- 著者
- ALEJANDRA ORTIZ YINGQI ZHANG CHANGZHU JIN YUAN WANG MIN ZHU YALING YAN CLARE KIMOCK CATALINA I. VILLAMIL KAI HE TERRY HARRISON
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.190331, (Released:2019-06-21)
- 被引用文献数
- 8
This study investigates the morphological variation and taxonomic affinities of 28 fossil gibbon molars from eight newly discovered Pleistocene cave sites in the area of Chongzuo, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. A recent descriptive analysis demonstrated that these fossil teeth form a uniform group that can be assigned to a single species of Nomascus. In this contribution, a two-dimensional morphometric approach is employed to examine the Chongzuo specimens in comparison with a large sample of extant hylobatids, as well as with previously reported hylobatid dental remains from the Pleistocene of China. Buccolingual and mesiodistal measurements and crown outline areas reveal that the Chongzuo molars correspond most closely with Nomascus and, to a lesser extent, Hoolock. Crown shape was investigated using elliptical Fourier analysis. Our results show that the Chongzuo specimens fall in most cases either within the range of variation of extant Nomascus to the exclusion of all other hylobatid genera, or their distance from the cluster represented by the Nomascus sample is relatively small. Similarly, the Mahalanobis distances for crown shape show a trend towards smaller morphological distances between the Chongzuo specimens and Nomascus, followed by Hoolock and Hylobates. The Chongzuo molars are also morphometrically distinct from Bunopithecus sericus, but fall within the range of overlap of other Pleistocene hylobatid dental remains from southern China. The balance of evidence indicates that the Chongzuo teeth can be attributed to cf. Nomascus. The fossil teeth are sufficiently distinct from those of extant Nomascus that they may represent an extinct species.
- 著者
- Liangzhen Gu Yanan Zhang Shuang Zhang Haijun Zhao Yuan Wang Dongfang Kan Yimin Zhang Liangqing Guo Jiajian Lv Qian Hao Xu Tian Changhong Liu ShiJun Wang Xiaochun Han
- 出版者
- Japan Oil Chemists' Society
- 雑誌
- Journal of Oleo Science (ISSN:13458957)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.5, pp.685-696, 2021 (Released:2021-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 8
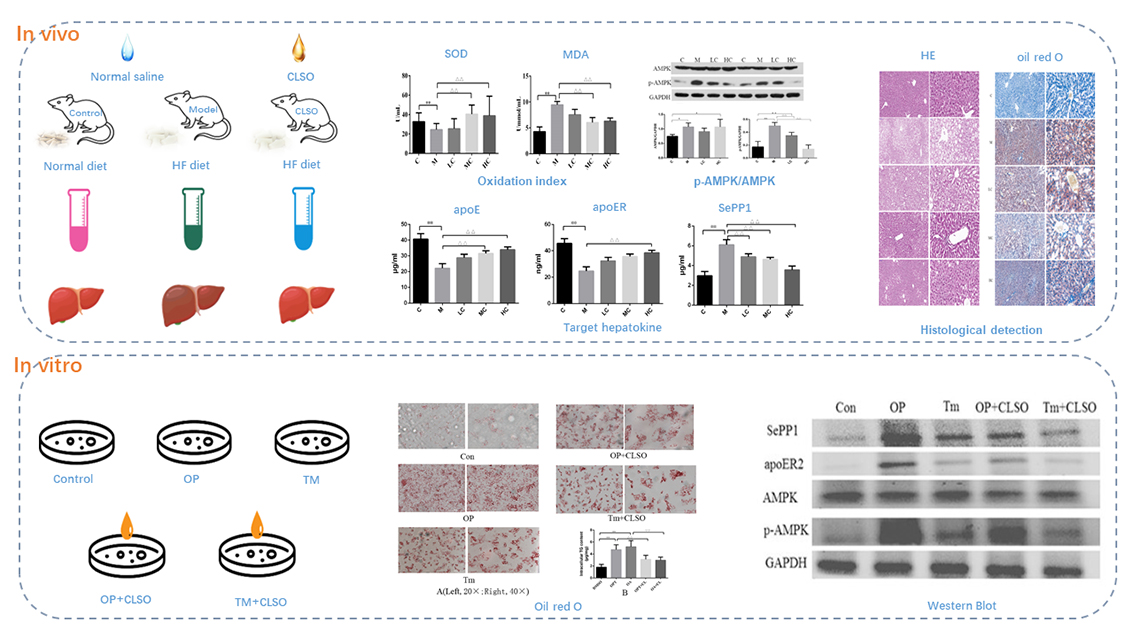
The lipid metabolism disorder is the key role of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Selenoprotein P plays an important role in the pathological process of lipid accumulation. Coix lacryma-jboi seed oil (CLSO) is an active component extracted from Coix lacryma-jobi seed (CLS) which has been found to be effective of reducing blood fat and antioxidative. But the effect and mechanism of CLSO on NAFLD are not clear. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effect and mechanism of CLSO in the treatment of NAFLD. Our result showed that CLSO decreased the liver/body weight ratio, lowered the total cholesterol (TC) and triacylglycerol (TG), and elevated the high density lipoprotein (HDL) in serum. CLSO reduced the lipid deposition in the liver of NAFLD rats. In addition, CLSO could bring down the abnormal expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Moreover, CLSO significantly declined the liver apolipoprotein E (apoE), apolipoprotein E receptor (apoER) and selenoprotein P 1 (SePP1) expression. In vivo, CLSO decreased the lipid droplets and TG level, reduced the protein expression of SePP1, apoER, phosphor-adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) in the cytoplasm of HepG2 cells induced by oleic acid and palmitic acid (OP). At the same time, lipid accumulation was observed in the Sepp1 high expression cells induced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) activator tunicamycin (Tm). CLSO could identically reduce the protein expression of SePP1, apoER, p-AMPK in the cytoplasm of HepG2 cells induced by Tm. This result not only proved the CLSO had therapeutic effect on NAFLD, but also confirmed its mechanism associated with degrading the phosphorylation of adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) which led to the decrease of the expression SePP1/apoER2 in order to reduce lipid accumulation. The study suggests CLSO has great medicinal value in treating NAFLD besides its edibility.
- 著者
- Pey-Yu Wang Takashi Kaneko Yuan Wang Masato Tawata Akio Sato
- 出版者
- Tohoku University Medical Press
- 雑誌
- The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine (ISSN:00408727)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.189, no.1, pp.59-70, 1999 (Released:2005-07-05)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 6 11
Some normal people are falsely classified as having impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) if they are given an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) when their last meal contained very few carbohydrates. In this study, the duration of carbohydrate restriction was extended to one and three days and the relationship between the carbohydrate restriction and the glucose tolerance after an OGTT was examined. Two different groups of normal subjects were placed on high-carbohydrate (80% carbohydrates) and low-carbohydrate (10%) diets before an OGTT; one group for one day and the other for 3 days. None of the subjects showed impairment of glucose tolerance when placed on the high-carbohydrate regimens. In contrast, 3 of 12 subjects and 2 of 8 subjects placed on the low-carbohydrate diets for 1 and 3 days, respectively, were classified as having IGT. The impairment of glucose tolerance was invariably accompanied by an increase in the fasting plasma free fatty acid level. The longer the period of carbohydrate restriction, the severer was the glucose tolerance impairment. However, the number of subjects who were classified as having IGT did not depend on the duration of carbohydrate restriction. The impairment of glucose tolerance after carbohydrate restriction may be associated with the Randle effect, which is the activation of the glucose-free fatty acid cycle.