3 0 0 0 OA 水の熱化学分解
- 著者
- 小貫 薫 野口 弘喜 田中 伸幸 竹上 弘彰 久保 真治
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面科学会
- 雑誌
- 表面科学 (ISSN:03885321)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.80-85, 2015-02-10 (Released:2015-02-19)
- 参考文献数
- 17
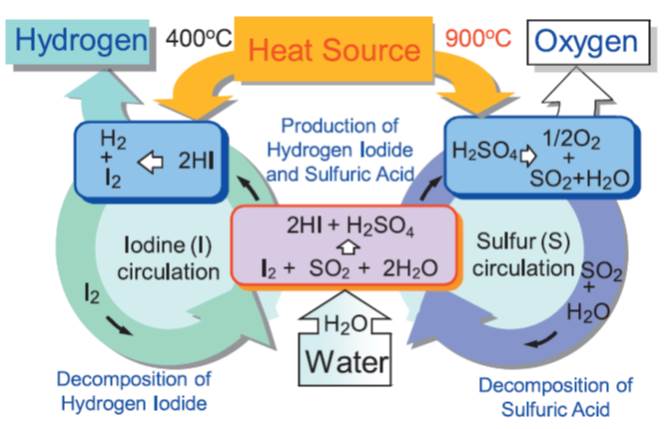
Thermochemical water-splitting process decomposes water using thermal energy by operating high temperature endothermic reaction(s) and low temperature exothermic reaction(s) cyclically, with which free energy of water decomposition is produced. The so-called sulfur family processes, which utilize thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid as the high temperature endothermic reaction, have attracted lots of interest among the many processes proposed so far. The IS process represents the pure thermochemical sulfur family processes. The continuous hydrogen production by IS process was demonstrated in laboratory, and the materials of construction for the IS process have been screened by corrosion tests performed in the severe process environment. At present, application of membrane technologies and development of catalysts are under study to improve the hydrogen production performance. Also, development is underway of the chemical reactors made of candidate materials such as ceramics.
2 0 0 0 宇宙線ミューオンによる HTTR 内部構造の可視化予備試験
- 著者
- 竹上 弘彰 高松 邦吉 伊藤 主税 日野 竜太郎 鈴木 敬一 大沼 寛 奥村 忠彦
- 出版者
- Atomic Energy Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- 日本原子力学会和文論文誌 (ISSN:13472879)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.1, pp.7-16, 2014
One of the important problems in the control of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is the removal of fuel debris. As preparation, a nondestructive inspection method for identifying the position of fuel debris is required. Therefore, we focused on a nondestructive inspection method using cosmic-ray muons, which is utilized for ground investigation. In this study, the applicability of this method for internal visualization of the reactor was confirmed by a preliminary test of the internal visualization of the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. By using cosmic-ray muons, main components in the HTTR reactor, such as concrete walls and the reactor core, can be observed from the outside of the containment vessel of the HTTR. From the results of the preliminary examination, it appears that the inspection method with muons is promising for searching for fuel debris in a reactor. Based on the results, we also proposed some improvements of this system for its application to inspection at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.<br>
2 0 0 0 OA 宇宙線ミューオンによる HTTR 内部構造の可視化予備試験
- 著者
- 竹上 弘彰 高松 邦吉 伊藤 主税 日野 竜太郎 鈴木 敬一 大沼 寛 奥村 忠彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本原子力学会
- 雑誌
- 日本原子力学会和文論文誌 (ISSN:13472879)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.1, pp.7-16, 2014 (Released:2014-02-15)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 1
One of the important problems in the control of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is the removal of fuel debris. As preparation, a nondestructive inspection method for identifying the position of fuel debris is required. Therefore, we focused on a nondestructive inspection method using cosmic-ray muons, which is utilized for ground investigation. In this study, the applicability of this method for internal visualization of the reactor was confirmed by a preliminary test of the internal visualization of the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. By using cosmic-ray muons, main components in the HTTR reactor, such as concrete walls and the reactor core, can be observed from the outside of the containment vessel of the HTTR. From the results of the preliminary examination, it appears that the inspection method with muons is promising for searching for fuel debris in a reactor. Based on the results, we also proposed some improvements of this system for its application to inspection at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.