- 著者
- Taisuke Konno Hiroyuki Suzuki Hitoshi Nakamura Yuriko Murai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b22-00050, (Released:2022-06-29)
- 参考文献数
- 15
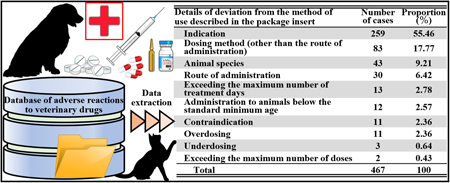
In veterinary medicine, various drugs are used on a daily basis. Using inappropriate medications poses health hazards to companion animals and humans; thus, assessing adverse events in veterinary medicine has great social significance but remains an untapped area of research. In this study, to promote the appropriate use of veterinary drugs and clarify common pharmaceutical issues in Japanese veterinary medicine, we analyzed information in the Veterinary Drug Side Effects Database (National Veterinary Assay Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan). We found that the number of reports has been increasing annually, including those on high-risk drugs, molecular-targeted drugs, and antibody-based drugs. The details of the reports were similar to those from the United States, including the misadministration of veterinary drugs to humans, improper drug management, and re-administering drugs with a history of side effects. Furthermore, 46.50% of all reports mentioned the administration of one or more drugs, with the highest number of concomitant drugs being 10. In addition, 37.78% of all reports described the use of drugs in manners deviating from the intended use indicated in the package insert. Therefore, to avoid adverse events, pharmacists may have to be involved in dispensing and aseptically preparing veterinary medicines and providing drug information and medication guidance. To optimize pharmacotherapy for ill companion animals, "veterinary pharmacy" and "veterinary medicine pharmacy" must be developed in line with clinical situations in Japan, while considering knowledge from countries that are advanced in terms of veterinary medicine.
- 著者
- Daisuke Nakamura Keisuke Yasumura Hitoshi Nakamura Yutaka Matsuhiro Koji Yasumoto Akihiro Tanaka Yasuharu Matsunaga-Lee Masamichi Yano Masaki Yamato Yasuyuki Egami Ryu Shutta Yasushi Sakata Jun Tanouchi Masami Nishino
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.2, pp.313-319, 2019-01-25 (Released:2019-01-25)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 2 19
Background: There are few reports about the differences between drug-eluting stents (DES) and bare metal stents (BMS) in neoatherosclerosis associated with in-stent restenosis (ISR), so we compared the frequency and characteristics of neoatherosclerosis with ISR evaluated by optical coherence tomography (OCT) in the present study. Methods and Results: Between March 2009 and November 2016, 98 consecutive patients with ISR who underwent diagnostic OCT were enrolled: 34 patients had a BMS, 34 had a 1st-generation DES, and 30 had a 2nd-generation DES. Neoatherosclerosis was defined as a lipid neointima (including a thin-cap fibroatheroma [TCFA] neointima, defined as a fibroatheroma with a fibrous cap <65 µm) or calcified neointima. As a result, lipid neointima, TCFA neointima and calcified neointima were detected in 39.8%, 14.3%, and 5.1%, respectively, of all patients. The frequency of neoatherosclerosis was significantly greater with DES than BMS (48.4% vs. 23.5%, P=0.018). The minimum fibrous cap thickness was significantly thicker with DES than BMS (110.3±41.1 µm vs. 62.5±17.1 µm, P<0.001). In addition, longitudinal extension of neoatherosclerosis in the stented segment was less with DES than BMS (20.2±15.1% vs. 71.8±27.1%, respectively, P=0.001). Conclusions: OCT imaging demonstrated that neoatherosclerosis with ISR was more frequent with DES than BMS and its pattern exhibited a more focal and thick fibrous cap as compared with BMS.
- 著者
- Taisuke Konno Hiroyuki Suzuki Hitoshi Nakamura Yuriko Murai
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.9, pp.1225-1231, 2022-09-01 (Released:2022-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
In veterinary medicine, various drugs are used on a daily basis. Using inappropriate medications poses health hazards to companion animals and humans; thus, assessing adverse events in veterinary medicine has great social significance but remains an untapped area of research. In this study, to promote the appropriate use of veterinary drugs and clarify common pharmaceutical issues in Japanese veterinary medicine, we analyzed information in the Veterinary Drug Side Effects Database (National Veterinary Assay Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan). We found that the number of reports has been increasing annually, including those on high-risk drugs, molecular-targeted drugs, and antibody-based drugs. The details of the reports were similar to those from the United States, including the misadministration of veterinary drugs to humans, improper drug management, and re-administering drugs with a history of side effects. Furthermore, 46.50% of all reports mentioned the administration of one or more drugs, with the highest number of concomitant drugs being 10. In addition, 37.78% of all reports described the use of drugs in manners deviating from the intended use indicated in the package insert. Therefore, to avoid adverse events, pharmacists may have to be involved in dispensing and aseptically preparing veterinary medicines and providing drug information and medication guidance. To optimize pharmacotherapy for ill companion animals, “veterinary pharmacy” and “veterinary medicine pharmacy” must be developed in line with clinical situations in Japan, while considering knowledge from countries that are advanced in terms of veterinary medicine.