- 著者
- Hiroshi Kadowaki Junichi Ishida Hiroshi Akazawa Hiroki Yagi Akiko Saga-Kamo Masahiko Umei Ryo Matsuoka Qing Liu Hiroshi Matsunaga Hisataka Maki Yusuke Sato Haruki Kume Issei Komuro
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-21-0008, (Released:2021-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Background:Axitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling and is approved for second-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Although the occurrence of hypertension with axitinib use has been documented, it is unclear whether a first-line TKI regimen can significantly affect the development of hypertension when axitinib is used as second-line therapy.Methods and Results:In this single-center retrospective study, advanced RCC patients treated with axitinib after first-line chemotherapy were divided into 2 groups according to the use of TKIs as part of first-line treatment before the initiation of axitinib. Clinical outcomes were compared between patients who were treated with (TKI(+); n=11) or without (TKI(–); n=11) a TKI. Although 63.6% of all patients had hypertension at baseline, axitinib-induced hypertension developed in 81.8% of patients, and 36.4% of patients experienced Grade 3 hypertension. After initiation of axitinib, both systolic and diastolic blood pressures and the hypertension grade were significantly elevated both in the TKI(+) and TKI(–) groups, and the number of antihypertensive drugs was significantly increased among all patients.Conclusions:This study suggests the need for proper monitoring and management of blood pressure in RCC patients treated with axitinib, regardless of a prior regimen with or without TKIs.
- 著者
- Yusuke Sato Tetsuji Morishita Yuya Matsunaka Tomohiro Shimizu Hiroyasu Uzui Hiroshi Tada
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0173, (Released:2023-05-09)
- 参考文献数
- 1
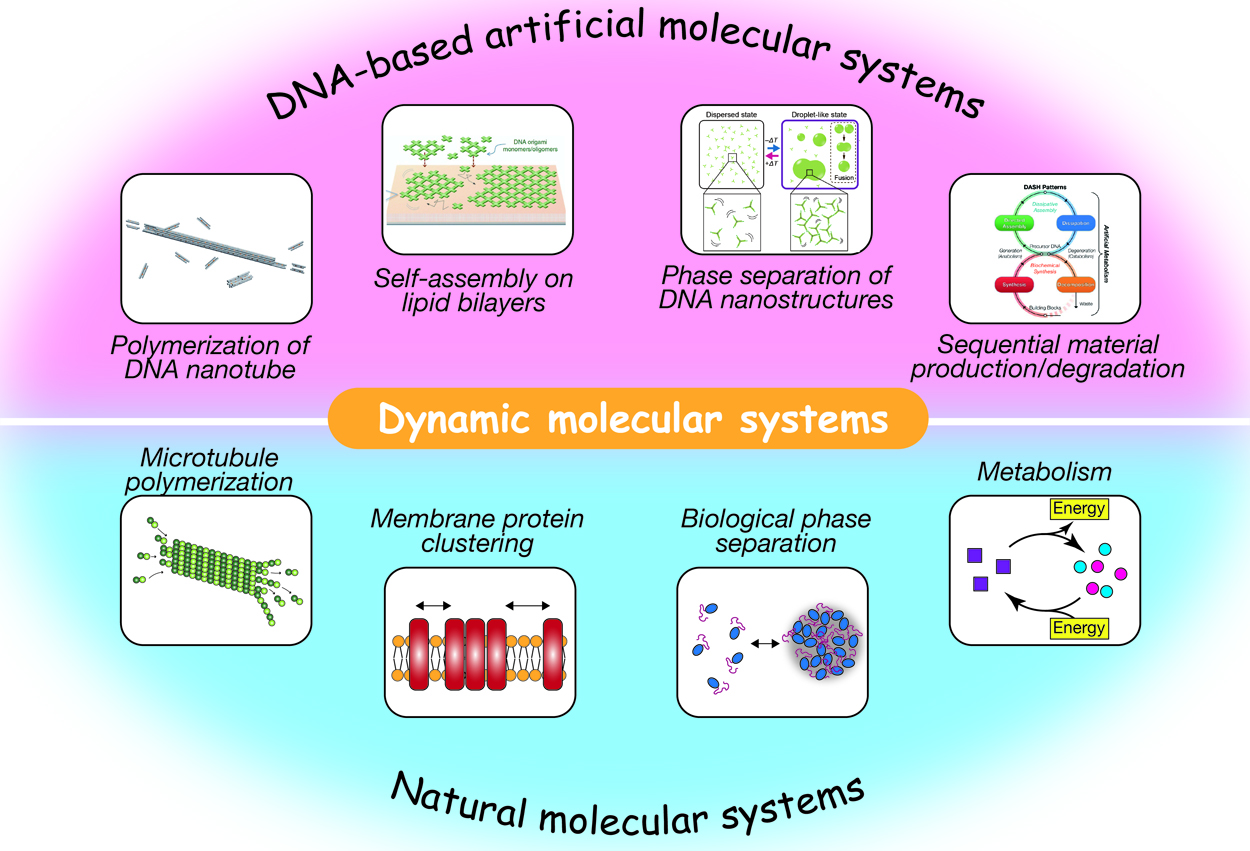
3 0 0 0 OA DNA nanotechnology provides an avenue for the construction of programmable dynamic molecular systems
- 著者
- Yusuke Sato Yuki Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.116-126, 2021 (Released:2021-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 80
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Self-assembled supramolecular structures in living cells and their dynamics underlie various cellular events, such as endocytosis, cell migration, intracellular transport, cell metabolism, and gene expression. Spatiotemporally regulated association/dissociation and generation/degradation of assembly components is one of the remarkable features of biological systems. The significant advancement in DNA nanotechnology over the last few decades has enabled the construction of various-shaped nanostructures via programmed self-assembly of sequence-designed oligonucleotides. These nanostructures can further be assembled into micrometer-sized structures, including ordered lattices, tubular structures, macromolecular droplets, and hydrogels. In addition to being a structural material, DNA is adopted to construct artificial molecular circuits capable of activating/inactivating or producing/decomposing target DNA molecules based on strand displacement or enzymatic reactions. In this review, we provide an overview of recent studies on artificially designed DNA-based self-assembled systems that exhibit dynamic features, such as association/dissociation of components, phase separation, stimulus responsivity, and DNA circuit-regulated structural formation. These biomacromolecule-based, bottom-up approaches for the construction of artificial molecular systems will not only throw light on bio-inspired nano/micro engineering, but also enable us to gain insights into how autonomy and adaptability of living systems can be realized.
- 著者
- Kodwo Amuzuah OBENG Shinji MOCHIZUKI Shinichiro KOIKE Yuka TOYOSHIMA Yusuke SATO Fumiaki YOSHIZAWA
- 出版者
- Center for Academic Publications Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (ISSN:03014800)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.4, pp.312-319, 2022-08-31 (Released:2022-08-31)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid important as a protein building block, but it also serves as substrate for the generation of several bioactive compounds with important physiological roles. Furthermore, tryptophan has been reported to have a unique role as a nutritional signaling molecule that regulates protein synthesis in mouse and rat liver. In the present study, the acute effects of tryptophan on protein synthesis were confirmed and compared with those of leucine in rats. Eighteen hours fasted rats were orally administered of tryptophan or leucine at a dose of 135 mg/100 g body weight by gavage and then sacrificed 1 h after administration. The effects of tryptophan and leucine on the rate of protein synthesis were evaluated by the surface sensing of translation (SUnSET) method. We also examined the ability of tryptophan to induce activation of the mTOR pathway by measuring phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and S6K1. Oral administration of tryptophan led to a stimulation of the rate of protein synthesis concomitant with activation of mTOR pathway in the liver, but not in skeletal muscle. We also investigated the sensitivity of liver protein synthesis to tryptophan administration. The half-maximal effective doses (ED50) of tryptophan in stimulating 4E-BP1 and S6K1 phosphorylation were both about 60% of daily intake. The effect of tryptophan on hepatic protein synthesis was similar to that of leucine on muscle protein synthesis, and the sensitivity of liver protein synthesis to tryptophan administration appeared to be almost the same or slightly lower than that of muscle protein synthesis to leucine administration.
- 著者
- Yusuke Sato
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.69, no.12, pp.1141-1159, 2021-12-01 (Released:2021-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 192
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Considerable efforts have been made on the development of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for delivering of nucleic acids in LNP-based medicines, including a first-ever short interfering RNA (siRNA) medicine, Onpattro, and the mRNA vaccines against the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which have been approved and are currently in use worldwide. The successful rational design of ionizable cationic lipids was a major breakthrough that dramatically increased delivery efficiency in this field. The LNPs would be expected to be useful as a platform technology for the delivery of various therapeutic modalities for genome editing and even for undiscovered therapeutic mechanisms. In this review, the current progress of my research, including the molecular design of pH-sensitive cationic lipids, their applications for various tissues and cell types, and for delivering various macromolecules, including siRNA, antisense oligonucleotide, mRNA, and the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated (Cas) system will be described. Mechanistic studies regarding relationships between the physicochemical properties of LNPs, drug delivery, and biosafety are also summarized. Furthermore, current issues that need to be addressed for next generation drug delivery systems are discussed.
1 0 0 0 OA 口向役人不正事件と江戸幕府の遠国都市政策
- 著者
- 佐藤 雄介 Yusuke Sato
- 出版者
- 學習院大學文學部
- 雑誌
- 研究年報 = The annual collection of essays and studies, Faculty of Letters (ISSN:04331117)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.68, pp.63-86, 2022-03-20