- 著者
- Takashi Kikukawa
- 出版者
- The Biophysical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biophysics and Physicobiology (ISSN:21894779)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, pp.317-326, 2021 (Released:2022-01-08)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 2
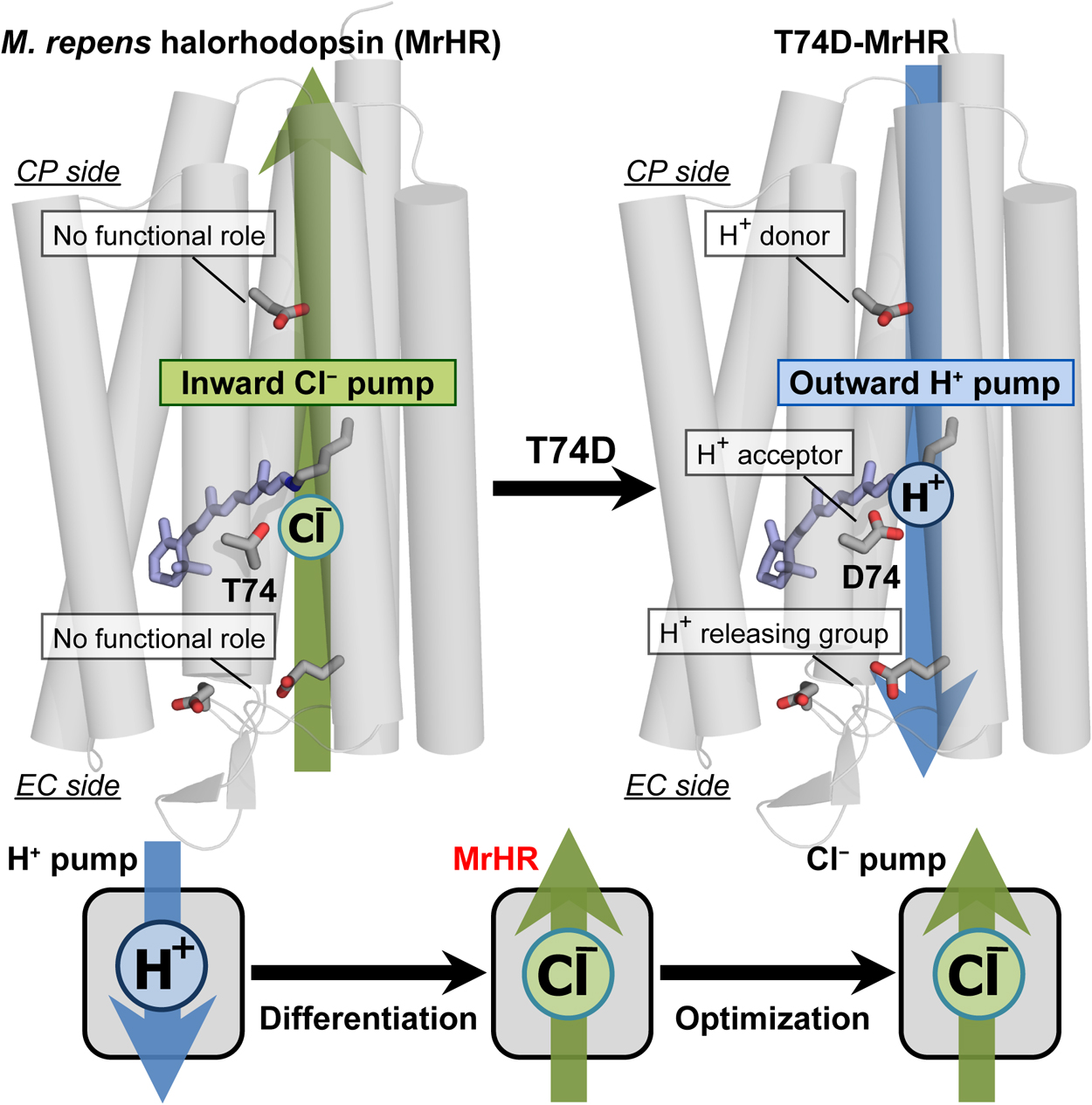
Microbial rhodopsin is a ubiquitous membrane protein in unicellular microorganisms. Similar to animal rhodopsin, this protein consists of seven transmembrane helices and the chromophore retinal. However, unlike animal rhodopsin, microbial rhodopsin acts as not only a photosignal receptor but also a light-activated ion transporter and light-switchable enzyme. In this article, the third Cl– pump microbial rhodopsin will be introduced. The physiological importance of Cl– pumps has not been clarified. Despite this, their mechanisms, especially that of the first Cl– pump halorhodopsin (HR), have been studied to characterize them as model proteins for membrane anion transporters. The third Cl– pump defines a phylogenetic cluster distinct from other microbial rhodopsins. However, this Cl– pump conserves characteristic residues for not only the Cl– pump HR but also the H+ pump bacteriorhodopsin (BR). Reflecting close similarity to BR, the third Cl– pump begins to pump H+ outwardly after single amino acid replacement. This mutation activates several residues that have no roles in the original Cl– pump function but act as important H+ relay residues in the H+ pump mutant. Thus, the third Cl– pump might be the model protein for functional differentiation because this rhodopsin seems to be the Cl– pump occurring immediately after functional differentiation from the BR-type H+ pump.
言及状況
外部データベース (DOI)
Twitter (7 users, 7 posts, 20 favorites)
シアノバクテリア由来のCl-ポンプロドプシンについての総説 "Unique Cl– pump rhodopsin with close similarity to H+ pump rhodopsin" が、Biophys. Physicobiol. から公開になりました。執筆の機会を頂きまして、誠に有難うございました。https://t.co/wJSTKkAXWl https://t.co/cv5WwFmeXw