Masaki Hirabatake Tohru Hashida Hobyung Chung Tetsuro Inokuma Nobuyuki Muroi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.3, pp.333-338, 2022-03-01 (Released:2022-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Proteinuria is one of the most frequently reported adverse events leading to the discontinuation of lenvatinib treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, there are no reports regarding the risk factors of proteinuria in patients with HCC or patients receiving lenvatinib. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients with HCC receiving lenvatinib at the Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital between April 2018 and December 2020. The severity of proteinuria was graded based on the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was employed to identify the risk factors of developing grade ≥2 proteinuria. Among the 37 patients included, 3 patients had grade-1 proteinuria at baseline and 10 patients had estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at baseline. Grades 1, 2, and 3 proteinuria were observed in 15 (40.5%), 10 (27.0%), and 2 (5.4%) patients, respectively, during lenvatinib treatment. The median value of eGFR was significantly lower in patients who developed grade ≥2 proteinuria than those with grade ≤1 proteinuria (59.6 vs. 78.1 mL/min/1.73 m2, p = 0.045). Multivariate analysis revealed that pre-existing proteinuria at baseline (hazard ratio (HR), 9.72; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.29–52.21; p = 0.030), and eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 at baseline (HR, 4.49; 95% CI, 1.32–16.07; p = 0.017) were significantly associated with developing grade ≥2 proteinuria. These patients should be monitored carefully, and our preliminary data should be confirmed by further studies.
- 著者
- Mayako Uchida Yasuhiro Mori Kenta Akiba Moena Miyasaka Tatsuya Hirano Hiroaki Ikesue Yuki Yamaguchi Aoi Takano Nami Maegawa Yoshimitsu Shimomura Keiko Hosohata Nobuyuki Muroi Takayuki Ishikawa Tohru Hashida Tsutomu Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1577-1582, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2
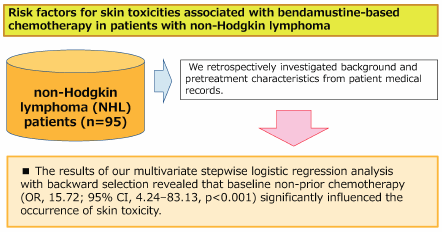
Bendamustine plays an especially important role as a treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). However, patients administered bendamustine alone or in combination with rituximab (BR) may experience drug-associated skin toxicities that can profoundly impact their health-related QOL through both physical discomfort and psychological distress. Moreover, worsening skin symptoms may lead to dose reduction or termination in the management of cancer chemotherapy. We retrospectively investigated patient backgrounds and pretreatment characteristics from medical records of NHL patients treated with bendamustine alone or BR therapy and identified predictive factors for skin toxicities at the start of chemotherapy. Patients were eligible for the study if they were 20 years older, diagnosed with NHL, and received bendamustine alone or BR therapy at the Department of Hematology, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, between April 1, 2011, and March 31, 2018. This study included 95 patients with newly diagnosed or refractory or relapsed NHL. Multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis with backward selection revealed that baseline non-prior chemotherapy (odds ratio (OR), 15.72; 95% confidence interval (CI), 4.24–83.13, p < 0.001) was a significant factor influencing the occurrence of skin toxicity. Our results demonstrated that non-prior chemotherapy was a significant risk factor for skin toxicities in patients with NHL receiving bendamustine alone or BR therapy. No patient experience serious side effects of grade 3 or higher and that bendamustine is very useful as a first-line treatment.
- 著者
- Mayako Uchida Yuki Yamaguchi Syuhei Hosomi Hiroaki Ikesue Yasuhiro Mori Nami Maegawa Aoi Takano Yuki Sato Keiko Hosohata Nobuyuki Muroi Keisuke Tomii Tohru Hashida Tsutomu Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.8, pp.1235-1240, 2020-08-01 (Released:2020-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We retrospectively obtained data of patient background and pretreatment characteristics from medical records and identified the predictive factors of febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with docetaxel alone or in combination with the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody bevacizumab. Patients were eligible for inclusion in the study if they were 20 years or older, diagnosed with NSCLC, and received docetaxel monotherapy alone or in combination with bevacizumab at the Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, between July 1, 2011, and March 31, 2018. Eighty-one patients with recurrent or advanced NSCLC were included. Multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis with backward selection revealed that lower baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG-PS) scores of 1 and 2 (odds ratio (OR), 5.098; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.045–24.879, p = 0.021) and baseline platelet count below 18.8 × 104/µL (OR, 3.861; 95% CI, 1.211–12.311, p = 0.022) were significant factors influencing the FN occurrence rate. Our results demonstrated that ECOG-PS 1–2 and lower baseline platelet count were significant risk factors of FN in patients with NSCLC receiving docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Moreover, the combination of anti-VEGF antibodies and docetaxel might be associated with increased FN frequency. Despite the limitations of this study including its retrospective design, single-center site, and small sample size, baseline ECOG-PS score and platelet count may be regarded as important indices to identify patients for prophylactic granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) treatment before docetaxel-based chemotherapy.