- 著者
- Chiyo MATSUSHITA Hiroyuki MIZUGUCHI Hitoshi NIINO Yuko SAGESAKA Keisuke MASUYAMA Hiroyuki FUKUI
- 出版者
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Society for WAKAN-YAKU
- 雑誌
- Journal of Traditional Medicines (ISSN:18801447)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.5+6, pp.133-142, 2008 (Released:2008-12-19)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 2
ヒスタミンはアレルギー反応における主要メディエーターである。 近年緑茶の抗アレルギー効果が報告されているがヒスタミンシグナルにおける緑茶の効果については明らかでない。 我々は toluene-2, 4-diisocyanate (TDI) 感作により作成した鼻過敏症モデルラットを用いて TDI 発作誘発に伴う鼻粘膜ヒスタミン H1 受容体 (H1R) 及び Th2 サイトカイン mRNA 上昇への緑茶の効果を検討した。 緑茶抽出液を 3 週間連日投与することにより TDI 誘発による鼻粘膜 Th2 サイトカイン mRNA レベル上昇が有意に抑制され H1R mRNA レベルも抑制傾向を示した。 抽出液をカラムクロマトにより分画し, 各画分における効果を検討したところ EGCG が主要成分である TOYOPEARL HW40EC カラム80% ethanol 溶出画分に RBL-2H3 細胞の抗原抗体刺激による Th2 サイトカイン mRNA 上昇の抑制効果が認められた。 EGCG は濃度依存的に IgE 刺激による IL-4 mRNA レベルの上昇及び PMA 刺激による H1R mRNA レベルの上昇を抑制した。 鼻過敏症モデルラットにおいても EGCG の 3 週間連日投与によりくしゃみ回数が減少し TDI 誘発による H1R 及び IL-4 mRNA 上昇が抑制された。 以上の結果より EGCG は鼻過敏症モデルラットの H1R および IL-4 遺伝子発現を抑制することにより IL-4 シグナルだけでなくヒスタミンシグナルも抑制し鼻過敏症症状を軽減することがわかった。
- 著者
- Shrabanti Dev Hiroyuki Mizuguchi Asish K. Das Chiyo Matsushita Kazutaka Maeyama Hayato Umehara Takayuki Ohtoshi Jun Kojima Kiyotaka Nishida Kunihiko Takahashi Hiroyuki Fukui
- 出版者
- The Japanese Pharmacological Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pharmacological Sciences (ISSN:13478613)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.107, no.2, pp.159-166, 2008 (Released:2008-06-20)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 26 29
It has been shown that probiotic bacteria are effective for the treatment of allergic diseases. As histamine plays a central role in allergic diseases, it is possible that probiotic bacteria affect the allergy-related histamine signaling. Here, we investigated the effect of Lac-B, a mixture of freeze-dried Bifidobacterium infantis and Bifidobacterium longum, on the allergy-related histamine signaling. In the nasal allergy model rats made by sensitization and provocation with toluene 2,4-diisocyanate (TDI) for 3 weeks, TDI provocation caused acute allergy–like behaviors along with significant up-regulation of histamine H1 receptor (H1R) and histidine decarboxylase (HDC) mRNA expression, increased HDC activity, histamine content, and [3H]mepyramine binding activity in nasal mucosa. Prolonged treatment with Lac-B (40 mg/rat, p.o.) significantly suppressed both the allergy-like behaviors and all of the above mentioned factors involved in histamine signaling. Our findings indicate that oral administration of Lac-B showed significant anti-allergic effect through suppression of both H1R and HDC gene expression followed by decrease in H1R, HDC protein level, and histamine content. Suppression of histamine signaling may be a novel target of probiotics in preventing allergic diseases.
- 著者
- Tomohito Tsukamoto Eiko Sakai Shunsuke Iizuka Marcos Taracena-Gándara Fuminori Sakurai Hiroyuki Mizuguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1089-1095, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 16
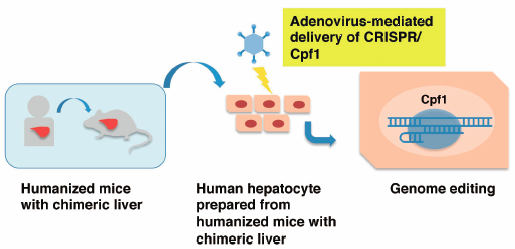
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein (Cas) 9 system is now widely used as a genome editing tool. CRISPR-associated endonuclease in Prevotella and Francisella 1 (Cpf1) is a recently discovered Cas endonuclease that is designable and highly specific with efficiencies comparable to those of Cas9. Here we generated the adenovirus (Ad) vector carrying an Acidaminococcus sp. Cpf1 (AsCpf1) expression cassette (Ad-AsCpf1) for the first time. Ad-AsCpf1 was applied to primary human hepatocytes prepared from humanized mice with chimeric liver in combination with the Ad vector expressing the guide RNA (gRNA) directed to the Adeno-associated virus integration site 1 (AAVS1) region. The mutation rates were estimated by T7 endonuclease I assay around 12% of insertion/deletion (indel). Furthermore, the transduced human hepatocytes were viable (ca. 60%) at two weeks post transduction. These observations suggest that the Ad vector-mediated delivery of the CRISPR/AsCpf1 system provides a useful tool for genome manipulation of human hepatocytes.
- 著者
- Sayaka Deguchi Kazuo Takayama Hiroyuki Mizuguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.4, pp.608-615, 2020-04-01 (Released:2020-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 50
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Liver transplantation and hepatocyte transplantation are effective treatments for severe liver injuries, but the donor shortage is a serious problem. Therefore, hepatocyte-like cells generated from human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells with unlimited proliferative ability are expected to be a promising new transplantation resource. The technology for hepatic differentiation from human iPS cells has made great progress in this decade. The efficiency of hepatic differentiation now exceeds 90%, making it possible to produce nearly homogeneous hepatocyte-like cells from human iPS cells. Because there is little contamination of undifferentiated cells, there is a lower risk of teratoma formation. To date, the transplantation of human iPS cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells has been shown to have therapeutic effects using various liver injury model mice. Currently, studies are underway using model animals larger than mice. The day when human iPS cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells can be used as cellular medicine is surely approaching. In this review, we introduce the forefront of regenerative medicine applications using human iPS cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells.
- 著者
- Aurpita Shaha Hiroyuki Mizuguchi Yoshiaki Kitamura Hiromichi Fujino Masami Yabumoto Noriaki Takeda Hiroyuki Fukui
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.9, pp.1440-1447, 2018-09-01 (Released:2018-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 23
The significant correlation between nasal symptom scores and level of histamine H1 receptor (H1R) mRNA in nasal mucosa was observed in patients with pollinosis, suggesting that H1R gene is an allergic disease sensitive gene. We demonstrated that H1R and interleukin (IL)-9 gene are the allergic rhinitis (AR)-sensitive genes and protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ) signaling and nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signaling are involved in their expressions, respectively. Honey bee products have been used to treat allergic diseases. However, their pathological mechanism remains to be elucidated. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism of the anti-allergic effect of royal jelly (RJ) and Brazilian green propolis (BGPP). Treatment with RJ and BGPP decreased in the number of sneezing on toluene 2,4-diissocyanate (TDI)-stimulated rats. The remarkable suppression of H1R mRNA in nasal mucosa was observed. RJ and BGPP also suppressed the expression of IL-9 gene. RJ and BGPP suppressed phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced Tyr311 phosphorylation of PKCδ in HeLa cells. In RBL-2H3 cells, RJ and BGPP also suppressed NFAT-mediated IL-9 gene expression. These results suggest that RJ and BGPP improve allergic symptoms by suppressing PKCδ and NFAT signaling pathways, two important signal pathways for the AR pathogenesis, and suggest that RJ and BGPP could be good therapeutics against AR.
- 著者
- Mitsuhiro Machitani Fuminori Sakurai Keisaku Wakabayashi Kosuke Nakatani Kazuo Takayama Masashi Tachibana Hiroyuki Mizuguchi
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, pp.272-277, 2017-03-01 (Released:2017-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9-mediated genome engineering technology is a powerful tool for generation of cells and animals with engineered mutations in their genomes. In order to introduce the CRISPR/Cas9 system into target cells, nonviral and viral vectors are often used; however, such vectors trigger innate immune responses associated with production of type I interferons (IFNs). We have recently demonstrated that type I IFNs inhibit short-hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing, which led us to hypothesize that type I IFNs may also inhibit CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome mutagenesis. Here we investigated this hypothesis. A single-strand annealing assay using a reporter plasmid demonstrated that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated cleavage efficiencies of the target double-stranded DNA were significantly reduced by IFNα. A mismatch recognition nuclease-dependent genotyping assay also demonstrated that IFNα reduced insertion or deletion (indel) mutation levels by approximately half. Treatment with IFNα did not alter Cas9 protein expression levels, whereas the copy numbers of guide RNA (gRNA) were significantly reduced by IFNα stimulation. These results indicate that type I IFNs significantly reduce gRNA expression levels following introduction of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in the cells, leading to a reduction in the efficiencies of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome mutagenesis. Our findings provide important clues for the achievement of efficient genome engineering using the CRISPR/Cas9 system.