- 著者
- YOUSUKE KAIFU REIKO T. KONO THOMAS SUTIKNA E. WAHYU SAPTOMO JATMIKO ROKUS DUE AWE HISAO BABA
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.123, no.2, pp.129-145, 2015 (Released:2015-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 90
- 被引用文献数
- 3 18
Dental remains of Homo floresiensis excavated during 2002–2004 at Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia, consist of one partial maxillary dentition, two nearly complete mandibular dentitions, and four isolated teeth. We present here morphological descriptions of all these specimens and report aspects of their dentition, occlusion, and oral health condition. This dental assemblage represents probably five but possibly four or six individuals. These different individuals share similar dental characteristics, supporting the view that the Liang Bua H. floresiensis assemblage represents a single population. We also reassess the previous claims for primitive and modern aspects of the H. floresiensis teeth. The previous studies reached conflicting conclusions: some researchers claim that these teeth are fully modern, whereas others highlight premolar and other morphologies that suggest their direct evolutionary link with the African earliest form of Homo or Australopithecus rather than with H. erectus. Neither of these views are supported. The H. floresiensis teeth exhibit a mosaic of primitive, derived, and unique characters, with the reported primitive aspects broadly comparable to the morphologies observed in H. erectus sensu lato. Although a more comprehensive comparative analysis is needed to fully illustrate dental morphological affinities of this dwarfed hominin species, we find no grounds for the hypothesis that H. floresiensis originated from the small-bodied, primitive hominins such as H. habilis sensu lato.
- 著者
- YOUSUKE KAIFU IWAN KURNIAWAN DAISUKE KUBO ERICK SUDIYABUDI GUNAWAN PONTJO PUTRO ENDANG PRASANTI FACHROEL AZIZ HISAO BABA
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.150702, (Released:2015-10-06)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 9
Ngawi 1 is an undated but well-preserved Homo erectus calvaria from Java. Previous craniometric and morphological studies have shown its similarities to late Javanese H. erectus from Ngandong as well as Sambungmacan (Sm 1 [and Sm 3]). Some researchers emphasize their morphological homogeneity, and suggest that this ‘Ngandong/Sambungmacan/Ngawi group’ is morphologically distinct from H. erectus from the Early Pleistocene of Sangiran and Trinil, possibly at a species-level. In this study, we reinvestigated Ngawi 1 based on the newly cleaned original specimen and using micro- computed tomography with the aim of testing if such morphological discontinuity really exists within the Javanese fossil record. We metrically and non-metrically examined 33 cranial characters that are useful to distinguish earlier and later Javanese H. erectus. We also evaluated the morphology of the three Sambungmacan crania (Sm 1, 3, and 4) in the same way. The results of these and multivariate analyses support previous studies that Ngawi 1 exhibits many characteristic features of Ngandong H. erectus. However, Ngawi 1 is more or less similar to earlier Javanese H. erectus in smaller cranial size, a weak but distinct supraglabellar depression, a relatively short temporal bone, limited posterior projection of the middle part of the occipital torus, a shallower and ‘roofed’ mandibular fossa, and a smaller mastoid process. The three Sambungmacan crania also show general affinities to Ngandong, but are similar to earlier Javanese H. erectus in a few or more characters. Such slightly shifted character distribution is at least consistent with the hypothesis of continuous evolution of H. erectus through the Pleistocene of Java. This minor but potentially meaningful pattern of morphological variation should not be overlooked when a morphological group is defined for the specimens from Ngandong, Sambungmacan, and Ngawi. We also determined the endocranial volume of Ngawi 1 to be 959 cm3.
- 著者
- JOSÉ MARÍA BERMÚDEZ DE CASTRO MARÍA MARTINÓN-TORRES
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.122, no.3, pp.149-155, 2014 (Released:2014-12-23)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 4 9 1
The Early Pleistocene human fossil remains recovered from the TD6 lithostratigraphic unit of the Gran Dolina cave site in the Sierra de Atapuerca, northern Spain, show a mosaic of primitive and derived features. Among the latter, the modern human-like midfacial topography, as well as several synapomorphies shared with some European Middle Pleistocene hominin and Neanderthals, represents a challenge for the phylogenetic interpretation of Homo antecessor. Using an ontogenetic approach of the maxilla ATD6-69, Freidline et al. (Journal of Human Evolution, 65: 404–423 (2013)) have confirmed previous observations that H. antecessor adults had a set of facial features characterizing H. sapiens. However, Freidline and collaborators proposed that the evolution of modern-looking facial morphology occurred independently in Africa, Asia, and Europe and at several times during the Early and the Middle Pleistocene. Following their line of reasoning, the presence in H. antecessor of some features shared with the European Middle Pleistocene hominins and the Neanderthal lineage could also be interpreted as convergences. However, instead of supposing multiple, parallel evolution, we suggest that a more parsimonious interpretation envisages the hypothetical existence of an Early Pleistocene hominin population, from which several hominin lineages originate and inherit particular combinations of derived features. The TD6 hominins probably represent a side branch of this cladogenetic event, which evolved in Western Europe.
52 0 0 0 質量分析を利用したプロテオミクスの考古学・古人類学における応用
- 著者
- 澤藤 りかい 蔦谷 匠
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.200213, (Released:2020-04-07)
従来の免疫的な手法によるタンパク質の検出と異なり,質量分析を利用したタンパク質の分析は,微量のタンパク質も検出でき,誤同定の恐れが小さく,処理能力が高く,未知のタンパク質を網羅的に解析できるという利点をもつ。2010年代以降,考古・人類学的な資料として学術的意味をもつ生物遺物体に存在する過去のタンパク質を,質量分析計を用いてハイスループットまたは網羅的に分析する古代プロテオミクスの研究が盛んになってきた。こうした古代プロテオミクスの手法は,特定のタンパク質のスペクトルパターンから分類群を判別するペプチドマスフィンガープリンティング(ZooMSなど)と,試料中に存在するタンパク質を網羅的に同定するショットガンプロテオミクスに分類できる。現在行なわれている古代プロテオミクスの研究は,生物試料の分類群の判別と系統推定,遺伝情報の推定,有機物の同定,生理状態をあらわすタンパク質の検出,食性の推定,という5つのカテゴリーに大別できる。質量分析によるプロテオミクスに一般的な問題や,過去の試料を分析する際に特有の問題があるものの,古代プロテオミクス分析の利点を活かした研究は今後さらに増加し多様化していくものと予想される。
- 著者
- HIDEAKI KANZAWA-KIRIYAMA TIMOTHY A. JINAM YOSUKE KAWAI TAKEHIRO SATO KAZUYOSHI HOSOMICHI ATSUSHI TAJIMA NOBORU ADACHI HIROFUMI MATSUMURA KIRILL KRYUKOV NARUYA SAITOU KEN-ICHI SHINODA
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.190415, (Released:2019-05-29)
- 被引用文献数
- 3 60
The Funadomari Jomon people were hunter-gatherers living on Rebun Island, Hokkaido, Japan c. 3500–3800 years ago. In this study, we determined the high-depth and low-depth nuclear genome sequences from a Funadomari Jomon female (F23) and male (F5), respectively. We genotyped the nuclear DNA of F23 and determined the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class-I genotypes and the phenotypic traits. Moreover, a pathogenic mutation in the CPT1A gene was identified in both F23 and F5. The mutation provides metabolic advantages for consumption of a high-fat diet, and its allele frequency is more than 70% in Arctic populations, but is absent elsewhere. This variant may be related to the lifestyle of the Funadomari Jomon people, who fished and hunted land and marine animals. We observed high homozygosity by descent (HBD) in F23, but HBD tracts longer than 10 cM were very limited, suggesting that the population size of Northern Jomon populations were small. Our analysis suggested that population size of the Jomon people started to decrease c. 50000 years ago. The phylogenetic relationship among F23, modern/ancient Eurasians, and Native Americans showed a deep divergence of F23 in East Eurasia, probably before the split of the ancestor of Native Americans from East Eurasians, but after the split of 40000-year-old Tianyuan, indicating that the Northern Jomon people were genetically isolated from continental East Eurasians for a long period. Intriguingly, we found that modern Japanese as well as Ulchi, Korean, aboriginal Taiwanese, and Philippine populations were genetically closer to F23 than to Han Chinese. Moreover, the Y chromosome of F5 belonged to haplogroup D1b2b, which is rare in modern Japanese populations. These findings provided insights into the history and reconstructions of the ancient human population structures in East Eurasia, and the F23 genome data can be considered as the Jomon Reference Genome for future studies.
- 著者
- JOSÉ MARÍA BERMÚDEZ DE CASTRO MARÍA MARTINÓN-TORRES
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.140827, (Released:2014-11-18)
- 被引用文献数
- 4 9
The Early Pleistocene human fossil remains recovered from the TD6 lithostratigraphic unit of the Gran Dolina cave site in the Sierra de Atapuerca, northern Spain, show a mosaic of primitive and derived features. Among the latter, the modern human-like midfacial topography, as well as several synapomorphies shared with some European Middle Pleistocene hominin and Neanderthals, represents a challenge for the phylogenetic interpretation of Homo antecessor. Using an ontogenetic approach of the maxilla ATD6-69, Freidline et al. (Journal of Human Evolution, 65: 404–423 (2013)) have confirmed previous observations that H. antecessor adults had a set of facial features characterizing H. sapiens. However, Freidline and collaborators proposed that the evolution of modern-looking facial morphology occurred independently in Africa, Asia, and Europe and at several times during the Early and the Middle Pleistocene. Following their line of reasoning, the presence in H. antecessor of some features shared with the European Middle Pleistocene hominins and the Neanderthal lineage could also be interpreted as convergences. However, instead of supposing multiple, parallel evolution, we suggest that a more parsimonious interpretation envisages the hypothetical existence of an Early Pleistocene hominin population, from which several hominin lineages originate and inherit particular combinations of derived features. The TD6 hominins probably represent a side branch of this cladogenetic event, which evolved in Western Europe.
- 著者
- EMILIANO BRUNER OSBJORN PEARSON
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.121, no.1, pp.31-41, 2013 (Released:2013-04-23)
- 参考文献数
- 76
- 被引用文献数
- 7 43
Jebel Irhoud 1 represents an almost complete cranium from the North African late Middle Pleistocene. Despite the good preservation of most of its anatomical regions, its phylogenetic position is still uncertain, particularly its relationship to the emergence of the modern human lineage. The present paper supplies a basic morphometric description and comparison of the endocast of Jebel Irhoud 1. The endocast’s maximum width is large when compared with the hemispheric length, with values similar to those of Neandertals. Conversely, the frontal width is less pronounced, showing proportions compatible with modern and non-modern human taxa. The vertical proportions are similar to those displayed by Homo erectus, while the lateral proportions are comparable to Neandertals. Furthermore, the upper parietal areas show a certain parasagittal lateral bulging, as in European Neandertals. It remains to be established if this trait evolved independently in both the Neandertal and modern human lineages, or if it was already present in a common ancestor of these two groups. Given that Jebel Irhoud 1 in North Africa and Herto in East Africa have similar geological age, similar facial morphology, but different vault proportions, it seems likely that the origin of the modern human lineage may have predated the origin of many aspects of the modern human brain.
21 0 0 0 OA アイヌから検出された JC ウイルス DNA の系統解析
- 著者
- 余郷 嘉明 鄭 懐穎 長谷川 政美 杉本 智恵 田中 新立 本庄 健男 小林 伸好 太田 信隆 北村 唯一
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.111, no.1, pp.19-34, 2003 (Released:2003-11-19)
- 参考文献数
- 57
- 被引用文献数
- 3 4
JC ウイルス (JCV) DNA の系統解析によりアイヌの起源を解明することを目的として, 北海道の3地域(浦河, 白老, 旭川)に住むアイヌ30名から尿を採取した。尿から検出された JCV DNA (n = 13) は5つのゲノム型 (MY-b, MY-x, MX, EU-a/Arc, EU-c) に分類された。MY-b, EU-a/Arc, EU-cは過去に近隣の人類集団から検出されたが, MY-xとMXは今回初めてアイヌから検出された。得られた知見から, (1) 東北アジアから渡来した複数の人類集団が現代アイヌを築いたこと, (2) ヨーロッパ人に近縁の東北シベリア先住民の祖先集団が現代アイヌの中核を形成したこと, (3) 縄文人を形成した集団や新規な東北アジア系集団も現代アイヌの形成に寄与したことが示唆された。
21 0 0 0 OA 鎌倉市由比ヶ浜地域出土中世人骨の刀創
- 著者
- 平田 和明 長岡 朋人 星野 敬吾
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.112, no.1, pp.19-26, 2004 (Released:2004-07-14)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 13 14
鎌倉市の由比ヶ浜地域には大量の中世人骨が出土している静養館遺跡,由比ヶ浜南遺跡(単体埋葬墓),中世集団墓地遺跡(No. 372)および材木座遺跡の4遺跡があり,これらの出土人骨の刀創の特徴を比較検討した。刀創受傷率は材木座遺跡が最も高く65.7%であり,次に静養館遺跡が6.6%で,中世集団墓地遺跡は1.4%,由比ヶ浜南単体埋葬人骨は1.3%であった。刀創人骨のうちの斬創が占める割合は,静養館遺跡が100%,由比ヶ浜南遺跡が66.6%,中世集団墓地遺跡が75.0%,材木座遺跡が2.7%であった。一方,掻創が占める割合は材木座遺跡が82.3%で圧倒的に高く,中世集団墓地遺跡は2個体だけで25.0%,静養館遺跡と由比ヶ浜南遺跡の出土人骨には掻創は認められなかった。由比ヶ浜地域(前浜)は主として14世紀に中世都市鎌倉の埋葬地として使用されたと考えられるが,遺跡間および同一遺跡内の各墓抗間においても人骨の埋葬形態に差異があることが明らかであり,今後の広範囲な分野から更なる解析・検討が必要である。
21 0 0 0 石器時代杭上.住居の跡は我國に存在せざるか
21 0 0 0 OA 天津北彊博物館に代表されし新石器時代の遺物(二)
- 著者
- リサン エ 松本 信廣譯
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- 人類學雜誌 (ISSN:00035505)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.3, pp.90-102, 1931-03-15 (Released:2010-06-28)
19 0 0 0 OA 東北地方にアイヌの足跡を辿る: 発掘人骨頭蓋の計測的・非計測的研究
- 著者
- 川久保 善智 澤田 純明 百々 幸雄
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.117, no.2, pp.65-87, 2009 (Released:2009-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 70
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
南東北(宮城・福島・山形)由来の古墳時代人・古代人と北東北(青森・岩手・秋田)由来の江戸時代人の頭蓋について,計測的分析と形態小変異の分析を行い,これら東北地方の古人骨に,縄文人やアイヌの形態的特徴が,どの程度遺残しているかを調べた。比較資料として,東日本縄文人,北海道アイヌ,関東の古墳時代人と江戸時代人,それに北部九州の古墳時代人と江戸時代人の頭蓋を用いた。計測的分析では,顔面平坦度計測を含めた18項目の頭蓋計測値を用い,マハラノビスの距離(D2)にもとづいた分析と線形判別分析を試みた。頭蓋形態小変異については,観察者間誤差が少なく,日本列島集団の類別に有効であることが知られている6項目に絞って,スミスの距離(MMD)にもとづく分析を行った。D2でもMMDでも,縄文人に最も近いのは北海道アイヌであったが,東北地方の古墳時代人(計測的分析では古代人も含む)がこれに次いでおり,古墳時代でも江戸時代でも,九州→関東→東北→北海道アイヌまたは東日本縄文人という,明瞭な地理的勾配が観察された。同様の地理的勾配は,判別分析においても確かめられた。このような地理的勾配から判断すると,今回研究の対象にすることができなかった北東北の古墳時代人は,南東北の古墳時代人よりも,さらに縄文・アイヌ群に近接するであろうと推測された。もし彼らが古代の文献に出てくる蝦夷(エミシ)に相当する人々であったとしても,東北地方の古代日本人(和人)と縄文・アイヌ集団の身体的特徴の違いは連続的であったと思われるので,古代蝦夷がアイヌであるか日本人であるかという“蝦夷の人種論争”は,あまり意味がある議論とは思われなかった。
15 0 0 0 OA アイヌの一系統サルンクルに就て
- 著者
- 河野 廣道
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- 人類學雜誌 (ISSN:00035505)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.4, pp.137-148, 1932-04-15 (Released:2010-06-28)
12 0 0 0 OA 九州大学出展人骨資料
- 著者
- 中橋 孝博
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.105, no.5, pp.259-266, 1997 (Released:2010-10-21)
- 参考文献数
- 27
12 0 0 0 OA 蛇王洞縄文早期人骨の人類学的研究
- 著者
- 地土井 健太郎
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.105, no.5, pp.293-317, 1997 (Released:2010-10-21)
- 参考文献数
- 58
- 被引用文献数
- 2
縄文時代早期に属すると推定されてきた岩手県蛇王洞洞穴出土人骨の性別, 死亡時年齢, 所属年代, および形態的特徴を調査した。年代推定については形態学的検討に加えて骨コラーゲンの放射性炭素測定を行った結果, 本人骨が縄文時代早期に属することが確実となった。そこでその個体的特徴を従来指摘されてきた早期人の諸特徴と比較検討してみたところ, 本人骨は全体として繊細であることなど, 概ね従来の指摘通りの形態的特徴を示した。しかしその一方で下顎を含めた顔面下部の形態, 脛骨後面の形態など, 平均的な早期人から逸脱した特徴も備えていることが明らかとなった。
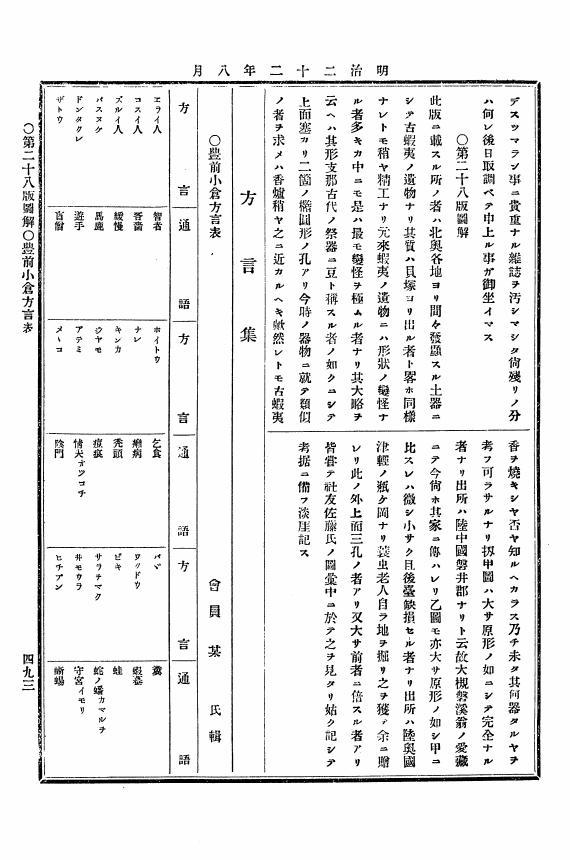
12 0 0 0 OA 方言集方言集(豊前, 駿河, 土佐, 山誠, 越中)
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- 東京人類學會雜誌 (ISSN:18847641)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.4, no.42, pp.493a-502, 1889-08-28 (Released:2011-12-05)
11 0 0 0 OA 北海道諸地方より出でたる古器物上に在る異躰文字
- 著者
- 坪井 正五郎
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- 東京人類學會雜誌 (ISSN:18847641)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.18, pp.280-281, 1887 (Released:2010-06-28)
- 著者
- NAOMICHI OGIHARA HIDEKI AMANO TAKEO KIKUCHI YUSUKE MORITA KUNIHIRO HASEGAWA TAKANORI KOCHIYAMA HIROKI C. TANABE
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (ISSN:09187960)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.123, no.1, pp.57-68, 2015 (Released:2015-04-23)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4 15 2
In order to discuss possible differences in brain anatomy between Neanderthals and early modern humans, the original antemortem appearance of fossil crania that enclosed the brain must somehow be correctly restored, as soft tissues such as the brain are generally not fossilized. However, crania are typically fractured, fragmented, and deformed due to compaction and diagenesis. Furthermore, recovery of all component fragments of fossil crania is rare. Restoration of the brain morphology of fossil crania therefore necessitates correct assembly of the available fragments, eliminating distortions, and compensating for missing parts as a first step. This paper reviews the current status of computerized reconstruction methods, then provides an overview and future directions toward digital reconstruction of fossil crania and the associated brain morphology.
8 0 0 0 OA 骨産道形態の時代変化
- 著者
- 高椋 浩史
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.119, no.2, pp.75-89, 2011 (Released:2011-12-22)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 1
縄文時代から現代に至る骨産道形態の時代変化を検討し,あわせて母親の産道形態が脳頭蓋形態に及ぼす影響について検討した。分析対象地域における骨産道形態の時代変化を検討した結果,縄文人集団の骨産道サイズが比較集団中で最大であった。また,骨産道入口部の形状については,弥生人集団および中世人集団では前後径が短く,横径が長かった。それ以降の近世,近現代,現代人集団の骨産道入口部は逆に前後径が長い特徴を持っていた。一方,骨産道出口部の大きさは縄文時代から時代とともに概ね減少する傾向が確認できた。その上で,分娩時に児頭形態との関係が重要とされている骨産道入口部と頭型の時代変化を比較した。その結果,骨産道入口部形態の時代変化と頭型の変化は概ね一致することが示された。このことから母親の産道形態が脳頭蓋の形態決定要因の一つである可能性が示された。さらに,骨産道サイズと相関があることが指摘されてきた身長との時代変化とについても検討した結果,弥生人集団以降,骨産道サイズの変化と身長の変化が概ね一致する傾向が確認できた。
8 0 0 0 OA 生活様式の復元における筋骨格ストレスマーカーの有効性
- 著者
- 米元 史織
- 出版者
- 日本人類学会
- 雑誌
- Anthropological Science (Japanese Series) (ISSN:13443992)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.120, no.1, pp.15-46, 2012 (Released:2012-08-22)
- 参考文献数
- 106
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
筋骨格ストレスマーカー(MSMs)を用いて,先史・古代人の日常的な活動を古人骨から推察するという研究は数多く行われている。しかし,その一方でMSMsの有効性そのものを疑う研究も提出されている。そこで,本稿ではMSMsから活動の復元を行うことの有効性を検討した。対象資料は考古学・文献記録・民俗調査から漁撈活動を行っていたと想定される吉母浜中世人骨と,埋葬様式より身分の推定が可能な江戸市中出土人骨,及びその比較資料として久世家などの出自の特定が可能な江戸時代人骨,合わせて313体を用いた。上肢(鎖骨・上腕骨・橈骨・尺骨)および下肢(大腿骨・脛骨)に付着する筋・靭帯・腱付着部29部位を対象とし,それぞれの発達度をスコアによって評価した。まず,吉母浜中世人骨では先行研究で指摘されている「肋鎖靭帯のスコアが顕著に高く,次いで大胸筋や三角筋のスコアが高い」という漁撈的特徴を示すことを確認した。次に江戸時代人骨の各埋葬様式群のMSMsの類似性や,男女差の検討を行った。これらの分析の結果,武士階層とされる埋葬様式の被葬者のMSMsは互いに類似し,庶民層とではMSMsのスコアの発達度が異なる傾向をみせることが確認された。具体的には,武士層とされる埋葬様式群では,下肢8部位のMSMsの発達度に類似性がみられ,その特徴は,剣術・弓術・馬術などの武芸や立ち居振る舞いなどの所作によって形成されうるものであると考えられた。本研究の結果は,MSMs分析が生活様式を復元する有力な方法の1つとなる可能性を示唆するものである。