1 0 0 0 OA Analysis and stabilizing design of self-excited oscillation in a loading cam using a wedge effect
- 著者
- Katsuhiko SANDO Takeshi YAMAMOTO Kenji SAWADA Tomoyuki TANIGUCHI Nobuyuki SOWA Hiroki MORI Takahiro KONDO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Mechanical Engineering Journal (ISSN:21879745)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, no.2, pp.20-00497, 2021 (Released:2021-04-15)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 1
This paper describes a design method of a friction reducer device using a loading cam to suppress unstable vibration. Nonlinear simulation and energy analysis of numerical solutions demonstrates that destabilization is caused by the large phase difference between the slipping velocity in the translation direction and that in the rotation direction. It was found that similarly unstable vibration occurs in various structures using wedge rollers with translational and rotational motion. The analytical equation could be simplified by focusing on the motion factor that affects the slip velocity of the power transmission surface, which is the factor of vibration. Consequently, the design method for suppressing vibration could be expressed by a mathematical formula. This equation is validated by using the results of experiments conducted in the previous work of the current authors. Furthermore, from this equation, we proposed that vibration could be suppressed by the parameter balance of the power transmission device without using damping. The power transmission surface slips when a quick torque is input and damping is used. The proposed design can handle a quick torque response and reduce the weight of the reducer. Specifically, the shape of the wedge roller is made lighter, so that the moment of inertia of the roller is not lowered, or the wedge roller is set as a small roller.
- 著者
- Hiroaki T.-KANEKIYO Shinjiro AGATA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing (ISSN:18813054)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.1, pp.JAMDSM0008, 2019 (Released:2019-01-23)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 2
An inventory management problem is theoretically discussed for a factory having effects of lead times in replenishing the inventory, where it stocks materials used for its products. It is assumed that the factory can dynamically control the size of ordering materials. By applying the stochastic control theory, the optimal control of the ordering size is derived, in which the expected total cost up to an expiration time is minimized. First, a new stochastic model is constructed for describing an inventory fluctuation of the factory by the use of a non-diffusive stochastic differential equation, where an analytic time is introduced so that the inventory process can be a Markov process even though it is affected by lead times. Next, an optimal control is formulated by introducing an evaluation function quantifying total costs. Based upon them, the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation is derived, whose solution gives the optimal control. Finally, the optimal control is quantitatively examined through numerical solutions of the HJB equation. Numerical results indicate that if time up to an expiration time is short then the optimal control is affected by it, otherwise, the optimal control does not depend on it.
1 0 0 0 OA Unified wall boundary treatment for fluid-rigid body strong coupling in a particle method
- 著者
- Shugo MIYAMOTO Seiichi KOSHIZUKA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Mechanical Engineering Journal (ISSN:21879745)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, no.5, pp.23-00127, 2023 (Released:2023-10-15)
- 参考文献数
- 18
Computational fluid dynamics has been widely used in the design and analysis of various fluid systems. The proper treatment of boundary conditions is crucial for the accurate simulation of fluid flow. However, in particle methods, such as smoothed particle hydrodynamics method and moving particle semi-implicit method, the treatment of boundary conditions has been a challenging problem. In this paper, starting from the incompressibility condition, we present a new theory for the unified treatment of both rigid bodies and wall boundaries, which allows the strong coupling of rigid bodies and incompressible fluids. Because the boundary models are based on signed distance functions and do not use particles, these models can avoid several problems, such as resolution dependence of particle representations, and unavoidable unevenness of surfaces. We also provide a way to efficiently handle rigid-body boundaries and wall boundaries without particles by finding the fundamental boundary weight function that does not change with time. Several numerical examples are presented to demonstrate the capability of our models and to compare them with theoretical and experimental results.
- 著者
- Jyun-Rong ZHUANG Hayato NAGAYOSHI Hirotoshi KONDO Keiichi MURAMATSU Keiichi WATANUKI Eiichiro TANAKA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing (ISSN:18813054)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, no.6, pp.JAMDSM0089, 2017 (Released:2017-12-22)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 3 6
Wearable assistive devices have been receiving considerable attention in academic circles. To make these devices efficient, we need additional research on the service lives of the mechanical elements used in these devices. The wearers of these devices frequently encounter unexpected movements that lead to motor failure in the devices. The purpose of this study is to develop an overload protection mechanism using a torque limiter, which can eliminate the overload torque delivered in the reverse direction to effectively prevent the device from breaking and ensure the safety of the user. To improve the service life of assistive walking devices, we designed a sandwich mechanism for the final gear of the servo motor. We made the material from rubber and configured it between a pair of circular plates. The surface tractive force delivered the required torque. When the surface load exceeded the maximum friction force, the circular plates slipped and protected the device. In this paper, we implement a torque limiter and prove its durability by performing experiments using two circular plate designs, one with grooves type and another without grooves type. We also use various materials to assess the applicability of the assistive walking device. The findings indicate that the with grooves type gives better torque performance; it achieves the same rated torque as the servo motor. Thus, this study recommends that with grooves type is particularly suitable for the elderly who require high assistive power. On the other hand, without grooves type is suitable for users who employ the device for extended periods because this type has an excellent service life. Our experiment proves that the torque limiter that we developed can withstand the load torque over 300 times for situations involving the loss of balance such as stumbling and slipping. Finally, we experimentally validate the improvement of walking performance by using this torque limiter.
- 著者
- Akisue KURAMOTO Motomu NAKASHIMA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Biomechanical Science and Engineering (ISSN:18809863)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22-00469, (Released:2023-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
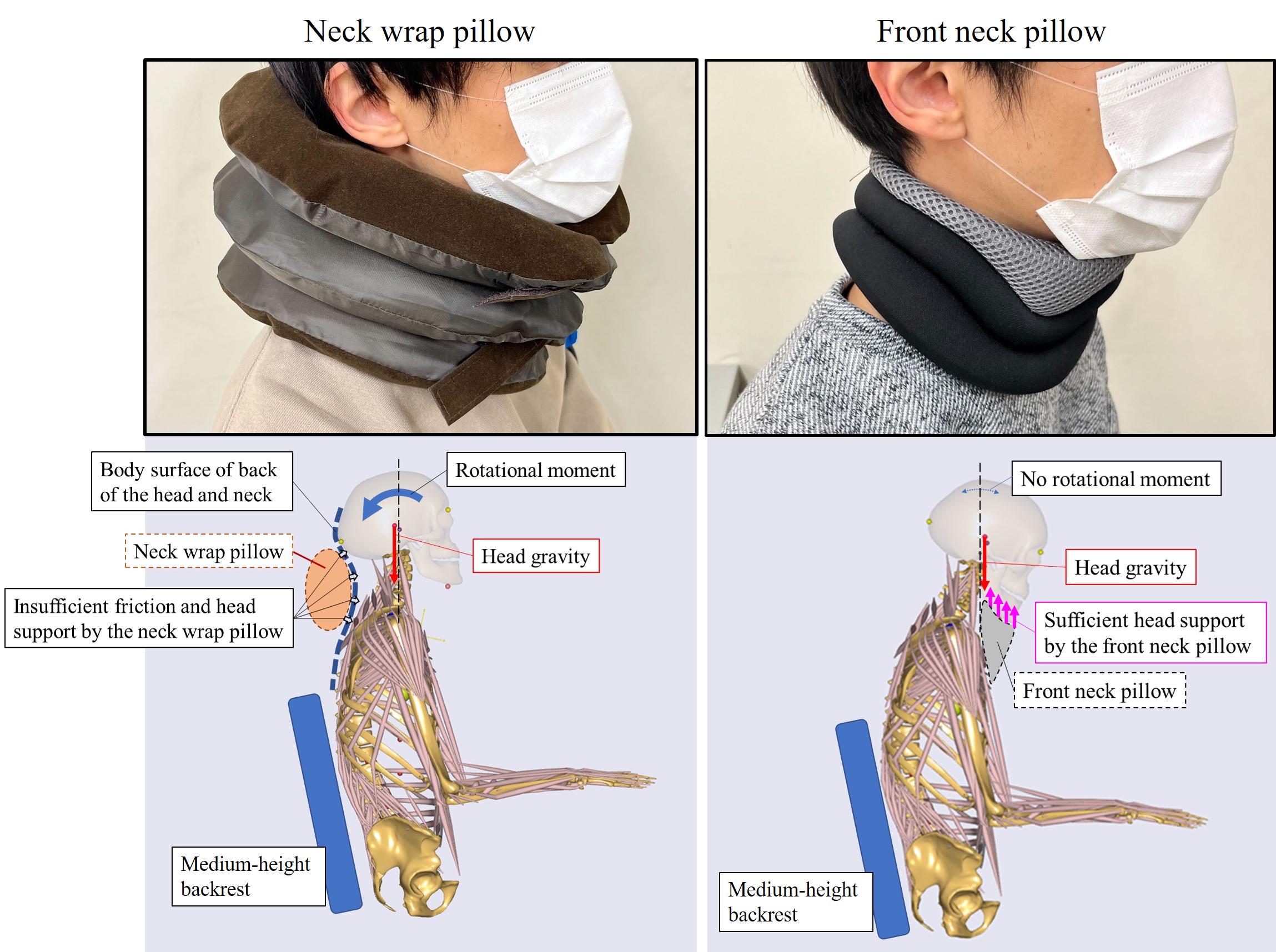
This study aims to confirm the effects of a neck pillow on the postural stability of the head and neck and the variance of center of mass in a sitting position. Experiments were conducted on keeping a sitting posture at rest with and without the use of two types of neck pillows; the neck wrap pillow and the front neck pillow. During experiments, whole body posture was recorded by a motion capture system. Differences in head-and-neck postural stability and center of mass variance in the resting sitting position were statistically compared among the neck pillow conditions. As a result, it was confirmed that the front neck pillow increases the postural stability of the head and neck in a resting sitting position and reduces the variation of the center of mass.
- 著者
- Ankit A. Ravankar Abhijeet Ravankar Takanori Emaru Yukinori Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会講演概要集 (ISSN:24243124)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.1P1-D16, 2020 (Released:2020-11-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
In this paper, we present a path planning approach for mobile robots using semantic maps. Semantic mapping is qualitative description of the robot’s surroundings, that aims to augment the navigation capabilities and task planning for robots operating in human-robot scenarios. It presents a knowledge layer over an existing map representation such that the knowledge information can be used by robots to learn tasks in a human friendly way. We present a planning scheme using such semantic maps, in order to improve the goal reaching capabilities of the robot in a task-planning scenario. Our method can integrates existing path planners into the topological graph planner that produces faster goal searches.
1 0 0 0 OA Long-term two-dimensional analysis of the flow field around a hovering flapping flat-plate wing
- 著者
- Tomoki YAMAZAKI Yoshiaki ABE Tomonaga OKABE
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (ISSN:18805558)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.2, pp.JFST0026, 2023 (Released:2023-06-28)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A flapping wing is considered as one of the most effective aerodynamic systems for micro air vehicles (MAVs). Many numerical studies have been attempted to investigate the flow field around a flapping wing; nevertheless, the long-term flow characteristics, which can cause a non-negligible effect on long-term hovering operations of MAVs have not been adequately clarified owing to the high computational cost involved. This study numerically investigates the long-term flow characteristics around a flapping flat-plate wing during hovering flight at a chord-based Reynolds number of 2.5 × 104. Based on the finite-volume method with the arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) method, two-dimensional laminar flow analyses were performed for 40 periods of flapping motions with stroke inversion angles of β = 30°, 45°, and 60°. The results showed that the lift coefficient CL was not completely periodic despite the periodic motion. To identify the CL characteristics for each β case, a half-stroke-period-based phase-average of CL was calculated over different time segments. Then, the phase-averaged CL using the fifth to 30th periods sufficiently provided converged aerodynamic characteristics: the β = 30° and 45° cases had a single peak of CL, whilst the β = 60° had double peaks; the second peak taking the maximum CL in the β = 60° case was delayed compared to others. The results of this study provide a guideline for the number of periods required in the numerical estimation of the CL characteristics and associated flow fields around flapping-type MAVs, which contributes to their further improvement of them.
- 著者
- Haoran GENG Masafumi MIYATAKE Qingyuan WANG Pengfei SUN Bo JIN
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Mechanical Engineering Journal (ISSN:21879745)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22-00360, (Released:2023-05-23)
- 参考文献数
- 16
The timetable of urban rail greatly affects its daily energy consumption. To improve the utilization of renewable energy between trains using timetabling has become an effective way to reduce energy consumption. Previous studies ignore or simplify the modelling of traction power supply network, which failed to accurately describe the flow of energy between trains through the power network. This paper proposed an optimisation method of energy efficiency timetabling considering the power flow of traction power supply network. First, an urban rail transit DC traction network model is established, and the current-vector iterative method is used to characterize the energy consumption. Then, a train timetable optimisation model is proposed to minimize the total energy consumption of the traction network system by adjusting the dwell time and section running time. The genetic algorithm is used to solve the optimisation problem. Finally, simulation result shows that the proposed method can accurately characterize the energy flow and effectively reduce the total energy consumption of the urban rail transit.
- 著者
- Yasuki Nakakura Kosuke Hayakawa
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- The Proceedings of International Symposium on Seed-up and Service Technology for Railway and Maglev Systems : STECH (ISSN:24243167)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp._356566-1_-_356566-4_, 2009-06-15 (Released:2017-06-19)
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
The Series N700 is the first Shinkansen rolling stock to employ a body inclining system, which allows speed increases on curves while maintaining riding comfort. For use in the Tokaido Shinkansen, such a system needs to be light-weight and possess a reliable means to provide high precision position data. Reliability is a crucial factor when considering that the Tokaido Shinkansen operates a maximum of 13 train-sets per hour. In order to meet these requirements, the Series N700 adopts a simple and light weight air-spring based body inclining mechanism, which combines the new automatic train control (ATC) technology capable of providing reliable high-precision position data, and control transmission technology that simultaneously transmits position data digitally to all the cars in a 16 car trainset.
- 著者
- Tatsuhiko IMAI Kenya KONDO Yasumasa SUZUKI Yuya MIKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (ISSN:18805558)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.1, pp.JFST0022, 2023 (Released:2023-04-26)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 1
In this study, oil film interferometry (OFI) was applied to the flow around the suction surface of a two-dimensional airfoil under high lift conditions to measure the wall shear stress. However, existing OFI methods have difficulty measuring the wall shear stress in images affected by reverse and secondary flows. Therefore, the particle image velocimetry (PIV) method was applied to the Fizeau fringe images to determine the direction of progress from the calculated velocity vector. An airfoil with a wing section of NACA0012 was used, the Reynolds number was set to 8 × 104, and angle of attack was set at 11°. A direct spatial domain correlation was used for the PIV analysis method. At x/c = 0.75 to 0.83, the measured local skin friction coefficient was good agreeing with the large eddy simulation calculated results reported by Miyazawa et al. (Transaction of the JSME, Series B, Vol.72, No.721 (2006)). However, a large difference between the measured and calculated local skin friction coefficients occurred at x/c = 0.17 near the re-attachment point. The wall shear stress is determined by calculating the dominant frequencies using fast Fourier transform (FFT) analysis from the matrix data obtained by mean of the pixel intensities in the analysis region in the span direction. If the Fizeau fringe image is uniform in the span direction, the program can calculate the periodic waves. When the Fizeau fringes are tilted to the analysis range, the FFT analysis of the obtained matrix data results in an error because the dominant frequency cannot be calculated. Therefore, velocity vectors were detected near the re-attachment point by adapting PIV to the Fizeau fringe images. The local skin friction coefficients were calculated by OFI measurements with the Fizeau fringe images that were rotated by the angle of the velocity vector determined by PIV.
- 著者
- Kosuke SUZUKI Masaya KOUJI Masato YOSHINO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (ISSN:18805558)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.1, pp.JFST0011, 2023 (Released:2023-04-26)
- 参考文献数
- 24
We conducted measurements of a butterfly’s motion in forward flight and numerical simulations using a computational model reflecting its motion. We measured the motion of a cabbage white butterfly (Pieris rapae), and then we constructed a computational model composed of a thorax, an abdomen, and four wings (i.e., left and right wings with fore and hind parts). Furthermore, we calculated the flow field and aerodynamic force and torque generated by the butterfly model using the immersed boundary–lattice Boltzmann method. In this simulation, we considered two types of periodic motions corresponding to slightly-descending and ascending forward flights. As a result, we found that the wing-tip and leading-edge vortices are formed on the wings and then released backward and downward in both flights. The major difference between the two flights is the flapping amplitude, indicating that the butterfly changes the flapping amplitude for each period and increases it to ascend. In addition, we considered a chimera model whose motion is based on the slightly-descending flight but partly given by the ascending flight. As a result, we found that the pitching angle and the angle of attack determine the traveling direction, but simply changing these angles does not achieve the ascending flight due to insufficient lift force. Thus, the butterfly should adjust the flapping and lead–lag angles in response to the pitching angle and the angle of attack to change the flight mode.
- 著者
- Mitsuru JINDAI Shunsuke OTA Toshiyuki YASUDA Tohru SASAKI
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing (ISSN:18813054)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.16, no.1, pp.JAMDSM0016, 2022 (Released:2022-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 13
Humans establish embodied interactions, such as bows and handshakes, when they first greet one another and display a feeling of rapport. It is believed that humans construct a relationship that is emotionally acceptable to each other by the synchronization of their embodied rhythms through their embodied interactions. Hug behaviors are expected to synchronize embodied rhythms effectively as they are an embodied interaction where whole bodies are in contact with each other. In hug behaviors between humans and robots, the same efficiency is expected. Furthermore, when a human approaches a robot, the robot should generate a hug request motion to promote embodied interactions. Therefore, in this study, a hug robot system for the generation of hug behavior with approaching humans is developed. The hug robot system that employs a hug behavior request model generates request motion of a hug when a human approaches the robot. Furthermore, a switching hug control was developed by combining the proposed hug behavior request model with the hug behavior response model. In the switching hug control, when an approaching human requests a hug, the robot generates a response motion. However, if the approaching human does not request a hug, the robot will request one to the human. Then, in hug behaviors between a human and a robot, the motion characteristics of the robot that are preferred by majority of research participants are analyzed using the developed hug robot system.
- 著者
- Jens Achenbach Marcus Fischer Bastian Lehrheuer Marco Guenther Stefan Pischinger
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- The international symposium on diagnostics and modeling of combustion in internal combustion engines (ISSN:24242918)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.A4-1, 2022 (Released:2023-01-25)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
High efficiency gasoline combustion engines with up to 50 % indicated efficiency are the target of current research work. To reach this goal, it’s essential to reduce all the combustion engine losses as much as possible. One major loss, with about 30 % of the total fuel energy, is the wall heat transfer loss. To reduce this loss, one solution is a temperature swing insulation, which is characterized by a low thermal conductivity and at the same time a low volumetric heat capacity. In order to analyze the thermal efficiency potential of different insulation materials, a thermal insulation model for one-dimensional engine process simulations has been developed and is presented in this paper. The insulation is discretized by a thermal node model and is coupled to an engine process simulation using the simulation tool GT-Power. The heat transfer and temperature swing behavior of the thermal insulation model is validated against 3D-CFD engine cycle simulations. A predictive detailed chemistry combustion model is used in 3D-CFD simulations to evaluate the influence of thermal insulations on the knocking tendency. Two different thermal insulation materials are investigated using the developed simulation model. One is yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as a common thermal sprayed coating. The second material is produced by an electrolytic oxidation of the piston surface (anodizing). With thermal piston insulation, there is only a small increase in thermal efficiency in the range of 0.2 % to 0.6 % possible with both materials, whereby the potential increases at low speeds and medium loads. The reason can be found in the relative heat losses, which increases with a constant center of combustion and increasing load. An efficiency loss analysis shows that the exhaust losses increase by about two third of the reduced heat losses. Due to its lower volumetric heat capacity and similar heat conductivity, the anodized piston surface shows a thermal efficiency advantage compared to YSZ. The simulation results are finally validated by measurements conducted with a single-cylinder research engine for an YSZ coated piston surface as well as a hard anodized piston surface.
- 著者
- Shota YABUI Takenori ATSUMI Tsuyoshi INOUE
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing (ISSN:18813054)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.13, no.4, pp.JAMDSM0078, 2019 (Released:2019-11-07)
- 参考文献数
- 28
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
To increase recording density, a head positioning control system of a hard disk drive (HDD) has to compensate for vibration due to mechanical resonances of the system. In this study, a novel scheme of an adaptive feedforward cancellation (AFC) is proposed to compensate for the vibration due to the mechanical resonances. Compared to a notch filter, which is commonly used to compensate for the vibration, the proposed AFC has the advantage of estimating the amplitude of the vibration from the output signal. In addition, although the proposed AFC can be implemented as a discrete system, the design parameters: frequency, damping ratio, and gain can be set directly in a digital signal processor. The proposed control system was applied to a dual-stage actuator system, which is the mainstream head positioning control system of the current HDDs. The results indicate that the proposed system could compensate for the vibration due to the mechanical resonance.
- 著者
- Soichiro TAKATA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Mechanical Engineering Journal (ISSN:21879745)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.10, no.1, pp.22-00002, 2023 (Released:2023-02-15)
- 参考文献数
- 12
This paper discusses a new identification method for a linear single-degree-of-freedom system that uses a Gaussian random response and is based on the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) method. The likelihood function of the proposed method consists of the analytical solution of the Fokker–Planck equation. We have already published a paper on theoretical and numerical considerations. However, in that study, the experimental verification of the proposed identification method was not performed. Therefore, in this study, we conduct an experimental verification of the proposed identification method. First, the identification algorithm is formulated in a spring-mass-damper system subjected to white noise excitation by a moving foundation to correspond to the actual experimental setup. A preliminary experiment in terms of the excitation source is conducted using a vibration speaker. In addition, the experimental modal analysis is performed to confirm the validity of the vibratory system. The fundamental operation test of the identification method is performed using the actual experimental random response data, and a dependency survey of the number of samples is conducted. From the results, the convergence behaviors of the estimation value are observed with an increasing number of samples in the spring constant and the ratio between the diffusion coefficient and the damping constant. In addition, benchmark tests are conducted using the half–power method (HPM) based on spectral analysis and the auto-regressive method (ARM) based on time–series analysis. In the case of spring constant estimation, the behaviors of the estimation value that converge to the true value are observed in all identification methods. In the ratio between the diffusion coefficient and damping constant, the behavior of the estimation value that converges to the true value is observed only in the proposed identification method.
- 著者
- Hikaru AONO Satoshi SEKIMOTO Makoto SATO Aiko YAKENO Taku NONOMURA Kozo FUJII
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Mechanical Engineering Journal (ISSN:21879745)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.4, pp.15-00233, 2015 (Released:2015-08-15)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 23 32
Characteristics of flow fields produced by a dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator in quiescent air are numerically investigated. A time-dependent localized body-force distribution is utilized to mimic the effect of the plasma actuator with modulated bursts. The computed time-averaged and instantaneous flow fields are compared with the experimental results by using high-speed schlieren photography and particle image velocimetry. The computed flow fields are in good agreement with the experimental results when the nondimensional parameter (Dc) is within the appropriate range. With an appropriate choice of Dc, the location and size of the induced flow structures, computed with respect to the maximum flow velocity parallel to the wall, are quantitatively in agreement with the experimental results. Also considered are the effects of the burst frequency (non-dimensionalized by the chord length and the free-stream velocity of assumed separated flow control experiment) on the induced flow. The results show that changes in the burst frequency cause insignificant changes in the magnitude of the time-averaged flow parallel to the wall, but they cause significant fluctuations in the amplitude and power spectral densities of that flow.
1 0 0 0 OA A Study on Voith-Schneider-Propeller
- 著者
- Tsuneyo ANDO
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Bulletin of JSME (ISSN:00213764)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.5, pp.23-29, 1959 (Released:2008-02-15)
- 参考文献数
- 3
Study on Voith-Schneider-Propeller is made much complicated by several factors even in two-dimensional treatment. When the chord length is small, however, the propeller may be regarded as composed of blades, each individually moving along a trochoidal path relative to uniform flow (quasi-steady state, interference disregarded), with suitable correction for advance speed. The author tried to make some account on the action of the propeller as two-dimensional under above principle, taking into consideration the curvature of blade path relative to the uniform flow, as well as the azimuthal location of the steering center and here are given some numerical examples. Also an application to cyclo-gyro aircraft is referred to. It is known that for air transportation purpose, the direction of blade rotation must be chosen in conformity with what sort of airfoil is used.
- 著者
- Yuta MURAYAMA Toshiyuki NAKATA Hao LIU
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Biomechanical Science and Engineering (ISSN:18809863)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.1, pp.22-00340, 2023 (Released:2023-01-16)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Flying animals such as insects, bats, and birds have acquired the ability to achieve diverse and robust flight patterns in various natural environments. Their sophisticated morphologies, kinematics, and dynamics have motivated engineers to develop bioinspired flying robots. Particularly, the capabilities of morphing wing and tail controls in birds have received significant attention. Such controls are expected to introduce novel mechanisms to achieve flight stabilization while maintaining high maneuverability with a low energy cost. While the control of tail posture and motion is considered to exhibit a significant influence on flight performance, there have been few studies focusing on control with multiple degrees of freedom in small flying robots. In this study, we developed a bird-inspired morphing tail mechanism; a model was fabricated and investigated its aerodynamic performance through wind tunnel experiments. The results indicate that the tail attitude can be controlled effectively to enable the enhancement of aerodynamic performance in terms of mechanical efficiency and controllability. We also verified that controlling the tail attitude is redundant in the control of aerodynamic force and moment production, implying the potential capability to achieve stable flight control strategies in response to various disturbances. Therefore, our results indicate that tail-attitude-based aerodynamic control may be able to cope with the conflicting requirements of improving stability and maneuverability of flyers.
- 著者
- Sakito KOIZUMI Toshiyuki NAKATA Hao LIU
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Biomechanical Science and Engineering (ISSN:18809863)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.18, no.1, pp.22-00347, 2023 (Released:2023-01-16)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Flying insects are capable of hovering and rapid maneuver under unpredictable environments. The principal wing-beat is generated by transmitting the rhythmical contractions of power muscles to the exoskeleton and wing-base articulation. Fine-tuning of the flapping wing kinematics is achieved by deforming the articulation with tiny steering muscles. This flapping mechanism of insect flight is distinct from that of conventional man-made aerial vehicles, enabling superior flight. In this study, we propose an insect-inspired flapping mechanism, which is comprised of two different types of actuators and a flexible wing-base structure. The flapping mechanism is driven by electric motors, which modulate wing kinematics by adjusting the flexible wing-base structure using electromagnetic actuators (EMAs). First, the EMA design was optimized based on analysis of the dynamic forces and displacements to enable deformations of the wing-base structure. A prototype flapping mechanism was then constructed, and its performance was evaluated experimentally by adjusting the actuation phase of the EMAs being synchronized with flapping motions of the wing. The results indicate that the wingbeat kinematics and aerodynamic performance are noticeably sensitive to the actuation timing of EMAs and can thus be controlled by tuning the EMA actuating timing and direction. The flapping mechanism can potentially be applied as a novel means for controlling body posture of flapping-wing micro air vehicles to achieve insect-inspired stable flights in natural environments.
1 0 0 0 OA Study of reflection models of gas molecules on water adsorbed surfaces in high-speed flows
- 著者
- Naoya UENE Hideki TAKEUCHI Yasutaka HAYAMIZU Takashi TOKUMASU
- 出版者
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- 雑誌
- Journal of Fluid Science and Technology (ISSN:18805558)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.15, no.1, pp.JFST0005, 2020 (Released:2020-01-30)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1 6
We consider a Couette flow of a rarefied Ar gas with heat transfer between two wall surfaces and investigate the scattering behavior of gas molecules reflected either at a clean Pt surface or at a surface contaminated with adsorbates. Water molecules abundantly present in the atmosphere were adopted as the adsorbates. The reflection of gas molecules on the lower wall surface was simulated by Molecular Dynamics (MD) method to obtain accommodation coefficients and velocity distribution functions of gas molecules. We applied the modified reflection model of gas molecule and investigated the velocity distribution functions of the model by comparing the MD results to verify the validity. The accommodation coefficients obtained by the MD method depend on the number of adsorbed water molecules on the lower wall surface. Specifically, tangential momentum accommodation coefficient (TMAC) tended to increase and then decrease with the increase in adsorbed water molecules, but normal momentum accommodation coefficient (NMAC) tended to decrease monotonically. The velocity distribution functions of the modified reflection model approximately show the good agreement with the MD calculation but the degree of coincidence depends on the speed difference between the upper and lower wall surfaces, and the number of adsorbed water molecules on the surface.