- 著者
- Hiroyuki Uchima Masayoshi Kumagai Junzo Shimbe Akihiro Tanabe Yuta Mizuno Yusuke Onuki
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.5, pp.998-1003, 2022-05-15 (Released:2022-05-24)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 9
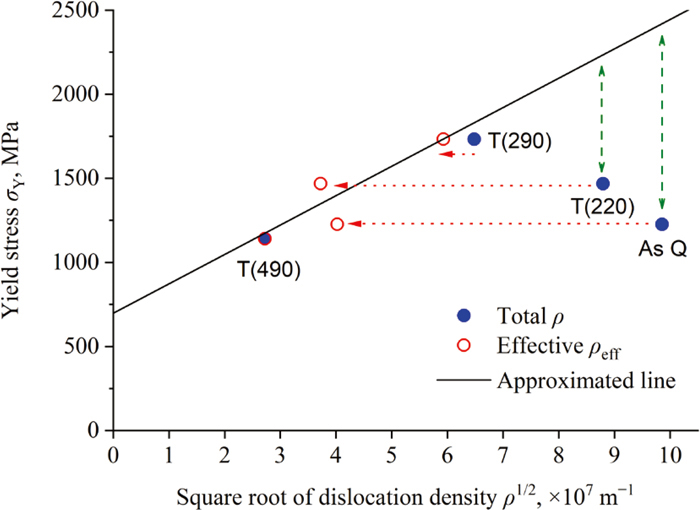
Middle-carbon martensite steels are vital materials for mechanical components and their mechanical properties have attracted significant interest. However, the decrease in the elastic limit of the as-quenched materials is one of the remaining puzzles. Herein, we quantitatively characterized the dislocation density and its structure in the as-quenched and tempered martensite steel by neutron diffraction line profile analysis and discussed their impact on the yield stress. The dislocation density in the as-quenched specimen was the highest at 9.7 × 1015 m−2, while it decreased with an increase in the tempering temperature. In addition, the component ratios of edge and screw dislocations decreased and increased, respectively, depending on the increase in the tempering temperature. The dislocation arrangement parameter (M) varied between the tempering temperatures of 220 and 290°C. Although there was a large difference between the yield stress obtained from the tensile test and that estimated from the dislocation density, the experimental results could be explained by correcting them with the inverse of M value as an index showing the effective dislocation density ratio.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Uchima Masayoshi Kumagai Junzo Shimbe Akihiro Tanabe Yuta Mizuno Yusuke Onuki
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.ISIJINT-2021-443, (Released:2022-01-07)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Middle-carbon martensite steels are vital materials for mechanical components and their mechanical properties have attracted significant interest. However, the decrease in the elastic limit of the as-quenched materials is one of the remaining puzzles. Herein, we quantitatively characterized the dislocation density and its structure in the as-quenched and tempered martensite steel by neutron diffraction line profile analysis and discussed their impact on the yield stress. The dislocation density in the as-quenched specimen was the highest at 9.7 × 1015 m-2, while it decreased with an increase in the tempering temperature. In addition, the component ratios of edge and screw dislocations decreased and increased, respectively, depending on the increase in the tempering temperature. The dislocation arrangement parameter (M) varied between the tempering temperatures of 220 and 290°C. Although there was a large difference between the yield stress obtained from the tensile test and that estimated from the dislocation density, the experimental results could be explained by correcting them with the inverse of M value as an index showing the effective dislocation density ratio.
- 著者
- Tatsutoshi Nakahata Tomonari Awaya Hsi Chang Yuta Mizuno Akira Niwa So-ichiro Fukada Shin'ichi Takeda Shinya Yamanaka Toshio Heike
- 出版者
- 日本神経学会
- 雑誌
- 臨床神経学 (ISSN:0009918X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.11, pp.889-889, 2010 (Released:2011-03-28)
- 被引用文献数
- 2 2