- 著者
- Masaharu Oshima Daisuke Mori Aki Takigawa Akihiko Otsuki Naoka Nagamura Shun Konno Yoshinobu Takahashi Masato Kotsugi Hiroshi Nohira
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Vacuum and Surface Science
- 雑誌
- e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (ISSN:13480391)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, pp.257-261, 2018-06-09 (Released:2018-06-09)
- 参考文献数
- 21
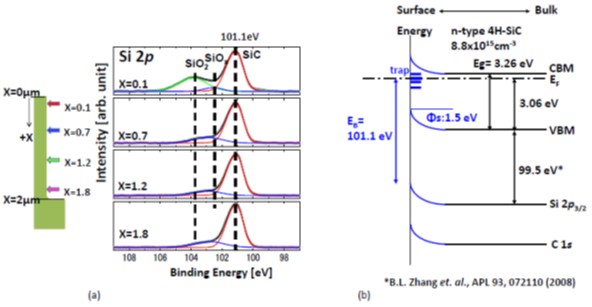
SiC trench structures having a width of 0.6 μm and a depth of 2.0 μm are fabricated by reactive ion etching (RIE) using a gas mixture of SF6, Ar, and O2. Further, SiC trench structures are cleaved to expose the sidewall for the channel region of a trench MOSFET. These structures were analyzed by pin-point photoelectron spectroscopy using a 100 nm soft-X-ray beam. It is observed that around 2 nm-thick homogeneous carbon-rich layer containing 1—2% F forms on the SiC sidewalls. This may be caused due to the re-deposition of RIE reaction products, CF4 and SiF4, under appropriate conditions to fabricate the trench walls that are approximately vertical using RIE. Further, a carbon-rich layer having a thickness of about 2.4 nm is also formed on the bottom of the SiC trench, suggesting the possibility of selective etching of Si from the SiC substrates. The position of the dominant peak that is associated with the SiC component remains constant regardless of the trench depth, suggesting homogeneous band bending due to the RIE defects, which may explain the reason for no variation being observed in the gate oxide/SiC interface trap density values. Further, the band bending of 1.50 eV that is observed on the sidewall can be attributed to a positively charged carbon vacancy (VC+). [DOI: 10.1380/ejssnt.2018.257]
- 著者
- Daisuke Mori Miho Sato Sou Taminato Nobuyuki Imanishi Kota Suzuki Masaaki Hirayama
- 出版者
- The Ceramic Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan (ISSN:18820743)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.131, no.10, pp.690-695, 2023-10-01 (Released:2023-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Li ionic conductors that are stable to lithium metal with high ionic conductivity are required as solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries with high energy density. Lithium dendrite growth leading to short-circuit is one of the major issues to solve for developing practical batteries using lithium metal electrodes. We have introduced Li3PO4 (LPO) and Li3BO3 (LBO) as a grain boundary phase in the garnet-type lithium ionic conductor, Li6.25Ga0.25La3Zr2O12 (LGLZ), by co-sintering. The lattice parameters, sinterability, elemental distribution, particle morphology, and electrochemical properties have been investigated. The sinterability has decreased with the introduction of LPO and LBO, while no significant change in the ionic conductivity is observed. The LGLZ with LPO was unstable to Li metal and did not exhibit the improvement of Li plating/stripping. Meanwhile, the LBO introduction into the grain boundary as a functional core increased the critical current density of the short circuit. Li dendrite growth could be suppressed by modifying the grain boundaries of the sintered body.
- 著者
- Sanae Kato Epifanio Bagarinao Haruo Isoda Shuji Koyama Hirohisa Watanabe Satoshi Maesawa Daisuke Mori Kazuhiro Hara Masahisa Katsuno Minoru Hoshiyama Shinji Naganawa Norio Ozaki Gen Sobue
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2020-0081, (Released:2020-10-27)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Purpose: The estimation of functional connectivity (FC) measures using resting state functional MRI (fMRI) is often affected by head motion during functional imaging scans. Head motion is more common in the elderly than in young participants and could therefore affect the evaluation of age-related changes in brain networks. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the influence of head motion in FC estimation when evaluating age-related changes in brain networks.Methods: This study involved 132 healthy volunteers divided into 3 groups: elderly participants with high motion (OldHM, mean age (±SD) = 69.6 (±5.31), N = 44), elderly participants with low motion (OldLM, mean age (±SD) = 68.7 (±4.59), N = 43), and young adult participants with low motion (YugLM, mean age (±SD) = 27.6 (±5.26), N = 45). Head motion was quantified using the mean of the framewise displacement of resting state fMRI data. After preprocessing all resting state fMRI datasets, several resting state networks (RSNs) were extracted using independent component analysis (ICA). In addition, several network metrics were also calculated using network analysis. These FC measures were then compared among the 3 groups.Results: In ICA, the number of voxels with significant differences in RSNs was higher in YugLM vs. OldLM comparison than in YugLM vs. OldHM. In network analysis, all network metrics showed significant (P < 0.05) differences in comparisons involving low vs. high motion groups (OldHM vs. OldLM and OldHM vs. YugLM). However, there was no significant (P > 0.05) difference in the comparison involving the low motion groups (OldLM vs. YugLM).Conclusion: Our findings showed that head motion during functional imaging could significantly affect the evaluation of age-related brain network changes using resting state fMRI data.
1 0 0 0 OA Masticatory function and cognitive function
- 著者
- Kin-ya KUBO Yukiko ICHIHASHI Chika KURATA Mitsuo IINUMA Daisuke MORI Tasuku KATAYAMA Hidekazu MIYAKE Shu FUJIWARA Yasuo TAMURA
- 出版者
- オカジマ・フォリア・アナトミカ・ヤポニカ編集部
- 雑誌
- Okajimas Folia Anatomica Japonica (ISSN:0030154X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.87, no.3, pp.135-140, 2010 (Released:2012-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 88
- 被引用文献数
- 5 21
Recent studies have suggest that masticatory (chewing) function is useful for maintaining neurocognitive function in the elderly. For example, a reduced ability to masticate, such as that resulting from toothlessness or soft-diet feeding, causes learning and memory deficits in aged animals and pathologic changes in the hippocampus. In addition, occlusal disharmony impairs hippocampal memory processes via chronic stress, and induces similar hippocampal pathology. Chewing, however, rescues stress-induced suppression of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus and the stress-induced impairment of hippocampal-dependent learning. These findings strongly suggest a link between mastication and neurocognitive function.