1 0 0 0 OA IF鋼の降伏強度に及ぼす混粒組織の影響
- 著者
- 的場 理一郎 中田 伸生 二村 裕一 土山 聡宏 高木 節雄
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.93, no.7, pp.513-517, 2007-07-01 (Released:2009-02-13)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 17 16
The “nominal grain size” (average grain size) is generally applied to Hall-Petch relationship to evaluate grain refinement strengthening in polycrystalline materials. However, the steels with wide grain size distribution (duplex-grained structure) may not deform uniformly but yield preferentially from larger grains to finer ones. This phenomenon is called “micro-yielding”. In this study, the effect of duplex-grained structure on the yield stress was investigated by using some IF steels with different grain size distribution. As a result of tensile testing, the yield stress of duplex-grained steels could be conventionally plotted on the Hall-Petch relationship as a function of (nominal grain size)-1/2 in the range from 100 to 10 μm, even though the micro-yielding phenomenon occurred within the coarse grains at a lower stress than the macroscopic yield stress. When the volume fraction of grains with identical size is summed from larger-sized ones, the summated volume fraction (defined as the integrated volume fraction) always reaches 70-80 vol% at the nominal grain size irrespective of the difference in grain size distribution. These results suggest that polycrystalline materials including duplex-grained structure materials cause the macroscopic yielding when the grains of 70-80 vol% are micro-yielded.
- 著者
- 横井 龍雄 首藤 洋志 池田 賢一 中田 伸生 土山 聡宏 大村 孝仁 峯 洋二 高島 和希
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.102, no.5, pp.244-252, 2016 (Released:2016-04-30)
- 参考文献数
- 38
Dual Phase (DP) steel is used in automotive body parts for weight saving and crashworthiness, however there is an issue of DP steel in low stretch flange ability evaluated by hole expanding tests. In order to improve stretch flange ability of DP steel, it is important to estimate the damage of punching quantitatively and to clarify the change of microstructure before and after punching because the hole expansion ratio is decided in the ductility remained after pre-strain equivalent to punching. Therefore we tried to measure the damage of punching by unique techniques of Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD), nano-indentation and micro-tensile testing and to observe fracture surface by Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM). Average EBSD-Kernel Average Misorientation (KAM) value and pre-strain damage have strong correlation, thus average KAM value can become the index of the damage. The nanohardness and tensile strength using micrometer-sized specimens increased with increasing average KAM value in the ferritic phase as approaching the punching edge. A shear type fracture occurred without necking in the specimen cut out in the area of the edge. The ultrafine-grained ferritic microstructure was observed in the sample cut out in the same area with STEM. It seems that the ductility loss of the punched DP steel was probably attributed to localized strain into the ultrafine-grained ferritic microstructure.
1 0 0 0 OA パーライトにおける内部応力の動的緩和と結晶方位関係の選択
- 著者
- 雨宮 雄太郎 中田 伸生 諸岡 聡 小坂 誠 加藤 雅治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- 鉄と鋼 (ISSN:00211575)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.105, no.2, pp.314-323, 2019 (Released:2019-01-31)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 5
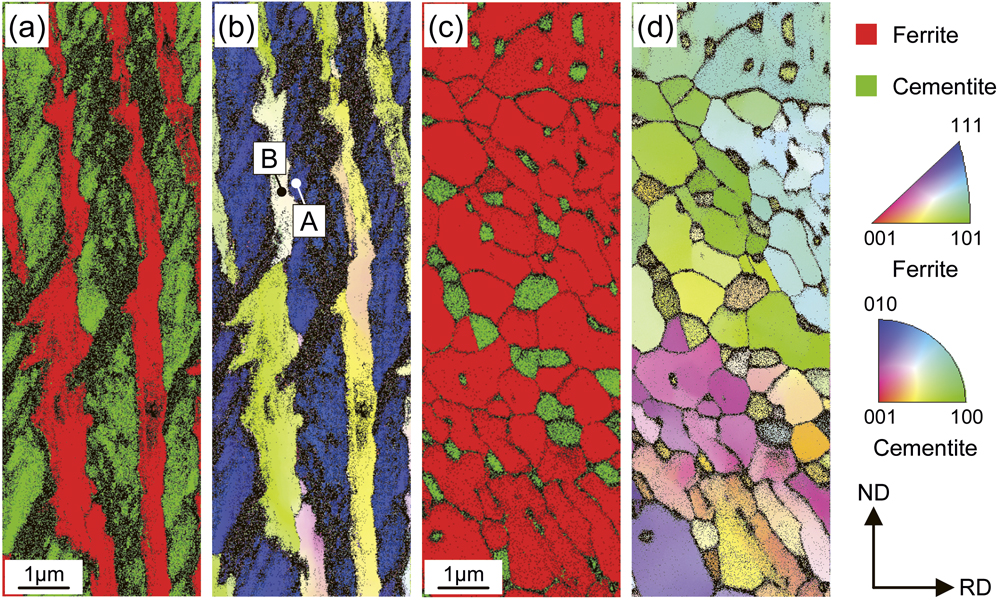
For deeper understanding of a dynamic accommodation mechanism of internal stress in pearlite originated from the lattice misfit between ferrite and cementite phases, the lattice parameter ratios of cementite, bθ/aθ and cθ/aθ, were locally analyzed in detail by using the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique. The EBSD analysis has revealed that lattice parameter ratios of cementite lamellae obviously differ from those of spheroidized cementite particles, which demonstrates that pearlite has a certain amount of internal stress as long as it maintains lamellar structure. The internal stress in pearlite gradually decreased during isothermal holding at 923 K after pearlitic transformation due to interfacial atomic diffusion of iron atoms. However, comparing with theoretical values under Pitsch-Petch orientation relationship, it was understood that large amount of internal stress had been already accommodated upon pearlitic transformation by introduction of misfit dislocations and structural ledges on ferrite/cementite lamellar interfaces. That is, the internal stress of pearlite is dynamically reduced by two different processes; built-in accommodation upon pearlitic transformation and additional time-dependent relaxation after pearlitic transformation. On the other hand, EBSD analysis and neutron diffraction technique gave remarkably different lattice parameters of cementite. From this result, it is concluded that various crystallographic orientation relationships between ferrite and cementite coexist in pearlite. Furthermore, elastic strain energy analysis suggests that the invariant-line criterion on ferrite/cementite interface plays an important role for the selection of orientation relationships in pearlite.
1 0 0 0 OA 炭化物とナノCu粒子を複合利用したハイブリッド鋼の提案
粒子分散強化は金属材料の基本的な強化機構の一つであり、鉄鋼材料の場合、セメンタイトを代表とする炭化物が一般的に強化分散粒子として使用されている。一方、近年ではナノテクノロジーによる鉄鋼材料の高機能化研究が盛んに行われており、数nm~数十nm の非常に微細な分散粒子(ナノ分散粒子)を利用して鉄鋼材料の高強度化を図ろうとする試みがなされ、その一つとしてナノCu 粒子が注目されている。ただし、ナノCu 粒子分散鋼の優れた機械的性質は、単に分散粒子のサイズが微細であることだけでなく、「分散Cu 粒子自体が鉄基地に比べて十分軟質である」というCu 粒子の特徴によってもたらされている事実も示唆されている。今後、大きな降伏強度と加工硬化率を有し高強度・高延性を兼ね備えた材料を得るためには、炭化物とCu 粒子を同時に最適な状態で分散させ、それぞれの特長を融合させてやること(ハイブリッド化)が有効であると考えられる。そのような鉄鋼材料、「ハイブリッド鋼」の有効性を証明することを本研究の最大の目的とし研究を遂行した。その結果、様々なハイブリッド鋼(フェライト型ハイブリッド鋼、マルテンサイト型ハイブリッド鋼、パーライト型ハイブリッド鋼など)の創製に成功し、炭化物とCu 粒子の複合析出により鋼の強度-延性バランスが大幅に改善することが明らかとなった。さらに、炭化物とCu 粒子それぞれの分散状態を制御することにより鋼の降伏強度と加工硬化率を独立して任意にコントロールできる可能性が示唆された。