- 著者
- Qichen Zhang Jia You Wenli Zhu Zhigang Wu Jingyuan Xiong
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20P038, (Released:2020-05-08)
- 著者
- Hiroka SUGAI Shunsuke TOMITA Ryoji KURITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.20R002, (Released:2020-04-03)
- 被引用文献数
- 13
- 著者
- Yusuke KITAMURA Takaaki TANIGUCHI Miwako TSUTSUMI Leanddas NURDIWIJAYANTO Tomoya MATSUO Yousuke KATSUDA Toshihiro IHARA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.4, pp.397-400, 2020-04-10 (Released:2020-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A fluorescent dye-labeled DNA probe was adsorbed and quenched on the monolayer of RuO2 nanosheets. Significant fluorescent recovery was observed upon the addition of complementary DNA due to desorption of the probe from the surface of the RuO2 nanosheet through duplex formation. The efficiency of fluorescence recovery was higher than that for graphene oxide, which was known as a quencher-free platform for the detection of nucleic acids in a homogeneous solution.
- 著者
- Yuki TOGO Kazunori NAKASHIMA Wilson MWANDIRA Satoru KAWASAKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.4, pp.459-464, 2020-04-10 (Released:2020-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 4
We developed a novel metal adsorbent composed of bio-based materials, cellulose and a protein. The approach involved the immobilization of a hexa-histidine tag (His6), which shows an affinity for an intermediate acid (metal ion) in Hard and Soft Acids and Bases (HSAB) theory, on cellulose by fusing with a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). The results show that CBM-His6-bound cellulose has adsorption selectivity reflecting the original properties of His6. Additionally, we prepared three configurations of CBM-His6 proteins, which were subsequently immobilized on filter paper for Ni2+ ion adsorption. Of these configurations, we found that the protein containing two His6 tags at each terminus (N– and C–) of CBM exhibited the highest metal adsorption ability. Furthermore, XPS analysis confirmed the binding of Ni2+ ions on the cellulose.
- 著者
- Yasumoto DATE Hiroyuki MASAKI Arata AOTA Kazuhiro SASAKI Yukie NAMIKI Thomas R. GLASS Naoya OHMURA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.4, pp.453-457, 2020-04-10 (Released:2020-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 1
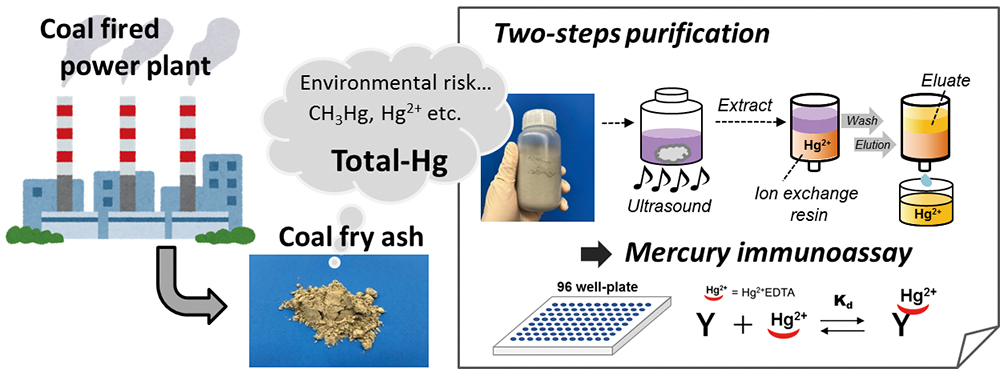
A simplified two-step mercury extraction procedure enabled the selective and reproducible mercury recovery from actual coal fly ash (CFA). The optimized extraction procedure involving conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based immunoassay allowed the ultra-sensitive quantification of total mercury content in CFA. The total mercury content of 41 CFA samples were successfully determined using the above-mentioned method, and the results were in agreement with those obtained by standard instrumental analysis (thermal decomposition atomic absorption spectrometry) within a 15% coefficient of variation. Our method for total mercury quantification is not only simple but suitable for management of the mercury content at coal-fired electric power plants and landfill sites, which deal with large amounts of waste CFA.
1 0 0 0 OA Development of Human Hair Reference Material Supporting the Biomonitoring of Methylmercury
- 著者
- Koichi HARAGUCHI Mineshi SAKAMOTO Akito MATSUYAMA Megumi YAMAMOTO Dang T. HUNG Hiromitsu NAGASAKA Keisuke UCHIDA Yasunori ITO Hitoshi KODAMANTANI Milena HORVAT Hing M. CHAN Matthew RAND Ciprian M. CIRTIU Byoung-Gwon KIM Flemming NIELSEN Akane YAMAKAWA Nikolay MASHYANOV Nikolai PANICHEV Elena PANOVA Tomoaki WATANABE Naoki KANEKO Jun YOSHINAGA Ranny F. HERWATI Alfrida E. SUOTH Hirokatsu AKAGI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19SBP07, (Released:2020-03-06)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
- 著者
- Sifan XU Shuqi YE Yunhui XU Feifan LIU Yushun ZHOU Qian YANG Hailong PENG Hua XIONG Zhong ZHANG
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.353-360, 2020-03-10 (Released:2020-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 12
To achieve a rapid, sensitive, and economical method for the detection of ascorbic acid (AA) in the presence of Fe3+, a nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots (N,S-co-CDs) based fluorescence sensing system was developed. In this work, N,S-co-CDs were successfully synthesized via a one-step microwave-assisted method within 2.5 min using ammonium citrate and L-cysteine as precursors. The fluorescence of N,S-co-CDs was quenched (off ) by Fe3+ through a static-quenching mechanism. Subsequently, the fluorescence was recovered (on) after introducing AA into the quenched system, which was attributed to the reduction effect of AA for Fe3+. Therefore, a switch-on sensor (N,S-co-CDs/Fe3+ system) was developed for AA detection. Under optimal conditions, the limit of detection (LOD) of 2.31 μmol/L for AA was obtained over a linear range from 0 to 150 μmol/L. Furthermore, the proposed sensing method was successfully applied to detect AA in processed fruit juice with satisfactory results. The most important is that the sensor derived from a microwave-assisted method has simple and eco-friendly synthesis processes, is rapid, and has high detection efficiency. Therefore, such a switch-on sensor may be a promising candidate sensor for AA detection in processed fruit samples.
- 著者
- Kuniaki NAGAMINE Ayako NOMURA Yusuke ICHIMURA Ryota IZAWA Shiori SASAKI Hiroyuki FURUSAWA Hiroyuki MATSUI Shizuo TOKITO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.291-302, 2020-03-10 (Released:2020-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 139
- 被引用文献数
- 26
This review describes recent advances in biosensors for non-invasive human healthcare applications, especially focusing on sweat analysis, along with approaches for fabricating these biosensors based on printed electronics technology. Human sweat contains various kinds of biomarkers. The relationship between a trace amount of sweat biomarkers partially partitioned from blood and diseases has been investigated by omic analysis. Recent progress in wearable or portable biosensors has enabled periodic or continuous monitoring of some sweat biomarkers while supporting the results of the omic analysis. In this review, we particularly focused on a transistor-based biosensor that is highly sensitive in quantitatively detecting the low level of sweat biomarkers. Furthermore, we showed a new approach of flexible hybrid electronics that has been applied to advanced sweat biosensors to realize fully integrated biosensing systems wirelessly connected to a networked IoT system. These technologies are based on uniquely advanced printing techniques that will facilitate mass fabrication of high-performance biosensors at low cost for future smart healthcare.
- 著者
- Elumalai SATHEESHKUMAR Jyisy YANG Venkatesan SRINIVASADESIKAN Ming-Chang LIN
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.10, pp.1115-1121, 2017-10-10 (Released:2017-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 3 19
In this work, a simple method was developed to simultaneously fabricate silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and modify their surfaces with recognition functional groups for colorimetric detection of Cu2+ ions. To prepare the AgNPs with proper functional group on their surface for detection of Cu2+ ions, photochemical reaction was employed and a photoactive species of tyrosine (Tyr) was used to trigger the photoreduction of AgNPs, while the oxidized Tyr (TyrOx) was used to functionalize the AgNPs surface at the same time. To understand the behaviors, the prepared color AgNPs colloidal solution was characterized by UV-visible spectrometer, FT-IR spectrometer, dynamic light scattering (DLS), X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS) and density functional theory (DFT). Based on DFT calculation results, TyrOx was adsorbed on the surface of AgNPs by the quinone ring and its functional group of amino acid was freely exposed to the aqueous media for rapid interaction of Cu2+ ions. Based on detection of different metal ions, TyrOx@AgNPs were selective to interact with Cu2+ ions through formation of highly stable Cu2+-TyrOx@AgNPs complexes. The evidence in formation of Cu2+-TyrOx@AgNPs complex could be obtained through the red shift of the surface plasmonic resonance (SPR) band of TyrOx@AgNPs located at 557 nm, which gives a color change from light yellow to brown color allowing visual identification of Cu2+ ions for rapid screening purposes. For quantitative analysis, a band intensity ratio of A557/(A404–A557) was constructed to correlate with the concentration of Cu2+ ions. A linear range up to 10 μM with a detection limit close to 150 nM was found.
- 著者
- Evan L. ANDERSON Blair K. TROUDT Philippe BÜHLMANN
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.187-191, 2020-02-10 (Released:2020-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Porous glass frits are frequently used to contain the salt bridges through which reference electrodes interface samples. Prior work with widely used glass frits with 4 – 10 nm diameter pores showed that, when samples have a low electrolyte strength, electrostatic screening of sample ions by charged sites on the glass surface occurs. This creates an ion-specific phase-boundary potential at the interface between the sample and frit, and it biases the potential of the reference half-cell. Use of frits with much larger pores eliminates this problem but results in the need for frequent replenishing of the bridge electrolyte. A methodical study to determine the optimum pore size has been missing. We show here that charge screening of sample ions occurs when the pore size of nanoporous glass frits is on the order of 1 – 50 nm and samples have a low electrolyte strength. An increase in pores size to 100 nm eliminates charge screening in samples with ionic strengths in the 1.0 M to 3.3 × 10−4 M range. However, the rates of electrolyte solution flow through frits with 1, 5, 20, 50, and 100 nm pores are still low, which makes diffusion the dominant mode of ion transport into and out of these frits. Consequently, the flow of bridge electrolyte into samples is not fast enough to prevent diffusion of ions and electrically neutral components from the sample diffusing into the salt bridge, which can result in cross contamination among samples.
- 著者
- Masateru TANIGUCHI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.161-175, 2020-02-10 (Released:2020-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 107
- 被引用文献数
- 2
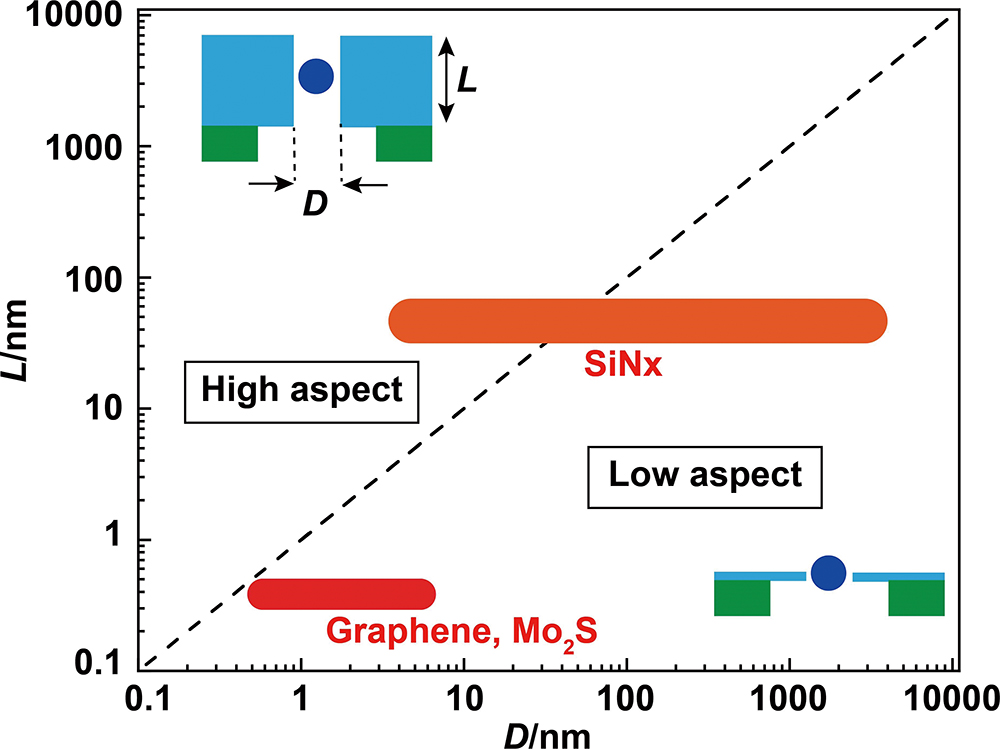
Low aspect ratio nanopores are expected to be applied to the detection of viruses and bacteria because of their high spatial resolution. Multiphysics simulations have revealed that the ion current–time waveform obtained from low aspect ratio nanopores contains information on not only the volume of viruses and bacteria, but also the structure, surface charge, and flow dynamics. Analysis using machine learning extracts information about these analytes from the ion current–time waveform. The combination of low aspect ratio nanopores, multiphysics simulation, and machine learning has made it possible to distinguish different types of viruses and bacteria with high accuracy.
1 0 0 0 OA Enzyme-responsive Fluorescent Ionic Liquid
- 著者
- Ryoutarou OISHI Tatsumi MIZUTA Kenji SUEYOSHI Tatsuro ENDO Hideaki HISAMOTO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.143-145, 2020-02-10 (Released:2020-02-10)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 被引用文献数
- 9
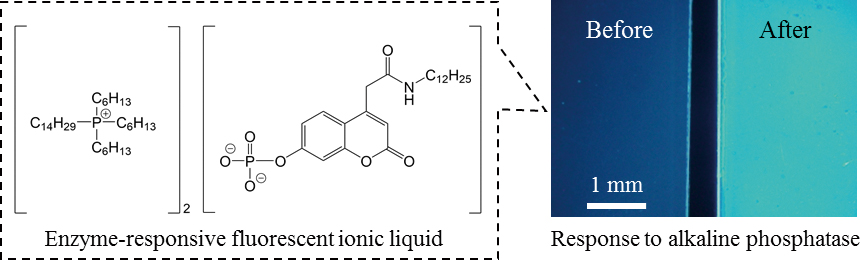
Herein, we describe the development of a novel material, “enzyme-responsive fluorescent ionic liquid”, which enabled a highly sensitive detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP). We prepared a plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) membrane using this new material as a plasticizer and quantified ALP in aqueous solutions. Preliminary results suggested that the PVC membrane responded to ALP at an interface between the membrane and the sample solution with anion extraction to maintain electroneutrality in the membrane phase. The developed PVC membrane showed an approximately six-times higher sensitivity than the conventional membrane, thereby demonstrating highly sensitive ALP detection. These results suggested the potential applicability of the proposed membrane for highly sensitive protein detection by using ALP-labeled antibodies.
1 0 0 0 OA Is the Oil | Water Interface the Simplest and Best Suited Model for Understanding Biomembranes?
- 著者
- Toshiyuki OSAKAI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.4, pp.361-366, 2019-04-10 (Released:2019-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 68
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Many studies have been conducted by using the oil (O) | water (W) interface as a simple model for understanding ion transfer (IT) or electron transfer (ET) across biomembranes. In this review, we revisit the usability of the O | W interface as a biomembrane model. For understanding biomembrane IT, the O | W interface is the simplest and best suited model. For example, the standard Gibbs transfer energy of drug ions at the O | W interface is a useful measure for evaluating their membrane permeability in a conventional in vitro assay, called PAMPA. However, the O | W interface is not necessarily a good model for understanding biomembrane ET. This is because no net current can be observed with the O | W interface, owing to the ET-coupled proton transfer. In such a case, the self-assembled monolayer (SAM) formed on a metal electrode serves as a better model for understanding biomembrane ET.
- 著者
- Etsu YAMADA Keisuke SASAI Ryota HIGA Hirotaka MIZUGUCHI Yasuro FUSE
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19P450, (Released:2020-01-17)
- 被引用文献数
- 3
- 著者
- Ke-Hsuan WANG Genta WATANABE Hayato IKEUCHI Siyang CUI I-Ping LIU Kanta YAMADA Masaaki YOSHIDA Takeshi KAWAI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.27-34, 2020-01-10 (Released:2020-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 6
A key requirement in developing oxygen evolution reaction (OER) electrocatalysts is increasing their surface area. Herein, we report the design of a hierarchical micro/nanostructured catalyst. Based on polystyrene colloidal template electrodeposition, an ordered microcup array surrounded by nanoflakes was fabricated. The effect of the deposition time on the formation of the catalyst and the corresponding OER performance of the catalyst were investigated using scanning electron microscopy, in situ X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy, and electrochemical analysis. The in situ XAFS measurements indicate that the structure of the hierarchical structured catalyst is similar to that of γ-FeOOH. The electrochemical analysis indicates that the hierarchical catalyst has a large surface area and a low charge transfer resistance, which lead to its excellent catalytic performance for the OER. Our study provides new insights in designing high-performance OER catalysts. Moreover, the synthesized hierarchical micro/nanostructured catalyst could be used as a platform for further studies on low-cost iron-based electrocatalysts.
- 著者
- Jens Rüdiger STELLHORN Shinya HOSOKAWA Shinji KOHARA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.5-16, 2020-01-10 (Released:2020-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 49
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Local- and intermediate-range atomic structures were investigated on amorphous phases of an ordinary phase-change material, Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST), and an exotic one, Cu2GeTe3 (CGT), by using anomalous X-ray scattering close to K absorption edges of each element to find a fast amorphous-crystalline phase-change mechanism. The obtained data were analyzed by using reverse Monte Carlo modeling to obtain partial structure factors, partial pair distribution functions, and three-dimensional atomic configurations. Ring statistics were carefully examined to clarify the similarity and difference compared with the corresponding crystal structures, and it was found that amorphous GST has a number of four-membered rings indicating fragments of crystal structure, and amorphous CGT has a remarkable number of three-membered rings showing a collapse of crystal structures composed of purely six-membered rings. A persistent homology analysis was carried out and long-range ring structures of the constituent elements were observed in the amorphous phase, which may originate from fragments of crystal structures with a long-range periodicity.
1 0 0 0 OA Chemometrics and Related Fields in Python
- 著者
- Shigeaki MORITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.1, pp.107-112, 2020-01-10 (Released:2020-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 146
- 被引用文献数
- 18
The Python programing language is becoming a promising tool for data analysis in various fields. However, little attention has been paid to using Python in the field of analytical chemistry, though recent advances in instrumental analysis require robust and reliable data analysis. In order to overcome the difficulty in accurate analysis, multivariate analysis, or chemometrics, has been widely applied to various kinds of data obtained by instrumental analysis. In the present work, the potential usefulness of Python for chemometrics and related fields in chemistry is reviewed. Many practical tools for chemometrics, e.g., principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares (PLS), support vector machine (SVM), etc., are included in the scikit-learn machine learning (ML) library for Python. Other useful libraries such as pyMCR for multivariate curve resolution (MCR), 2Dpy for two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2D-COS), etc. can be obtained from GitHub. For these reasons, a computational environment for chemometrics is easily constructed in Python.
- 著者
- Niu Yuqi Gao Wenhui Li Hui Zhang Jingxuan Lian Yunhe
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19P421, (Released:2020-01-03)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
- 著者
- Mercedes BECERRA-HERRERA Valentina MIRANDA Pablo RICHTER
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19P409, (Released:2019-12-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 6
- 著者
- Yukihiro ESAKA Saki KUNISHIMA Hiromitsu ARUGA Takuhei YAMAMOTO Hiroya MURAKAMI Norio TESHIMA Bunji UNO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.19N023, (Released:2019-08-30)
- 被引用文献数
- 3