- 著者
- Hideyuki Katsura Yukio Suga Anna Kubo Hayato Sugimura Kaname Kumatani Kazunobu Haruki Miwa Yonezawa Ayaka Narita Rei Ishijima Hiroaki Ikesue Hitomi Toi Naoko Takata
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.1, pp.98-103, 2024-01-01 (Released:2024-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Hypomagnesemia commonly occurs as a side effect of panitumumab treatment. In severe cases, temporary discontinuation or dose reduction of panitumumab may be necessary. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are reportedly potential risk factors for hypomagnesemia. We conducted a multicenter study to assess the impact of PPIs on the risk of grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) receiving panitumumab. We adjusted for potential bias using a propensity score-matched analysis and retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients. Hypomagnesemia severity was graded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5.0. A total of 165 patients were enrolled in this study. The incidence of grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia was significantly higher in the PPI group than in the non-PPI group, both before (20.0% [30/60] vs. 8.0% [8/105], p = 0.026) and after propensity score matching (16.2% [6/37] vs. 0% [0/37], p = 0.025). In the propensity score-matched cohort, the risk of grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia was significantly higher in the PPI group (odds ratio, 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.69–2.84; p = 0.025). These findings suggest that concomitant use of PPIs significantly increases the risk of grade 3–4 hypomagnesemia in patients with mCRC receiving panitumumab. Therefore, close monitoring of these patients is imperative.
- 著者
- Yukio Suga Mayako Uchida Shinya Suzuki Hideki Sugawara Kazuhiro Torigoe Akihiko Futamura Yoshihiro Uesawa Takayuki Nakagawa Hisamitsu Takase
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.5, pp.801-806, 2019-05-01 (Released:2019-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 10
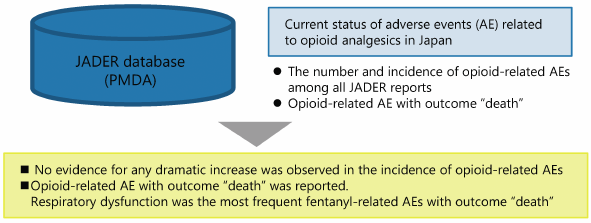
Opioid analgesics have greatly contributed to the advancement of pain management. However, although opioids have been appropriately used in Japan, they rarely induce serious adverse events, such as respiratory depression. The present study aimed to investigate the temporal changes in the occurrence of opioid-related adverse events and deaths between 2004 and 2017 in Japan using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) database. We analyzed the following points using data extracted from JADER website: 1) temporal changes in the number and proportion of opioid-related adverse event reports; 2) temporal changes in the number of morphine-, oxycodone-, and fentanyl-related adverse event reports per annual consumption; and 3) cases in which the reported outcome following opioid-related adverse events was death. Our results showed no dramatic changes in the overall incidence of opioid-related adverse events, despite the temporal changes in the annual consumption and shared component of each opioid during the survey period. However, the number and rate of fentanyl-related adverse events and their outcome “death” increased since 2010, being the highest among all adverse event including those related to morphine and oxycodone. Outcome “death” by fentanyl-related adverse events was caused mainly due to respiratory depression. These findings suggest that, although opioid-related adverse events can be controlled through proper monitoring and management by medical personnel in Japan, extra caution should be continuously paid for the rare but serious fentanyl-induced adverse events.
- 著者
- Shinya Suzuki Mayako Uchida Yukio Suga Hideki Sugawara Hideya Kokubun Yoshihiro Uesawa Takayuki Nakagawa Hisamitsu Takase
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.7, pp.1164-1171, 2019-07-01 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 2 12
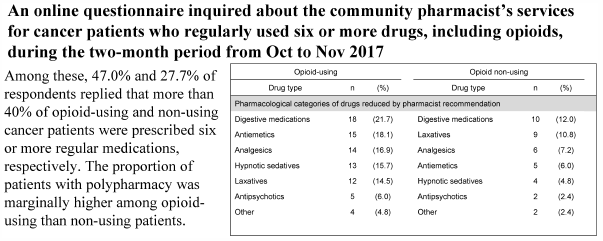
No nationwide study on polypharmacy in palliative care among Japanese community pharmacies has yet been conducted. We conducted an online questionnaire survey for community pharmacist members of The Japanese Society for Pharmaceutical Palliative Care and Sciences regarding their contributions to cancer patients who regularly used six or more drugs, including opioids, in service during the two-month period from October to November 2017. Of 579 community pharmacists, 83 responded to the survey (14.3%). Among them, 47.0 and 27.7% of respondents replied that more than 40% of opioid-using and non-using cancer patients were prescribed six or more regular medications, respectively. The proportion of patients with polypharmacy was marginally higher among opioid-using than non-using patients. Additionally, 31.3 and 22.9% of respondents replied that a low or moderate rate of opioid-using and non-using patients with polypharmacy received inappropriate prescriptions, respectively, including “unnecessary medications,” “adverse drug reactions” and “duplication of pharmacological effect.” The proportion of patients who received inappropriate prescriptions was significantly higher among opioid-using than non-using patients. Furthermore, 37.3 and 19.3% of respondents replied that pharmacist’s recommendations contributed to drug reduction in opioid-using and non-using patients with polypharmacy who received inappropriate prescriptions, respectively. The responders with higher confidence in palliative care showed more success rate for reducing inappropriate medications. Our findings suggest that opioid use can be associated with an increased risk of polypharmacy in cancer patients, and that recommendations by a population of community pharmacists can reduce inappropriate medications and improve adverse drug reactions in both opioid-using and non-using cancer patients with polypharmacy.