- 著者
- Shungo Imai Kenji Momo Hitoshi Kashiwagi Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.10, pp.1519-1525, 2020-10-01 (Released:2020-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 7
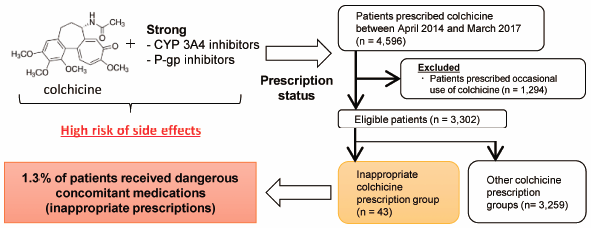
The anti-inflammatory agent colchicine may cause toxic effects such as rhabdomyolysis, pancytopenia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome in cases of overdose and when patients have renal or liver impairment. As colchicine is a substrate for CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), drug–drug interactions are important factors that cause fatal colchicine-related side effects. Thus, we conducted a nation-wide survey to determine the status of inappropriate colchicine prescriptions in Japan. Patients prescribed the regular use of colchicine from April 2014 to March 2017 were identified using the Japanese large health insurance claims database. As the primary endpoint, we evaluated the concomitant prescription proportions of strong CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inhibitors classified as “contraindications for co-administration” with colchicine in patients with renal or liver impairment. We defined these cases as “inappropriate colchicine prescriptions.” Additionally, factors affecting inappropriate colchicine prescriptions were analyzed. Among the 3302 enrolled patients, 43 (1.30%) were inappropriately prescribed colchicine. Of these 43 patients, 11 had baseline renal and/or liver impairment. By multiple regression analysis, the primary diseases “gout” and “Behçet’s disease” were extracted as independent factors for inappropriate colchicine prescriptions with odds ratios of 0.40 (95% confidence interval: 0.19–0.84) and 4.93 (95% confidence interval: 2.12–11.5), respectively. We found that approximately 1% of patients had important colchicine interactions. Particularly, Behçet’s disease was a risk factor for inappropriate prescriptions, with approximately 25% of patients showing renal and/or liver impairment (classified as “contraindications for co-administration”). These findings may be useful for medical professionals who prescribe colchicine therapy.
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Yoh Takekuma Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.1, pp.188-193, 2020-01-01 (Released:2020-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 22
This study aimed to construct an optimal algorithm for initial dose settings of vancomycin (VCM) using machine learning (ML) with decision tree (DT) analysis. Patients who were administered intravenous VCM and underwent therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) at the Hokkaido University Hospital were enrolled. The study period was November 2011 to March 2019. In total, 654 patients were included in the study. Patients were divided into two groups, training (patients who received VCM from November 2011 to December 2017; n = 496) and testing (patients who received VCM from January 2018 to March 2019; n = 158) groups. For the training group, DT analysis of the classification and regression tree algorithm was performed to construct an algorithm (called DT algorithm) for the initial dose settings of VCM. For the testing group, the rates of attaining the VCM therapeutic range (trough value = 10–15 and 10–20 mg/L) with the DT algorithm and three conventional dose-setting methods were compared for model evaluation. The DT algorithm was constructed to be used for patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥50 mL/min and body weight ≥40 kg. As a result, the recommended daily doses ranged from 20.0 to 58.1 mg/kg. In model evaluation, the DT algorithm obtained the highest rates of attaining the VCM therapeutic range compared to conventional dose-setting methods. Therefore, our DT algorithm can be applied to clinical practice. In addition, ML is useful for setting drug doses.
- 著者
- Shunsuke Nashimoto Shungo Imai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.2, pp.230-236, 2023-02-01 (Released:2023-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 32
The Child–Pugh score is widely used to assess liver function and estimate drug clearance in patients with liver cirrhosis. Recently, the albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) score, which objectively assesses liver function based only on albumin and total bilirubin levels, was developed as a new method. The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationship between the liver function assessment method and the plasma concentration of voriconazole (VRCZ), an antifungal drug for patients with liver cirrhosis. This single-center retrospective study enrolled 159 patients who received VRCZ between 2012 and 2020. In patients administered VRCZ orally, the median concentration to dose (C : D) ratio increased with the progression of Child–Pugh and ALBI grades. Positive correlations between the ALBI score and VRCZ C : D ratio were observed in patients with cirrhosis (r = 0.52 (95% confidence interval, 0.069–0.79); p < 0.05). In addition, a highly negative correlation was observed between the ALBI score and VRCZ daily maintenance dose (r=−0.79 (95% confidence interval, −0.92 to −0.50); p < 0.0001). In contrast, for patients administered VRCZ intravenously, no increase in C : D ratio was observed for both Child–Pugh and ALBI scores compared to the non-liver cirrhosis group. This may be because the injection is often used in severely ill patients, and factors other than impaired liver function may affect the plasma concentrations of VRCZ. In conclusion, the ALBI score was shown to be useful in predicting VRCZ clearance as well as the Child–Pugh score, and the initial dose of VRCZ might be determined according to the ALBI score.
- 著者
- Yuki Sato Yoh Takekuma Takayuki Daisho Hitoshi Kashiwagi Shungo Imai Mitsuru Sugawara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.4, pp.421-428, 2022-04-01 (Released:2022-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 3
It is important to select appropriate antibiotics for infection control. Linezolid and tedizolid are newly developed and synthesized oxazolidinone antibacterial agents. It has been pointed out that there is a relationship between a high plasma concentration of the target drug and incidence of adverse effects, although it has been reported that neither linezolid nor tedizolid requires dose adjustment according to renal function. Due to the high incidence of adverse effects, both are often switched. Precise plasma concentration control by therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is desirable for reducing the adverse effects of both drugs and obtaining a better therapeutic effect. In this study, we aimed to establish a method for simultaneous quantification of linezolid and tedizolid in human plasma using LC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Sample preparation was performed by a simple operation with acetonitrile. Linezolid and tedizolid were separated by an octadecylsilyl column using a gradient elution of acetonitrile in aqueous 0.1% formic acid solution and were detected in the positive ion electrospray mode with multiple reaction monitoring. Quantification of linezolid and tedizolid ranged from 0.5 to 50 and 0.5 to 20 µg/mL, respectively. The intra-day and inter-day precision and accuracy of data were assessed and found to be acceptable. The developed method was successfully applied to measurement of the concentrations of linezolid and tedizolid. This simple method, which can simultaneously quantify both drug concentrations for daily TDM, could contribute to safer treatment of patients.
- 著者
- Shinsuke Yamashita Shungo Imai Kenji Momo Hitoshi Kashiwagi Yuki Sato Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.8, pp.1151-1155, 2021-08-01 (Released:2021-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Olanzapine is effective for schizophrenia management; however, it is contraindicated in diabetes patients. In addition, olanzapine is useful for treating nausea and vomiting, such as in the case of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). Therefore, we hypothesized that the contraindicated prescription of olanzapine likely occurs among cancer patients with diabetes, especially by non-psychiatric physicians. Hence, we conducted a nationwide survey to elucidate the situation of such contraindicated prescriptions and the associated risk factors. We extracted the data of patients who were newly prescribed olanzapine between April 2015 and March 2017 from the health insurance claims database developed by JMDC, Inc., Tokyo. The patients who were prescribed contraindicated olanzapine were defined as those who were prescribed olanzapine after a diagnosis of diabetes and diabetes drug prescription. In all, the data of 7181 patients were analyzed. We evaluated the proportion of diabetes patients who were prescribed contraindicated olanzapine from among those who were prescribed olanzapine. Furthermore, we investigated the background of patients who were prescribed olanzapine for information such as olanzapine prescribers and history of cancer chemotherapy. In all, 100 diabetes patients (1.39%) were prescribed olanzapine. In these patients, the frequency of olanzapine prescription was higher by non-psychiatry/neurology physicians than by psychiatry/neurology physicians (3.25 and 0.85%, respectively). Additionally, all olanzapine prescriptions in cancer chemotherapy-treated diabetes patients were issued by non-psychiatry/neurology physicians. Thus, our study revealed there were diabetes patients who were prescribed olanzapine. Additionally, olanzapine for CINV management was more likely to be a contraindicated prescription.
- 著者
- Masayoshi Kumai Shungo Imai Shintaro Kato Ryo Koyanagi Kenkichi Tsuruga Takehiro Yamada Yoh Takekuma Mitsuru Sugawara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.4, pp.593-598, 2021-04-01 (Released:2021-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Nausea is a typical adverse event associated with opioids. In this study, we performed logistic regression analysis with the aim of clarifying the risk factors for nausea induced by extended-release oxycodone (ER-OXY). Furthermore, we constructed a decision tree (DT) model, a typical data mining method, to estimate the risk of oxycodone-induced nausea by combining multiple factors. A retrospective study was conducted on patients who newly received ER-OXY for cancer pain during hospitalization at Hokkaido University Hospital in Japan from April 2015 to March 2018. In logistic regression and DT analyses, the dependent variable was the presence or absence of nausea. Independent variables were the potential risk factors. First, univariate analyses were performed to screen potential factors associated with oxycodone-induced nausea. Then, multivariate and DT analyses were performed using factors with p-values <0.1 in the univariate analysis. Of 267 cases included in this study, nausea was observed in 30.3% (81/267). In multivariate logistic regression analysis, only female sex was extracted as an independent factor affecting nausea (odds ratio, 1.98). In the DT analysis, we additionally revealed that an age <50 years was a risk factor for nausea in female patients. Thus, our DT model indicated that the risk of ER-OXY-induced nausea was highest in the subgroup comprising females <50 years of age (66.7%) and lowest in male patients (25.1%). The DT model suggested that the factor of young women may be an increased risk of ER-OXY-induced nausea.
- 著者
- Takehiro Yamada Shungo Imai Yasuyuki Koshizuka Yuki Tazawa Keisuke Kagami Naoki Tomiyama Ryosuke Sugawara Akira Yamagami Tsuyoshi Shimamura Ken Iseki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1112-1118, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 15 17
Therapeutic drug monitoring for voriconazole, an antifungal agent, is essential for maximizing efficacy and preventing toxicity. The aim of this study was to elucidate the optimal maintenance dose of voriconazole in patients with severe liver cirrhosis (Child–Pugh class C) by reviewing the plasma trough concentrations obtained by therapeutic drug monitoring and daily doses of voriconazole. We retrospectively evaluated 6 patients with Child–Pugh class C cirrhosis who received oral voriconazole treatment and were liver transplant recipients or were awaiting liver transplantation. We compared their voriconazole trough concentrations and daily maintenance doses to those of patients who did not have liver cirrhosis (n=56). We found that plasma voriconazole trough concentrations in all patients with Child–Pugh class C were almost within therapeutic range, and the median plasma trough concentration at steady state was not significantly different from that of patients who did not have liver cirrhosis. In addition, the median daily maintenance dose of voriconazole was significantly lower (2.13 mg/kg/d) than that of the control patients (6.27 mg/kg/d), suggesting that trough voriconazole concentrations are elevated in Child–Pugh class C patients. Thus, we conclude that oral voriconazole maintenance doses in patients with Child–Pugh class C should be reduced to approximately one-third that of patients with normal liver function, with the follow-up dose adjusted by therapeutic drug monitoring.
- 著者
- Keisuke Ikegami Megumi Saito Shungo Imai Hayato Kizaki Osamu Yasumuro Ryohkan Funakoshi Satoko Hori
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.95-101, 2023-01-01 (Released:2023-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 15
To prevent denosumab-induced hypocalcemia in patients with renal dysfunction, combination therapy with 1α,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 (active vitamin D) is recommended. We previously developed a risk prediction model for hypocalcemia in patients with cholecalciferol/calcium (natural vitamin D). However, the prescription status and the risk factors of patients with active vitamin D have not been identified, so we designed this retrospective observational study using a large practice database covering June 2013 to May 2020 to analyze prescription status and risk factors. Patients were classified according to vitamin D type. After that, factors associated with development of hypocalcemia in patients with active vitamin D were explored. Univariate analysis was conducted to compare patient backgrounds between the hypocalcemia and non-hypocalcemia groups. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was conducted to evaluate the predictive potential of the extracted factors. Of the 33442 patients who received denosumab, 22347 and 3560 patients were co-administered natural and active vitamin D, respectively. Patients with active vitamin D had significantly lower renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) median: 74.0 vs. 69.7 mL/min/1.73 m2), but some patients (23.6%) with sufficient renal function (eGFR ≥90) were also receiving active vitamin D. Of the 3560 patients with active vitamin D, non-hypocalcemia (n = 166) and hypocalcemia (n = 17) groups who met the study criteria were analyzed. Renal function was lower in the hypocalcemia group, and alkaline phosphatase gave the best discrimination. High aspartate aminotransferase (AST), renal dysfunction, high alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and low hemoglobin may be significant factors in risk prediction for hypocalcemia in patients with active vitamin D.
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Kenji Momo Hitoshi Kashiwagi Yuki Sato Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- Society for Clinical Epidemiology
- 雑誌
- Annals of Clinical Epidemiology (ISSN:24344338)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.1, pp.6-10, 2022 (Released:2022-01-07)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Yasuyuki Nasuhara Kenji Momo Hiromitsu Oki Hitoshi Kashiwagi Yuki Sato Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.10, pp.1499-1505, 2021-10-01 (Released:2021-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 4
A major adverse effect of benzbromarone is hepatotoxicity. Therefore, periodic liver function tests are required at least for the first 6 months of benzbromarone administration. However, it is not clear whether the relevant blood tests are implemented appropriately. Here, we performed a cross-sectional survey of the implementation status of liver function tests in patients who were newly prescribed benzbromarone, using the Japanese large claims database. Male patients who were newly prescribed benzbromarone from January 2010 to December 2016 were included. We targeted patients who continued benzbromarone during the observation period (up to 180 d from the start of administration). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients in whom periodic liver function tests were implemented. A periodic liver function test was defined as one or more liver function tests performed during both 1–90 and 91–180 d of initial benzbromarone administration. We labeled the tests as a “periodic test” or “non-periodic test” based on whether periodic liver function tests were performed or not, respectively. Furthermore, factors influencing non-periodic test were analyzed. Periodic testing was implemented only in 28.7% of patients. Additionally, factors such as number of hospital beds ≤19 (compared to 100–199 beds) and duration of the first prescription of benzbromarone were associated with non-periodic testing. Our study revealed that periodic liver function tests are not performed sufficiently in Japan. Thus, clinicians prescribing benzbromarone should be educated about the test. Our blood-test-based approach should be applied to other drugs and countries in future research.
- 著者
- Shungo Imai Kenji Momo Hitoshi Kashiwagi Takayuki Miyai Mitsuru Sugawara Yoh Takekuma
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.3, pp.448-452, 2021-03-01 (Released:2021-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 23
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) is a typical side effect of antibiotic treatment, especially in children. Amoxicillin (AMPC) and amoxicillin/clavulanate (AMPC/CVA) are associated with high risk of AAD; however, these antibiotics are important in the pediatric field. Recent research suggests that probiotics prevent pediatric AAD, including that caused by AMPC and AMPC/CVA. Indeed, guidelines for acute otitis media in children recommend the concomitant use of probiotics. However, the prescription status of probiotics for pediatric patients with otitis media receiving oral AMPC and AMPC/CVA remains unknown. We therefore conducted a survey to clarify the current status of these prescriptions and, in particular, to identify specific populations with a low proportion of probiotic prescriptions. Pediatric patients (≤15 years of age) newly prescribed oral AMPC or AMPC/CVA for otitis media between April 2016 and March 2017 were identified from a Japanese health insurance claims database. Eligible patients were divided into the AMPC (1303 patients) and AMPC/CVA (424 patients) groups, in which 659 (50.6%) and 293 (69.1%) patients were prescribed probiotics, respectively. Of the patients receiving probiotic prescriptions in the AMPC and AMPC/CVA groups, 632 (95.9%) and 286 (97.6%) patients received antibiotic-resistant probiotic prescriptions, respectively. When classified by the prescribing clinical department and patient age, the proportions of probiotic prescriptions in Internal Medicine and Pediatrics departments were lower than those in the Otorhinolaryngology department regardless of age. These results indicate the probability of insufficient probiotic prescriptions for pediatric patients with otitis media. Solving this issue may lead to the provision of safer antimicrobial therapy.