- 著者
- Kotomi Kikukawa Ryota Sato Masaaki Iwamoto Takumi Higaki
- 出版者
- Japan Mendel Society, International Society of Cytology
- 雑誌
- CYTOLOGIA (ISSN:00114545)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.3, pp.189-194, 2021-09-25 (Released:2021-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Cell segmentation from microscopic images is conventionally used to investigate cell morphology. However, the time expense for manual segmentation becomes extreme with increasing numbers of cells to be analyzed. Recent progress in automated image analysis techniques can facilitate efficient and accurate cell segmentation in wide-range confocal images. Pavement cells, which mainly comprise the epidermal tissue of plant leaves, show jigsaw puzzle-like shapes and provide a model for elucidating the mechanisms underlying the complex morphology of plant cells. This mini-review demonstrates the effectiveness of using a confocal image processing pipeline for morphometric analysis and mechanical simulation using Arabidopsis thaliana cotyledon pavement cells as an example. We examined A. thaliana cotyledon surfaces using wide-range confocal images and used an image processing pipeline in ImageJ software to extract epidermal cell contours. We then used the segmented epidermal cell images to provide examples of how this information can be used for morphometry and mechanical simulation. The use of this high-throughput segmentation method is not limited to plant epidermal tissue and can be applied to various biological materials. Therefore, our approach to microscopic image analysis will hopefully contribute to the advancement of quantitative cell morphology research.
- 著者
- Keitaro Akita Yutaro Kaneko Ryota Sato Keisuke Iguchi Kenichiro Suwa Yuichiro Maekawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0922, (Released:2021-12-02)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- Toru Shirai Ryota Sato Yasuo Kawata Yoshitaka Bito Hisaaki Ochi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2021-0043, (Released:2022-11-12)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Purpose: Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) is useful for obtaining biological information. To calculate susceptibility distribution, it is necessary to calculate the local field caused by the differences of susceptibility between the tissues. The local field can be obtained by removing a background field from a total field acquired by MR phase image. Conventional approaches based on spherical mean value (SMV) filtering, which are widely used for background field calculations, fail to calculate the background field of the brain surface region corresponding to the radius of the SMV kernel, and consequently cannot calculate the QSM of the brain surface region. Accordingly, a new method calculating the local field by expansively removing the background field is proposed for whole brain QSM.Methods: The proposed method consists of two steps. First, the background field of the brain surface is calculated from the total field using a locally polynomial approximation of spherical harmonics. Second, the whole brain local field is calculated by SMV filtering with a constraint term of the background field of the brain surface. The parameters of the approximation were optimized to reduce calculation errors through simulations using both a numerical phantom and a measured human brain. Performance of the proposed method with the optimized parameters was quantitatively and visually compared with conventional methods in an experiment of five healthy volunteers.Results: The proposed method showed the accurate local field over the expanded brain region in the simulation studies. It also showed consistent QSM with conventional methods inside of the brain surface and showed clear vein structures on the brain surface.Conclusion: The proposed method enables accurate calculation of whole brain QSM without eroding the brain surface region while maintaining same values inside of the brain surface as the conventional methods.
1 0 0 0 OA Usefulness of Intraoperative Electrocorticography for the Localization of Epileptogenic Zones
- 著者
- Ryohei CHIBA Rei ENATSU Aya KANNO Tomoaki TAMADA Takuro SAITO Ryota SATO Nobuhiro MIKUNI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0252, (Released:2022-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 1
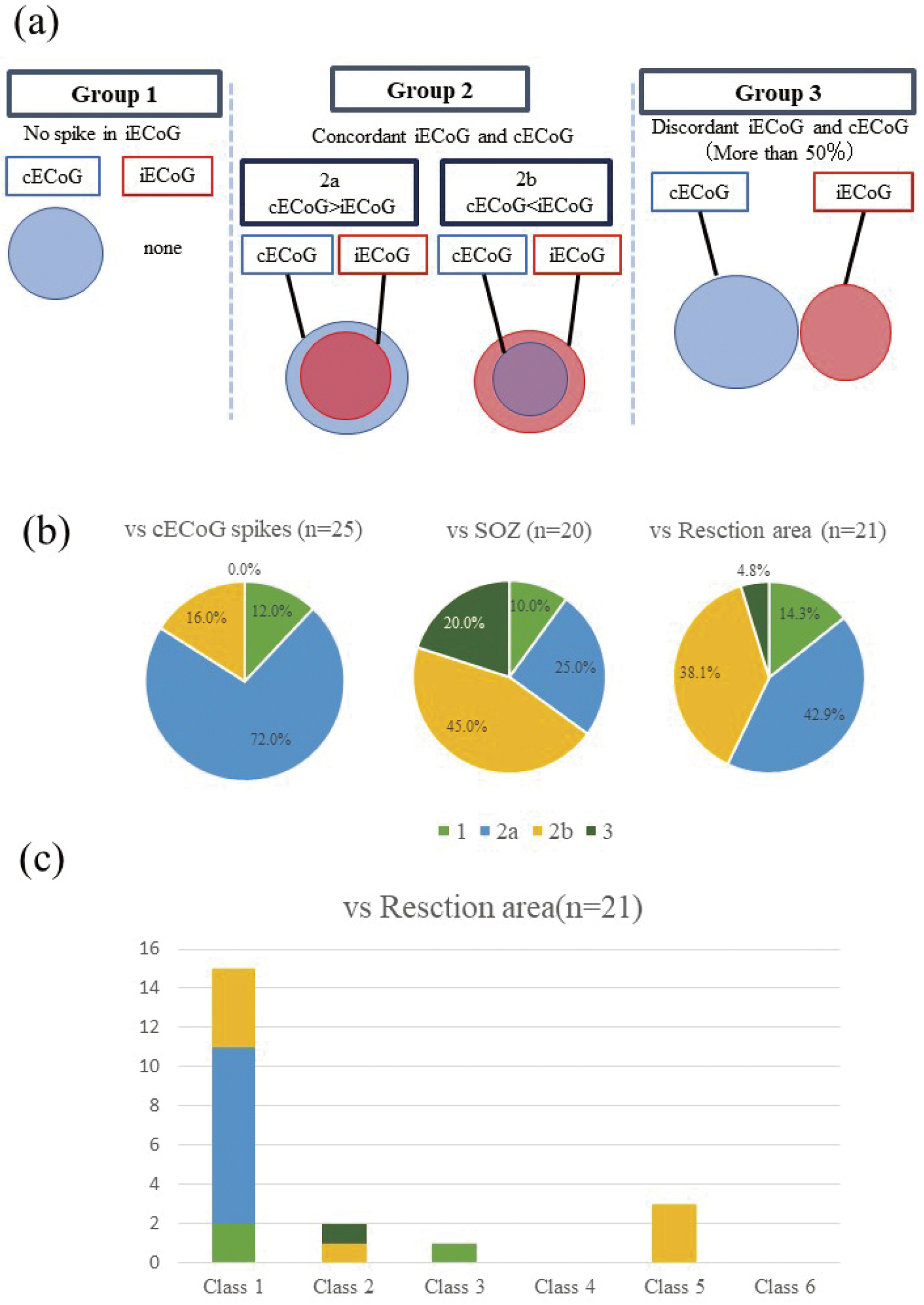
Intraoperative electrocorticography (iECoG) is widely performed to identify irritative zones in the cortex during brain surgery; however, several limitations (e.g., short recording times and the effects of general anesthesia) reduce its effectiveness. The present study aimed to evaluate the utility of iECoG for localizing epileptogenic zones. We compared the results of iECoG and chronic electrocorticography (cECoG) in 25 patients with refractory epilepsy. Subdural electrodes were implanted with iECoG under general anesthesia (2% sevoflurane). cECoG recordings were performed for 3-14 days. The distribution of iECoG spikes was compared with cECoG spike, seizure onset zone, and resection areas. The concordance patterns of each distribution were classified into four patterns: Group 1: No spike in iECoG, Group 2: concordant (2a: iECoG smaller, 2b: iECoG larger, Group 3: discordant >50%). The concordance rate of interictal spikes, seizure onset zones, and resection areas were 88.0% (Group 2a: 72.0%, Group 2b: 16.0%), 70.0% (Group 2a: 25.0%, Group 2b: 45.0%), and 81.0% (Group 2a: 42.9%, Group 2b: 38.1%), respectively. The resection of iECoG spike areas significantly correlated with good surgical outcomes. The indication and limitations of iECoG need to be realized, and the complementary use of iECoG and cECoG may enhance clinical utility.
- 著者
- Takenori Ikoma Taro Narumi Keitaro Akita Ryota Sato Takayuki Masuda Hanami Kaneko Masahiro Toda Satoshi Mogi Makoto Sano Kenichiro Suwa Yoshihisa Naruse Hayato Ohtani Masao Saotome Yuichiro Maekawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.0697-22, (Released:2022-11-30)
- 参考文献数
- 34
Objective The cardiac function, blood distribution, and oxygen extraction in the muscles as well as the pulmonary function determine the oxygen uptake (VO2) kinetics at the onset of exercise. This factor is called the VO2 time constant, and its prolongation is associated with an unfavorable prognosis for heart failure (HF). The mitochondrial function of skeletal muscle is known to reflect exercise tolerance. Morphological changes and dysfunction in cardiac mitochondria are closely related to HF severity and its prognosis. Although mitochondria play an important role in generating energy in cardiomyocytes, the relationship between cardiac mitochondria and the VO2 time constant has not been elucidated. Methods We calculated the ratio of abnormal cardiac mitochondria in human myocardial biopsy samples using an electron microscope and measured the VO2 time constant during cardiopulmonary exercise testing. The VO2 time constant was normalized by the fat-free mass index (FFMI). Patients Fifteen patients with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM) were included. Patients were divided into two groups according to their median VO2 time constant/FFMI value. Results Patients with a low VO2 time constant/FFMI value had a lower abnormal mitochondria ratio than those with a high VO2 time constant/FFMI value. A multiple linear regression analysis revealed that the ratio of abnormal cardiac mitochondria was independently associated with a high VO2 time constant/FFMI. Conclusions An increased abnormal cardiac mitochondria ratio might be associated with a high VO2 time constant/FFMI value in patients with NICM.
- 著者
- Yo Taniguchi Suguru Yokosawa Toru Shirai Ryota Sato Tomoki Amemiya Yoshihisa Soutome Yoshitaka Bito Hisaaki Ochi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2021-0045, (Released:2022-07-30)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Purpose: MR parameter mapping is a technique that obtains distributions of parameters such as relaxation time and proton density (PD) and is starting to be used for disease quantification in clinical diagnoses. Quantitative susceptibility mapping is also promising for the early diagnosis of brain disorders such as degenerative neurological disorders. Therefore, we developed an MR quantitative parameter mapping (QPM) method to map four tissue-related parameters (T1, T2*, PD, and susceptibility) and B1 simultaneously by using a 3D partially RF-spoiled gradient echo (pRSGE). We verified the accuracy and repeatability of QPM in phantom and volunteer experiments.Methods: Tissue-related parameters are estimated by varying four scan parameters of the 3D pRSGE: flip angle, RF-pulse phase increment, TR and TE, performing multiple image scans, and finding a least-squares fit for an intensity function (which expresses the relationship between the scan parameters and intensity values). The intensity function is analytically complex, but by using a Bloch simulation to create it numerically, the least-squares fitting can be used to estimate the quantitative values. This has the advantage of shortening the image-reconstruction processing time needed to estimate the quantitative values than with methods using pattern matching.Results: A 1.1-mm isotropic resolution scan covering the whole brain was completed with a scan time of approximately 12 minutes, and the reconstruction time using a GPU was approximately 1 minute. The phantom experiments confirmed that both the accuracy and repeatability of the quantitative values were high. The volunteer scans also confirmed that the accuracy of the quantitative values was comparable to that of conventional methods.Conclusion: The proposed QPM method can map T1, T2*, PD, susceptibility, and B1 simultaneously within a scan time that can be applied to human subjects.
- 著者
- Akinori Yamaguchi Kohsuke Kudo Ryota Sato Yasuo Kawata Niki Udo Masaaki Matsushima Ichiro Yabe Makoto Sasaki Masafumi Harada Noriyuki Matsukawa Toru Shirai Hisaaki Ochi Yoshitaka Bito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2021-0015, (Released:2022-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Purpose: Studies on quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) have reported an increase in magnetic susceptibilities in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Despite the pathological importance of the brain surface areas, they are sometimes excluded in QSM analysis. This study aimed to reveal the efficacy of QSM analysis with brain surface correction (BSC) and/or vein removal (VR) procedures.Methods: Thirty-seven AD patients and 37 age- and sex-matched, cognitively normal (CN) subjects were included. A 3D-gradient echo sequence at 3T MRI was used to obtain QSM. QSM images were created with regularization enabled sophisticated harmonic artifact reduction for phase data (RESHARP) and constrained RESHARP with BSC and/or VR. We conducted ROI analysis between AD patients and CN subjects who did or did not undergo BSC and/or VR using a t-test, to compare the susceptibility values after gray matter weighting.Results: The susceptibility values in RESHARP without BSC were significantly larger in AD patients than in CN subjects in one region (precentral gyrus, 8.1 ± 2.9 vs. 6.5 ± 2.1 ppb) without VR and one region with VR (precentral gyrus, 7.5 ± 2.8 vs. 5.9 ± 2.0 ppb). Three regions in RESHARP with BSC had significantly larger susceptibilities without VR (precentral gyrus, 7.1 ± 2.0 vs. 5.9 ± 2.0 ppb; superior medial frontal gyrus, 5.7 ± 2.6 vs. 4.2 ± 3.1 ppb; putamen, 47,8 ± 16.5 vs. 40.0 ± 15.9 ppb). In contrast, six regions showed significantly larger susceptibilities with VR in AD patients than in CN subjects (precentral gyrus, 6.4 ± 1.9 vs. 4.9 ± 2.7 ppb; superior medial frontal gyrus, 5.3 ± 2.7 vs. 3.7 ± 3.3 ppb; orbitofrontal cortex, –2.1 ± 2.7 vs. –3.6 ± 3.2 ppb; parahippocampal gyrus, 0.1 ± 3.6 vs. –1.7 ± 3.7 ppb; putamen, 45.0 ± 14.9 vs. 37.6 ± 14.6 ppb; inferior temporal gyrus, –3.4 ± 1.5 vs. –4.4 ± 1.5 ppb).Conclusion: RESHARP with BSC and VR showed more regions of increased susceptibility in AD patients than in CN subjects. This study highlights the efficacy of this method in facilitating the diagnosis of AD.
- 著者
- Masato Yoshikawa Kohsuke Kudo Taisuke Harada Kazutaka Harashima Jun Suzuki Koji Ogawa Taro Fujiwara Mutsumi Nishida Ryota Sato Toru Shirai Yoshitaka Bito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- 雑誌
- Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences (ISSN:13473182)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.mp.2020-0175, (Released:2021-09-04)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Purpose: The staging of liver fibrosis is clinically important, and a less invasive method is preferred. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) has shown a great potential in estimating liver fibrosis in addition to R2* relaxometry. However, few studies have compared QSM analysis and liver fibrosis. We aimed to evaluate the feasibility of estimating liver fibrosis by using QSM and R2*-based histogram analyses by comparing it with ultrasound-based transient elastography and the stage of histologic fibrosis.Methods: Fourteen patients with liver disease were enrolled. Data sets of multi-echo gradient echo sequence with breath-holding were acquired on a 3-Tesla scanner. QSM and R2* were reconstructed by water–fat separation method, and ROIs were analyzed for these images. Quantitative parameters with histogram features (mean, variance, skewness, kurtosis, and 1st, 10th, 50th, 90th, and 99th percentiles) were extracted. These data were compared with the elasticity measured by ultrasound transient elastography and histological stage of liver fibrosis (F0 to F4, based on the new Inuyama classification) determined by biopsy or hepatectomy. The correlation of histogram parameters with intrahepatic elasticity and histologically confirmed fibrosis stage was examined. Texture parameters were compared between subgroups divided according to fibrosis stage. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was also performed. P < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.Results: The six histogram parameters of both QSM and R2*were significantly correlated with intrahepatic elasticity. In particular, three parameters (variance, percentiles [90th and 99th]) of QSM showed high correlation (r = 0.818–0.844), whereas R2* parameters showed a moderate correlation with elasticity. Four parameters of QSM were significantly correlated with fibrosis stage (ρ = 0.637–0.723) and differentiated F2–4 from F0–1 fibrosis and F3–4 from F0–2 fibrosis with areas under the ROC curve of > 0.8, but those of R2* did not.Conclusion: QSM may serve as a promising surrogate indicator in detecting liver fibrosis.
1 0 0 0 OA Ten Cases of Intestinal Tuberculosis which Were Initially Misdiagnosed as Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- 著者
- Ryota Sato Hideaki Nagai Hirotoshi Matsui Akira Yamane Masahiro Kawashima Katsuyuki Higa Sumie Nakamura Nobuharu Ohshima Astuhisa Tamura Akira Hebisawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine
- 雑誌
- Internal Medicine (ISSN:09182918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2361-18, (Released:2019-03-28)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 13
Objective Intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) frequently present with similar clinical, endoscopic and pathological features, therefore it is difficult to differentiate between them. The aim of this study was to elucidate the diagnostic delay and prognosis of ITB cases, initially misdiagnosed as IBD. Methods ITB cases were selected from the hospitalized patient list between April 2004 and March 2017 in a tuberculosis center in Japan. We retrospectively evaluated the initial diagnosis, clinical characteristics, endoscopic and pathological findings, bacterial examinations, treatment and prognosis. Results Among 66 ITB patients, ten patients were initially misdiagnosed as IBD. Seven patients were male and the median age was 60.5 years (23-74 years). After the diagnosis of IBD, all the patients were treated with mesalazine, in addition to corticosteroids in two patients and sequential azathioprine and infliximab in one. The median duration of diagnostic delay was 5.5 months (range 0.5-17 months). Eight patients had active pulmonary tuberculosis at the diagnosis of ITB. Acid-fast bacilli were confirmed in four of seven patients by reevaluation of the pathological specimens at the IBD diagnosis. Two patients needed intestinal resection and one with erroneous corticosteroid use for IBD died due to respiratory failure in spite of receiving appropriate treatment for tuberculosis. Conclusion ITB patients were frequently misdiagnosed and treated as IBD, thus resulting in a poor clinical outcome even after finally making a correct diagnosis and administering appropriate treatment. On diagnosis of IBD and/or treatment failure, chest radiograph and acid-fast bacilli of the pathological specimens should be carefully evaluated in order to rule out tuberculosis.