16 0 0 0 OA 消化管スパイスセンサーとその機能:辛味は胃腸でも味わう
- 著者
- 堀江 俊治 田嶋 公人 松本 健次郎
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.138, no.8, pp.1003-1009, 2018-08-01 (Released:2018-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Capsaicin is a constituent of chili pepper, and induces the burning sensation on the tongue. The site of action for capsaicin has been discovered as transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (TRPV1) that resides on the membranes of pain- and heat-sensing primary afferent nerves. The immunohistochemical study on the stomach revealed that nerve fibers expressing TRPV1 exist along gastric glands in the mucosa, around blood vessels in the submucosa, in the myenteric plexus, and in the smooth muscle layers. High numbers of TRPV1-immunoreactive axons were observed in the rectum and distal colon. Therefore, capsaicin stimulates TRPV1 not only on the tongue but also in the gut. In this review, the mechanism of gastrointestinal mucosal defense enhanced by capsaicin was summarized. TRPV1 plays a protective role in gastrointestinal mucosal defensive mechanism. Hypersensitivity of afferent fibers occurs during gastrointestinal inflammation. Abnormalities of primary afferent nerve fibers are strongly associated with the visceral hypersensitive state in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The alteration of TRPV1 channels in mucosa contributes to the visceral hypersensitivity in colitis model mice. TRPV1-expressing neurons in the gut are thought to be extrinsic sensory afferent neurons that operate to maintain gastrointestinal functions under physiological and inflammatory states.
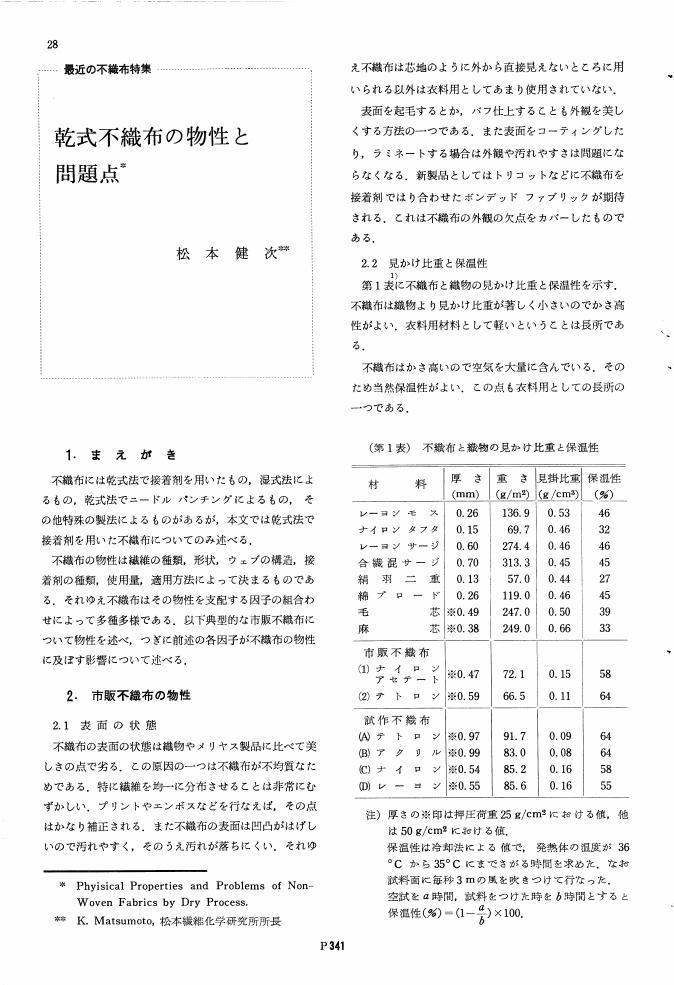
3 0 0 0 OA 乾式不織布の物性と問題点
- 著者
- 松本 健次
- 出版者
- 社団法人 日本繊維機械学会
- 雑誌
- 繊維工学 (ISSN:18838731)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.5, pp.P341-P347, 1966-05-20 (Released:2010-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 14
1 0 0 0 OA 炎症性腸疾患モデル動物における温度感受性受容体TRPV1とセロトニンシグナリングの変化
- 著者
- 松本 健次郎
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- YAKUGAKU ZASSHI (ISSN:00316903)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.134, no.11, pp.1165-1170, 2014-11-01 (Released:2014-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Primary afferent nerve fibers are highly associated with visceral hypersensitivity state of inflammatory bowel disease. Hypersensitivity of afferent fibers occurs during inflammation, and therefore to gain insight into the alteration of receptors and channels, we examined receptors such as 5-HT receptors and transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1), which are expressed in primary afferent neurons. The current study was designed to investigate the time-dependent dynamic changes of 5-HT3 receptors, 5-HT4 receptors, TRPV1 channels, and 5-HT regulatory factors in DSS-induced colitis model mice. Colitis was induced by 3% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) solution given as drinking water in C57BL/6J mice. Immunohistochemical analysis and visceromotor responses to colorectal distension were measured during induction of DSS colitis (day 0, 4 and 7). Progress of the inflammation led to down regulation of serotonin transporter immunoreactivities with concomitant increases in 5-HT and tryptophan hydroxylase-1 positive cell numbers. TRPV1-expressing nerve fibers gradually increased during DSS treatment. Abundant non-neuronal TRPV1-immunopositive cell like structure was observed on day 7 of DSS treatment, but not on day 4. The number of 5-HT3 receptor-expressing nerve fibers increased in mucosa on day 7. On the other hand, 5-HT4 receptor-expressing nerve fibers decreased on day 7. TRPV1 antagonist and 5-HT3 receptor antagonist attenuated the visceral hyperalgesia to control level in the DSS-induced colitis model. We made the novel observations of increased neuronal/non-neuronal TRPV1 channel and 5-HT3 receptor expression, and decreased 5-HT4 receptor expression in mucosa. Moreover, we show that a correlation existed between the mucosal changes and visceral hypersensitivity in experimental colitis.
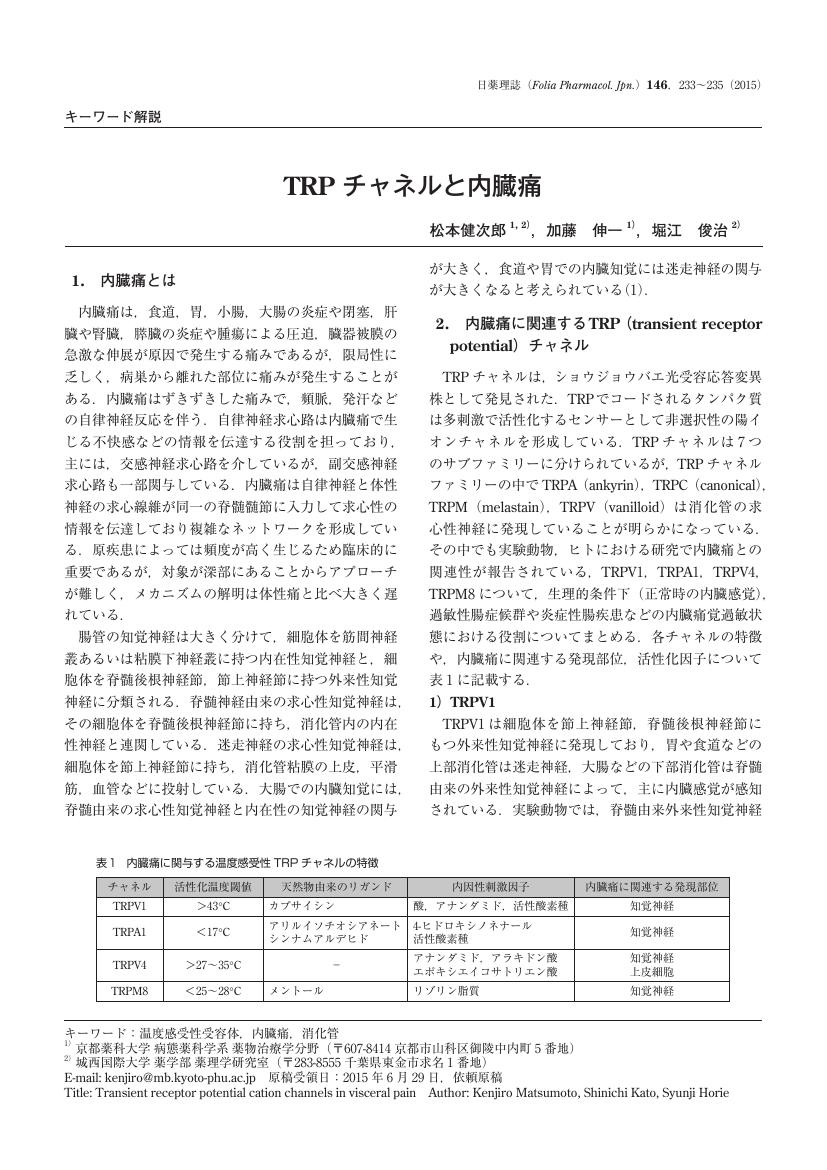
1 0 0 0 OA TRPチャネルと内臓痛
- 著者
- 松本 健次郎 加藤 伸一 堀江 俊治
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬理学会
- 雑誌
- 日本薬理学雑誌 (ISSN:00155691)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.146, no.4, pp.233-235, 2015 (Released:2015-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 25