- 著者
- Takayuki Miyauchi Shotaro Sasaki Yoko Sasaki Takuma Mogamiya Rumi Tanemura Kunji Shirahama
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本作業療法士協会
- 雑誌
- Asian Journal of Occupational Therapy (ISSN:13473476)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.1, pp.236-242, 2023 (Released:2023-10-20)
- 参考文献数
- 24
Introduction: Stroke rehabilitation that considers attention deficits and effectively improves activities of daily living (ADL) requires sufficient evaluation of attention functions. Attention function evaluations are generally performed using neuropsychological tests in patients with stroke. However, such tests become unviable for patients with acute stroke due to fatigue-related unstable general conditions and cannot determine how attention deficits affect ADL. Hence, developing an appropriate observational rating scale is crucial. Therefore, we investigated the factors related to independence in ADL in patients with acute stroke and the usefulness of the Moss Attention Rating Scale (MARS) score in predicting independence in ADL.Methods: In this cross-sectional single-center study, we included 154 patients admitted to Acute Hospital, Japan for stroke treatment between April 2016 and April 2020 who consented to participate. The primary outcome was the motor functional independence measure (m-FIM) score. The secondary outcome measures were the Glasgow Coma Scale score, Brunnstrom recovery stage, grip strength, one-leg standing time (1LST), Mini-Mental State Examination-Japanese score, Visual Cancellation Task score, Symbol Digit Modalities Test score, and MARS score.Results: The 1LST and MARS scores were associated with independence in ADL. The cutoff values were 2.99 seconds for 1LST (average), 89 points for MARS total score, and 58.87 points for MARS logit score.Discussion: The MARS score and 1LST might be useful indices for predicting independence in ADL. Thus, behavioral assessments might be appropriately performed by implementing these indices to determine the degree of ADL independence in patients with stroke, and thereby establishing targeted rehabilitation strategies.
1 0 0 0 OA Nonfinite Clauses and the Control Cycle
- 著者
- Shotaro Sasaki
- 出版者
- The English Literary Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- 英文学研究 支部統合号 (ISSN:18837115)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.14, pp.217-230, 2022 (Released:2022-02-14)
- 著者
- Akiko Omori Yuki Fujisawa Shotaro Sasaki Kazumi Shimono Takashi Kikukawa Seiji Miyauchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.5, pp.678-685, 2021-05-01 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 6
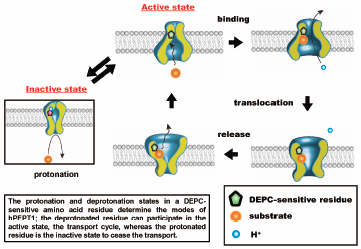
To clarify the role of an amino acid residue in the pH-dependent efflux process in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the human oligopeptide transporter hPEPT1 (CHO/hPEPT1), we determined the effect of extracellular pH on the hPEPT1-mediated efflux process. The efflux of glycylsarcosine (Gly-Sar), a typical substrate for hPEPT1, was determined using an infinite dilution method after cells were preloaded with [3H]-Gly-Sar. The efflux of [3H]-Gly-Sar was stimulated by 5 mM unlabeled hPEPT1 substrates in the medium. This trans-stimulation phenomenon showed that hPEPT1 mediated the efflux of [3H]-Gly-Sar from CHO/hPEPT1 and that hPEPT1 is a bi-directional transporter. We then determined the effect of extracellular pH (varying from 8.0 to 3.5) on the efflux activity. The efflux activity by hPEPT1 decreased with the decrease in extracellular pH. The Henderson–Hasselbälch-type equation, which fitted well to the pH-profile of efflux activity, indicated that a single amino acid residue with a pKa value of approximately 5.7 regulates the efflux activity. The pH-profile of the efflux activity remained almost unchanged irrespective of the proton gradient across the plasma membrane. In addition, the chemical modification of the histidine residue with diethylpyrocarbonate completely abolished the efflux activity from cells, which could be prevented by the presence of 10 mM Gly-Sar. These data indicate that the efflux process of hPEPT1 is also regulated in a pH-dependent manner by the protonation state of a histidine residue located at or near the substrate recognition site facing the extracellular space.