2 0 0 0 OA 核はどのようにして細胞の中心を見つけるのか?
- 著者
- 谷本 博一 木村 健二 木村 暁
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.5, pp.271-274, 2016 (Released:2016-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
The various molecules and organelles in a eukaryotic cell are suitably positioned within the cell to carry out their functions at the appropriate time. This intracellular positioning is accomplished through interplay among the active transport mechanisms, intracellular fluctuations, and physical properties of the components inside the cell. Here, we review the recent advances in research on how the nucleus moves toward, and maintains its position at, the geometrical center of the cell. This question has attracted researchers from various fields, and is a good subject for interdisciplinary collaboration.
2 0 0 0 OA Bacteroidia綱細菌の付着装置・V型線毛の形成機構
- 著者
- 柴田 敏史
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.32-35, 2022 (Released:2022-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 19
ヒトの口腔内,腸内細菌叢の主要構成細菌であるBacteroidia綱細菌はヒトの健康に大きく関わっている.これらが持つ付着装置の線毛はピリンがリポタンパク質として菌体表面に輸送され,プロテアーゼ依存性のストランド交換反応によって根本から伸長するユニークな形成機構を持ったV型線毛である.
2 0 0 0 OA エントロピーからはじめる熱力学
- 著者
- 冨樫 祐一
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.4, pp.246-246, 2016 (Released:2016-07-25)
2 0 0 0 OA ヘキサンジオールは細胞内のクロマチンを凝縮させる
- 著者
- 伊藤 優志 井手 聖 前島 一博
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.6, pp.385-388, 2021 (Released:2021-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 10
2 0 0 0 OA タンパク質の安定性 水溶性タンパク質と膜タンパク質の比較
- 著者
- 美宅 成樹
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.28, no.6, pp.317-322, 1988-11-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 15
This paper describes the analysis of amino acid sequence as well as the denaturation experiment of soluble globular and membrane proteins. The two kinds of proteins were discriminated by amino acid sequence almost completely, using only the hydrophobicity. The denaturation measurements lead to the conclusion that the hydrophobic interaction determines the form of proteins (i.e. globular or membrane proteins), while the polar interactions play major role in the tertiary structure formation.
2 0 0 0 OA 古細菌の進化的位置と真核生物の起源
- 著者
- 岩部 直之
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.2, pp.91-98, 1991-01-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
All extant organisms are thought to be classified into three primary kingdoms, eubacteria, eukaryotes, and archaebacteria. Based on the analyses of a pair of duplicated genes, elongation factors EF-Tu/l α and EF-G/2, and catalytic and noncatalytic subunits of ATPase (ATPsynthase), archaebacteria are more closely related to eukaryotes than eubacteria. While this relatedness is certified, phylogenetic relationship among several major groups of archaebacteria (extreme thermophiles, extreme halophiles, and methanogens) and eukaryotes is still unsettled because the phylOgenetic tree topologies among them vary with the genes analysed. The ambiguous situation suggests that archaebacterial major groups and eukaryotes were diverged during very short period in the long course of evolution.
2 0 0 0 OA 海外だより ~欧米の研究気質比較~
- 著者
- 浅利 宏紀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.5, pp.347-348, 2021 (Released:2021-09-28)
2 0 0 0 OA リレーエッセイ:私が影響を受けた論文(12) 生物学の引力と斥力
- 著者
- 木寺 詔紀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.6, pp.419-420, 2021 (Released:2021-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 4
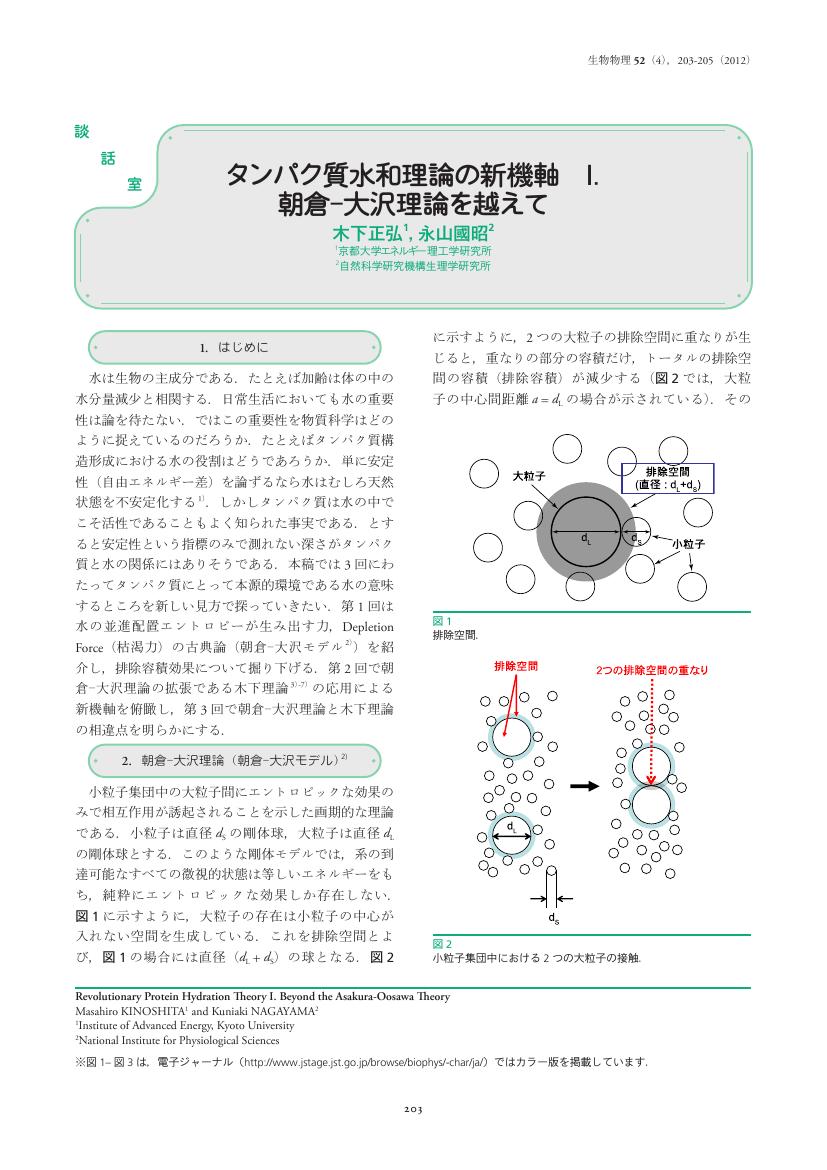
2 0 0 0 OA タンパク質水和理論の新機軸 I.朝倉―大沢理論を越えて
- 著者
- 木下 正弘 永山 國昭
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.4, pp.203-205, 2012 (Released:2012-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 8
2 0 0 0 OA アブラナ科植物の自家不和合性における自他識別機構の構造生物学
- 著者
- 村瀬 浩司 高山 誠司
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.5, pp.321-323, 2021 (Released:2021-09-28)
- 参考文献数
- 8
2 0 0 0 OA 若手の会だより ~九州支部での活動について~
- 著者
- 岩下 皇藏
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.5, pp.345-346, 2021 (Released:2021-09-28)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 1
2 0 0 0 OA 大沢さん追悼:50年先への千里眼(5) 生きている系の統計力学
- 著者
- 岡田 康志
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.3, pp.188-189, 2020 (Released:2020-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 5
2 0 0 0 OA 多重配列アラインメント―最近のソフトウェアについて
- 著者
- 加藤 和貴 三沢 計治
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.6, pp.312-317, 2006 (Released:2006-12-07)
- 参考文献数
- 25
Multiple sequence alignment is an important tool for computational analysis of nucleotide or amino acid sequences. It is also a challenging combinatorial optimization problem in computer science. As a large amount of sequence data is becoming available from genome and other large-scale sequencing projects, efficiency, as well as accuracy, is currently required for a multiple sequence alignment program. Several new programs are being developed aiming at improving both efficiency and accuracy. We overview the algorithms and performances of new programs including that by ourselves.
2 0 0 0 OA 交通流と翻訳過程
- 著者
- 御手洗 菜美子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.1, pp.015-019, 2013 (Released:2013-01-29)
- 参考文献数
- 20
Messenger RNAs (mRNA), that code sequences of amino acids by using triplets of nucleotides (codons), are translated by multiple ribosomes. Usually more than one codon corresponds to an amino acid. The ribosome speed is known to dependent on the codon, thus there is a room to keep an amino acid sequence (protein) and change the ribosome speed. We model the ribosome traffic with codon-dependent rate estimated for E. coli and show that some wild type codon sequences can regulate “traffic jam” by placing slow codons at the begging of the mRNA. We discuss possible roles of slow codons in translation process.
2 0 0 0 OA 1分子観察から見えてきた大腸菌ヘリカーゼUvrDのDNA巻き戻し機能と多量体形成
- 著者
- 横田 浩章
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.4, pp.227-231, 2021 (Released:2021-07-30)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The Escherichia coli UvrD protein is a superfamily 1, non-hexameric DNA helicase that plays a crucial role in repair mechanisms. Previous studies suggested that wild-type UvrD has optimal activity in its oligomeric form. Nevertheless, a conflicting monomer model was proposed using a UvrD mutant lacking the C-terminal 40 amino acids (UvrDΔ40C). Here, single-molecule direct visualization of UvrDΔ40C revealed that two or three UvrDΔ40C molecules were simultaneously involved in DNA unwinding, presumably in an oligomeric form, similar to that with wild-type UvrD. Thus, single-molecule direct visualization of nucleic acid-binding proteins provides quantitative and kinetic information to address their fundamental mechanisms.
2 0 0 0 OA 遺伝子はどのように進化するか
- 著者
- 宮田 隆
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.24, no.2, pp.82-90, 1984-03-25 (Released:2009-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 46
Some possible mechanisms of gene evolution were examined from the aspect of dynamical mode associated with drastic changes of DNA and genetic information. There is growing evidence that eukaryotic multigene families often underwent exchange of genetic information between members of each family during evolution by mechanism of either gene conversion or double unequal crossing-overs. A detail examination of many examples for such genetic information exchange reported to date revealed that they are classified into four categories. Some evolutionary implications for such genetic process were also discussed. Alternation of intron splicing mode associated with conversion of exon into intron was emphasized as a mechanism responsible for the emergence of a new gene which differs radically in structure and function from its ancestor. Gene shuffling and joining of adjacent genes by an intron would be a mechanism that is important for generating a variety of genes having diverse functions in evolution. Two major steps of evolution through such process was suggested to have occurred since the early evolution of organisms. A novel mechanism for the evolution of viral multifunctional genes was proposed; by integrating a foreign piece of DNA carrying a certain function, viruses could acquire a new function.
2 0 0 0 OA エピジェネティクス制御におけるメチル化DNAの認識
- 著者
- 有吉 眞理子 白川 昌宏
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.3, pp.124-127, 2011 (Released:2011-05-25)
- 参考文献数
- 19
DNA methylation is a heritable epigenetic mark that enables the tissue-specific gene expression accompanied by modulation of chromatin structure. Interpretation and maintenance of DNA methylation pattern on genome are crucial for a wide range of biological processes such as genomic imprinting, embryogenesis and carcinogenesis. Recent crystallographic studies of methylated DNA binding proteins have provided a new insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying epigenetic regulation. This review focuses on a structure basis for strict recognition of the methylation status of the CpG site by DNA binding domains in MBD family proteins and UHRF1.
2 0 0 0 OA アクチン特異的ADPリボシル化毒素の構造と機能
- 著者
- 津下 英明
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.4, pp.168-173, 2003 (Released:2003-07-23)
The family of mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase includes not only bacterial toxins but also mammalian enzymes. Recently, crystal structures of arginine-specific ADP-ribosyltransferase have been revealed, giving a better understanding of type IV toxin. They are VIP2 from Bacillus and Ia from Clostridium perfringens. VIP2 and Ia ADP-ribosylate the Arg177 of actin. They consist of topologically similar N- and C-domains, which have not been expected from the amino acid sequence. C-domain is an enzymatic domain. N-domain interacts with VIP1 and Ib, respectively. C-domain structures were basically the same but the surface charge of N-domain was found significantly different between VIP2 and Ia. Rat ART2.2 and rho-targeted C3 toxin(asparagine-specific)consist of only one domain and the structure is similar to the C-domain of Ia. We summarize the crystal structure and the reaction mechanism of Ia.
2 0 0 0 OA ゼブラフィッシュ実験ガイド
- 著者
- 坂内 博子
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.110_1, 2021 (Released:2021-03-25)
2 0 0 0 OA 生体リズムの頑健性と可塑性
- 著者
- 畠山 哲央 金子 邦彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本生物物理学会
- 雑誌
- 生物物理 (ISSN:05824052)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.4, pp.186-190, 2017 (Released:2017-07-28)
- 参考文献数
- 20
Robustness and plasticity are important characteristics common to a variety of biological systems and have attracted much attention not only from biologists but also from physicists interested in biosystems. Whereas robustness concerns insensitivity to perturbations against external changes, plasticity concerns changeability upon external inputs. How these two properties are compatible with each other is an important question to be addressed. Recently we have uncovered universal reciprocity relationship between the robustness of period and plasticity of phase in biochemical oscillators such as circadian clocks. We review this relationship and discuss its theoretical origin and biological relevance.