- 著者
- Corey Adam Myers Takao Nakagaki
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.4, pp.687-696, 2019-04-15 (Released:2019-04-17)
- 参考文献数
- 105
- 被引用文献数
- 1 9
A prediction of the nucleation lag time of iron and steelmaking melts solely from elemental composition and temperature was produced via deep neural networks trained on data available in the literature. To the best of our knowledge, this constitutes the first published instance of prediction of nucleation lag time that does not require composition specific empirical data. Control of the nucleation process is critical for the production of ground granulated blast furnace slag, control of slag properties for heat recovery or utilization, and the optimization of slag for CO2 mineralization. The deep neural network achieved an average absolute scaled error (AASE) over a testing set of 947 points covering 7 orders of magnitude of 39.9%. Performance was further improved by bootstrapping with a prediction of liquidus temperature from a separate deep neural network (AASE = 33.4%). Bootstrapping using DNN-generated viscosity data did not increase prediction accuracy. The negligible calculation load of the trained deep neural networks allows for rapid design, analysis, and optimization of novel slag compositions and treatment methods. This ability was demonstrated by calculating the necessary continuous cooling rate to generate amorphous slag across all CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 and CaO–FeO–SiO2 compositions and the potential to use additives to alter said cooling rate.
- 著者
- Hiroshi Nogami Jun-ichiro Yagi Shin-ya Kitamura Peter Richard Austin
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.12, pp.1759-1766, 2006 (Released:2006-12-21)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 35 55
The iron and steelmaking industry has been receiving social pressure to reduce energy consumption and environmental load as recent increase in the social awareness on environmental and resource problems. The ironmaking system consumes more than a half of overall energy input to the steelwork and its improvement is expected as a countermeasure for such problems. Numerous attempts through improving the blast furnace operation have been made. This paper analyzes material and energy balances of ironmaking system that consists of hot stove, coke oven, CDQ, sintering and blast furnace. The operation statuses of the blast furnace with natural gas injection, metallic charging and top gas recycling that have been obtained by the kinetic-based numerical simulations are applied to this analysis. The results suggested that the metallic charging to blast furnace decreases both energy input and CO2 emission. The natural gas injection operation decreases the CO2 emission from the iron making system while the decrease in the energy input is small. The top gas recycling operation increases the CO2 emission due to the scrubbed CO2 from the recycled top gas.
- 著者
- Hideyuki Matsuta
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.1, pp.213-217, 2015-01-15 (Released:2015-02-06)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 5 8
When non-metallic atoms are excited in a low-pressure glow discharge plasma, absorption transitions can be observed in the 640–930 nm wavelength range where laser diodes are commercially available. These excited atoms can be sensitively probed by diode laser atomic absorption spectrometry (DL-AAS). Because an atomic absorption transition can also be detected by coherent forward scattering (CFS) spectrometry and CFS spectrometry with a diode laser has more attractive features than DL-AAS, diode laser coherent forward scattering spectrometry (DL-CFS) was employed to investigated the absorption transition of excited argon atom at 842.46 nm. Ar (I) 842.46 nm line was adopted due to the tunable wavelength range of available diode laser in this experiment. Excited argon atoms were produced in a glow discharge plasma. CFS signal intensity at 842.46 nm attained maximum at discharge current of 20 mA in 3 Torr (399 Pa) of argon and at magnetic field of 160 mT. Calibration curve of argon was prepared to mix a small amount of argon into 6 Torr (798 Pa) of helium. The signal intensity depended on the 4.4th power of the number density of argon. The 4.4th power dependence is too large to be explained by the theoretically predicted quadratic dependence. When a small amount of molecular nitrogen was mixed into argon plasma, strong suppression of CFS intensity was observed. Molecular gases such as air were found to be unsuitable for the plasma gas to excite the target atoms.
- 著者
- Alya Naili Rozhan Mohd Hanafi Ani Hamzah Mohd Salleh Tomohiro Akiyama Hadi Purwanto
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.2, pp.436-440, 2015-02-15 (Released:2015-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 1 6
This paper presents a technology to utilize bio-char and bio-tar from the pyrolysis of oil palm empty fruit bunch, EFB. In this study, tar vapor from pyrolysis of EFB was infiltrated within porous bio-char and carbon deposition occurred on the pore surface by chemical vapor infiltration process. For preparation, EFB particles were made into pellets. In the first part of experiments, porous bio-char pellets were produced by slowly heating the EFB pellets in a tube furnace in argon atmosphere to terminal temperatures of 500–800°C. In the second part, the porous bio-char pellets were used as precursor for tar decomposition process to deposit carbon within the bio-char pores. Tar vapor was obtained from the pyrolysis of EFB at 400–500°C at a fast heating rate for tar decomposition to occur. The purpose of this research is to investigate the amount of carbon deposited within bio-char by this tar carbonization process as compared to carbon contents of metallurgical coke. We showed how EFB bio-char was used as the tar filter and in the process to produce carbon-infiltrated bio-char, a useful renewable energy source for ironmaking process.
1 0 0 0 OA Understanding the Structure and Structural Effects on the Properties of Blast Furnace Slag (BFS)
- 著者
- Muhammad Sajid Chenguang Bai Muhammad Aamir Zhixiong You Zhiming Yan Xueming Lv
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.7, pp.1153-1166, 2019-07-15 (Released:2019-07-13)
- 参考文献数
- 96
- 被引用文献数
- 37
Evolving knowledge of the structure and physical properties of metallurgical slags is summarized in current review. Slag structure, compositional effects, role of cations in structural modifications, parameters used to represent the structure, structural analysis techniques and effects of structure on properties of blast furnace slag (BFS) studied in details. The basicity, polymerization (Q) or depolymerization (NBO/T), optical basicity, Qn values, concentrations of bridging O’s (Oo), non-bridging O’s (O−) and free O’s (O2−) in slag are useful to represent the structure of slag. Methods and techniques utilized to study the slags are also discussed. The BFS is characterized by using X-ray Diffraction and Spectroscopy, Raman Spectroscopy, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. The physical properties such as surface tension, viscosity, density, thermal expansion and diffusion, electrical conductivity and resistivity of slags are reviewed thoroughly which are heavily dependent on structure of slag. Viscosity is affected by polymerization or depolymerization of slag structure and cation size; electrical resistivity depends on Q, size of cations and number of available cations; thermal expansion depends on Q and cation field strength (i.e. z/r2); thermal conductivity is linked with rigidity of slag network which is also dependent on Q and metal-oxygen (M–O) bond strength. Degree of polymerization or depolymerization of slag structure also effect the surface and interfacial tension, it decreases as metal-oxygen (M–O) bond strengths (i.e. z/r2, cation field strength) decrease.
- 著者
- KAWAI H. TAKAHASHI H.
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ international (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.7, pp.1140-1149, 2004-07-15
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 5 25
One of recent discussions is on the floating and sinking motion of packed bed in the hearth part of blast furnace while the molten liquid is stored in and tapped out of the hearth. Such a repetition motion might be profoundly related to the renewal of deadman particles. Thus, further analysis for deadman motion with the iron liquid is necessary to develop a method for controlled or stable furnace operation. In this study, the experiment is performed using a two-dimensional cold model with foaming polymer particles and water. Gas flow is not considered. The particle descending velocity in the shaft of the model is found to decrease with floating of the hearth packed bed and increase with the sinking motion. The deadman renewal rate that is the solid moving rate forced into raceway from the inside of deadman, is estimated by subtracting the descending rate from the total particle discharge rate being controlled at a constant rate. The numerical treatment called Discrete Element Method is also carried out to clarify the renewal mechanism with storing/tapping liquid. It is confirmed from both the experimental and numerical that the deadman particles move gradually into the raceway while storing/tapping liquid is repeated and the renewal of particles occurs in such a way that the older particles are forced to go out of deadman by buoyancy and the new particles comes in to fill deadman through near the top of the deadman during tapping the liquid. The simulation indicates also that the wall normal contact force in the hearth part increases considerably when the particle bed floats.
- 著者
- Masato Yamashita Hiroo Nagano Toshihei Misawa Herb E. Townsend
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.285-290, 1998-03-15 (Released:2007-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 37 68
A protective and adherent rust layer develops on weathering steels during outdoor exposure. This layer acts as a barrier which slows further corrosion, thus enabling weathering steel to be used in structural applications without painting. To aid in understanding the mechanism of protective rust formation, studies have been made on the composition and microstructure of these layers. The present study was jointly conducted on Japanese weathering steel exposed in the industrial environment of Amagasaki, and US weathering steel exposed in the industrial environment of Bethlehem. The rust layers were studied by use of optical microscopy, electron microscopy with X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, and micro-Raman spectroscopy. The results of this collaboration show that, in general, the rust layers formed during long-term exposure are composed of one or more alternating layers of goethite and lepidocrocite, with scattered patches of maghemite and/or magnetite.
- 著者
- Tatsuro Ariyama Michitaka Sato Taihei Nouchi Koichi Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.10, pp.1681-1696, 2016-10-15 (Released:2016-10-15)
- 参考文献数
- 59
- 被引用文献数
- 4 46
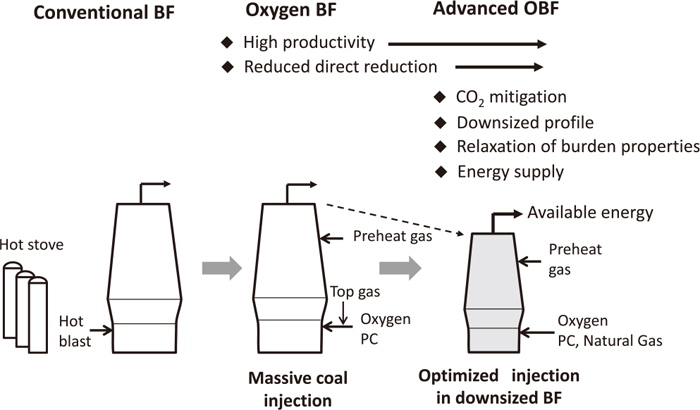
Blast furnace has been regarded as a highly optimized process as a result of various technological improvements over its long history. However, from the viewpoints of resources, energy and global warming, continuing evolution toward reductant flexibility and CO2 mitigation is desired. This review focuses on the progressive design of an ambitious blast furnace for the future.First, the history of techniques for reducing coke rate and reducing agent in the blast furnace are reviewed. Pulverized coal injection is currently common; however a more innovative process is desired in order to address the global warming issue. The low temperature blast furnace based on charging of high reactivity coke is a realistic process. The combination of the oxygen blast furnace with top gas recycling is also attractive. Although the top gas recycling process based on the oxygen blast furnace is very effective for reducing CO2 emissions, a total evaluation considering the role of the blast furnace to keep the energy self-sufficiency in the integrated steel works is necessary. The oxygen blast furnace enables injection of a large amount of natural gas, and optimized injection of natural gas and pulverized coal makes it possible to mitigate CO2 emissions while maintaining the energy supply to downstream processes. Moreover, owing to the high productivity of the oxygen blast furnace, the blast furnace profile can be downsized. The characteristics of several processes are quantitatively examined, and the concept of the advanced oxygen blast furnace as a next-generation process toward carbon dioxide mitigation is discussed.
- 著者
- OH Jin Taek JUNG Bong Bu PARK Hyun Chul
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ international (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.49, no.8, pp.1167-1173, 2009-08-15
- 参考文献数
- 15
Rollers are used widely in the transfer of the steel plate in steel mills. This method causes very loud impact noise because of the deflection of the steel plate and causes noise pollution in the labor environment. In this paper, the relationship between the impact noise and the impact force was examined. Also, a method for reducing the impact force was implemented in order to reduce the impact noise. The noise index was introduced to quantify the relation between impact noise and impact force. Dynamic and impact analyses were carried out using the finite element method. Experiments on impact were also carried out in order to validate the results.
- 著者
- Jun Kariya Junichi Ryu Yukitaka Kato
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.2, pp.457-463, 2015-02-15 (Released:2015-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 1 24
New composite materials were developed for application in chemical heat storage (CHS) systems based on the calcium oxide/water/calcium hydroxide (CaO/H2O/Ca(OH)2) reaction. It was found that the mixtures of expanded graphite (EG) and Ca(OH)2 enhance the reaction performance and moldability, which are important factors for the application in a packed-bed CHS heat exchanger. The reaction kinetics was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. The maximum mean heat output of a mixture containing 11 wt% EG was 1.76 kW (kg-material)−1, which is twice as high as that of the pure Ca(OH)2 (0.85 kW (kg-material)−1). A repetitive dehydration-hydration experiment was carried out and it was confirmed that the positive effect of EG was preserved during the investigated 10 cycles. Therefore, based on our results, these composite materials can enhance the thermal performance of the CaO/H2O/Ca(OH)2 reaction cycle in CHS systems.
- 著者
- Jin Jia Shang-lei Yang Wei-yuan Ni Jian-ying Bai Yang-shenglan Lin
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.12, pp.2881-2889, 2014-12-15 (Released:2015-01-06)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 5
この記事は撤回されました
1 0 0 0 OA Innovative Methodology for Separating of Rare Earth and Iron from Bayan Obo Complex Iron Ore
- 著者
- Yingui Ding Jingsong Wang Guang Wang Qingguo Xue
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.10, pp.1772-1777, 2012 (Released:2012-10-15)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 8 42
A new process was proposed in this research, in order to address the problems of difficult treatment, low efficiency and heavy pollution of Bayan Obo complex iron ore. The isothermal reduction experiments, using carbon-bearing pellets which were mainly made of Bayan Obo complex iron ore and pulverized coal, were investigated in the temperature range of 1623–1723 K with different heating time. The results indicate that the pellets could not melt well at 1623 K and 1723 K, and the iron nugget and slag can separate in a clear manner at 1673 K for 12 min. The contents of C and S in iron nugget are 2.09% and 1.62% respectively. The iron nugget can be used partly to substitute the steel scrap for EAF steelmaking. The RE2O3 content is 14.19% in the rare-earth-rich slag. Nearly all rare earth is concentrated into one phase during solidification, which is identified as cefluosil ([7(Ca, Ce, La, Nd)2·SiO4] (F, O)10). The slag was leached by hydrochloric acid and the leaching efficiency of rare earth is 98.70%. After being filtered, the solution can be used to extract rare earth and the leached residue will be treated to recover CaF2 and ThO2.
- 著者
- Ho Yu Il Seop Choi Kyung-Lyong Han Jae Yeon Choi Goobong Chung Jinho Suh
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.12, pp.2609-2617, 2015-12-15 (Released:2015-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 25
Handling heavy-load materials is the most common operation in iron and steel making processes. There are numerous operations in which workers directly deal with heavy loads without equipment. The refractory constructions in the converter and AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) furnaces are representative examples. Transferring thousands of heavy materials repeatedly over a long period of time can not only cause musculoskeletal diseases, which occur 70% on the waist and 30% on other parts such as wrists, elbows, shoulders, etc. but also contain latent risks of safety accidents.In this paper, a novel stand-alone powered exoskeleton robot suit was developed for assisting the strength of waist, lower back, and hip joints that are physically vulnerable during handling heavy-load materials. The simple robot structure reduces the frame weight as well enabling easy motion control. The robot is capable of moving freely due to the stand-alone actuators. The developed novel clutch system generates a smooth transition against various working conditions. This technology significantly diminishes the physical fatigue of operators and will subsequently prevent further muscular skeletal disorders as well as safety accidents.
- 著者
- Shigeru Suzuki Koji Hotta Eui Pyo Kwon Shun Fujieda Kozo Shinoda Masayoshi Kumagai Kentaro Kajiwara Masugu Sato Shigeo Sato
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.10, pp.2158-2165, 2015-10-15 (Released:2015-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Electron backscatter diffraction was used to observe the microstructure of an austenitic high-manganese twinning-induced plasticity steel and investigate the crystal orientation of grains in this steel. The results showed that mechanical twins are formed in a grain with a high Schmid factor during the tensile test. The orientation data obtained were used to estimate the anisotropic elasticity of the grains in the steel. The microscopic stress and strain evolved in the microstructure of the steel unloaded after plastic deformation were estimated using finite element method simulation in which the elastic anisotropy of the steel was taken into account. The simulation indicated that the evolution of microscopic stress and strain in the microstructure is considerably influenced by the crystal orientation of the grains. Furthermore, white X-ray diffraction with microbeam synchrotron radiation was used to characterize the evolution of microscopic stress and strain in the grains of the steel. The stress analysis during white X-ray diffraction indicated the formation of residual microscopic stress after tensile deformation, which was found to be distributed heterogeneously in the steel. It was also shown that the direction of the maximum principal stresses at different points in the microstructure under loading were mostly oriented along the tensile direction. These results are fairly consistent with the results obtained by the simulation, although absolute values of the real principal stresses may be influenced by the heterogeneously evolved strain and the several assumptions used in the simulation.
1 0 0 0 OA Modeling of CCT Diagrams and Ferrite Grain Size Prediction in Low Carbon Nb–Mo Microalloyed Steels
- 著者
- Nerea Isasti Pedro Manuel García-Riesco Denis Jorge-Badiola Mitra Taheri Beatriz López Pello Uranga
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.9, pp.1963-1972, 2015-09-15 (Released:2015-09-29)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 6
In this paper a multi-linear regression analysis is developed to predict continuous cooling (CCT) diagrams in low carbon Nb and Nb–Mo microalloyed steels. The inputs to the analysis include the weight percentage of alloying elements, the prior austenite grain size, the retained strain and the cooling rate. To develop the model, 11 steels with different combinations of Nb and Mo were considered. In some cases, the resulting equations have been validated with external data from the literature. Additionally, the model was also employed to predict hardness and ferrite grain size with the aim of providing a tool to link microstructural features with mechanical property predictions. Both Nb and Mo additions promote a reduction of ferrite and bainite start temperatures, where the effect is more pronounced for Nb in the bainitic region. Both microalloying elements contribute to an increase in hardness and a refinement of the microstructure.
1 0 0 0 OA Residual Stress Analysis of Cold-drawn Pearlite Steel Wire Using White Synchrotron Radiation
- 著者
- Masayoshi Kumagai Shigeo Sato Shigeru Suzuki Muneyuki Imafuku Hitoshi Tashiro Shin-ichi Ohya
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.7, pp.1489-1495, 2015-07-15 (Released:2015-07-30)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
Measurement of the residual stresses in cold-drawn pearlitic steel wire was conducted using an energy dispersive X-ray diffraction technique. The residual stresses of the ferrite and cementite phases were determined for different crystal orientations and large residual stresses were found to exist in the cold-drawn pearlitic steel wire. The residual stresses in the ferrite phase were compressive in the axial direction but nearly zero in the hoop and radial directions. In addition, the residual stresses of the reflection indices for the ferrite phase were similar to one another. For the cementite phase, while tensile residual stress existed in the axial direction, compressive residual stress existed in the hoop and radial directions. These stresses in the ferrite phase in the axial direction and cementite phase in all directions decreased along the radial positions. A residual stress state model was proposed on the basis of the aligned lamellar structure along the drawing direction; the model explains the effect of the lamellar direction on residual stress. Reanalysis of the wire sample using the proposed model provided residual strains and stresses in the lamellar direction that were different from the average values estimated using the simple stress analysis method.
- 著者
- Cho Hyun-Jin Jung Sung-Hoon Kim Sang-Joon Lee Hae-Geon Kang Youn-Bae
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.11, pp.2559-2568, 2014
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Decarburization of Fe–C droplet was investigated by fluid dynamics numerical simulation based on physical properties under gas phase mass transfer controlled regime. Fluid flow and species concentration fields around the droplet implementing a reaction of carbon with oxidant gas at the interface were calculated by a commercial CFD package which solves a set of transport equations. Overall decarburization rate of the molten Fe–C droplet was obtained by the simulation, and it was additionally validated by the present authors' own experiment using gas-liquid drop reaction in a levitation melting equipment. It was observed by the simulation that decarburization rate on the surface of a droplet was not homogeneous due to inhomogeneous gas distribution around the droplet. A new concept of local mass transfer coefficient ratio was proposed in the present study as a ratio of <i>effective</i> local mass transfer coefficient at a specific site over average mass transfer coefficient, as a function of <i>θ</i> (angle between direction of gas flow and direction to reaction site on the droplet surface from the droplet center) and dimensionless numbers regarding fluid flow:<br><img align="middle" src="./Graphics/abst-54_2559_eq_1.jpg"><br>Furthermore, effect of distance between two droplets was investigated by the present numerical model for decarburization of multiple droplets. The local mass transfer coefficient was found to have a significant impact on decarburization rate of a droplet when the other droplet locates very close. Relation between decarburization rate of two droplets and distance between them were analyzed.
1 0 0 0 OA Intermediate Temperature CO2 Electrolysis by Using La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O3 Oxide Ion Conductor
- 著者
- Shijing Wang Tatsumi Ishihara
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.2, pp.381-386, 2015-02-15 (Released:2015-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1 4
Solid oxide electrolysis cell for electrolysis of CO2 to CO was studied with the cell using LaGaO3-based electrolyte at the intermediate temperature (i.e. 973–1173 K). Various metal additives to Ni were examined for cathode to CO2 reduction and it was fund that Ni added with Fe shows high activity and the current density of 1.5 A/cm2 was achieved at 1.6 V and 1073 K on Ni–Fe (9:1) cathode. Improved electrolysis activity was explained by the expanded reaction site which may be assigned the fine particle of Ni. Furthermore, effects of additives to Ni cathode were studied and it was found that the electrolysis current could be much improved by addition of Fe to Ni. Effects of oxide ion conductor mixing with Ni–Fe were further studied and it was found that mixing La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.9Mn0.1O3 with Ni–Fe bimetal is the most effective for achieving high electrolysis current of CO2 of 2.07 A/cm2 at 1.6 V and 1073 K.
- 著者
- Hirokazu Tsukahara Takuro Masumura Toshihiro Tsuchiyama Setsuo Takaki Koichi Nakashima Kazukuni Hase Shigeru Endo
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本鉄鋼協会
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.1, pp.312-318, 2015-01-15 (Released:2015-02-06)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 3
The range of chemical compositions that can obtain an austenitic single structure was defined for medium-manganese (Mn) carbon (C) steels. Among the potential compositions, Fe-5%Mn-4%Cr-(0.8–1.4)%C (mass%) was selected as the optimized composition range to form a stable austenitic structure. The tensile properties and deformation substructure were investigated in the austenitic steels having this composition. The work hardening behavior of the steels varied depending on the carbon content, which was closely related to the deformation microstructure. In the 0.8%C steel, both a deformation-induced martensitic phase as well as the formation of deformation twins generated a high work hardening until fracture. With an increasing carbon content, which increased the stacking fault energy (SFE), the deformation tended to shift towards dislocation slipping, resulting in a lower work hardening rate. This trend appears similar to conventional twinning-induced plasticity steel where the work hardening behavior is tied to the SFE.
- 著者
- Nakajima Kenichi Nansai Keisuke Matsubae Kazuyo Nagasaka Tetsuya
- 出版者
- The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan
- 雑誌
- ISIJ International (ISSN:09151559)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.11, pp.2657-2662, 2014
- 被引用文献数
- 8
Recently, sustainable management of resources has become an increasingly recognized issue. Accordingly, interest in understanding the relationship between natural resources consumption and the global product supply chain has also been increasing. Material flow analysis (MFA) is a useful tool for understanding resource consumption and material cycles in national economies. However, detailed MFA studies of the materials embedded in foreign trade flows are rare.<br>This study identified global trade flow of iron embedded in bilateral trade between 231 countries by multiplying the trade volume of the commodities in the BACI (Base pour l'Analyse du Commerce International) database and the iron content of each commodity. We focused on the cases of Japan, China, and United States, and estimated the mass of iron embedded in imports and export. The identified total flows of iron embedded in international trade were 1.15 × 10<sup>9</sup> t-Fe with 35.2% of the flows concentrated in three countries, Japan, China and United States, which are major crude steel production countries.