3 0 0 0 OA バドミントンシャトルコックの空力安定性
- 著者
- 中川 健一 長谷川 裕晃 村上 正秀 大林 茂
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会
- 雑誌
- 日本機械学会論文集 (ISSN:21879761)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.856, pp.17-00165-17-00165, 2017 (Released:2017-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Badminton is one of the most popular sports in the world and is famous as the sport having the fastest initial velocity of a batted ball among all ball games. Initial velocity immediately after smashing may reach up to 408 km/h (113 m/s) at maximum. A badminton shuttlecock generates significant aerodynamic drag and it was confirmed that the high deceleration characteristics was related to the slots located at the leg portion of a shuttlecock in the previous study. Turnover refers to the flipping experienced by a shuttlecock when undergoing heading change from nose pointing against the flight path at the moment of impact and a shuttlecock indicates the aerodynamically stable feature for the flip movement just after impact. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of gaps on the aerodynamic stability (turnover stability) of a badminton shuttlecock during the flip phenomenon. In the present study, the flow field around the shuttlecock during impulsive change of an angle of attack (flip movement) was measured by using the smoke flow visualization and the behavior of the shuttlecock during the flip movement was evaluated in comparison with that of the conic model (with no gaps). The turnover stability of a badminton shuttlecock is affected by gaps of the shuttlecock skirt.
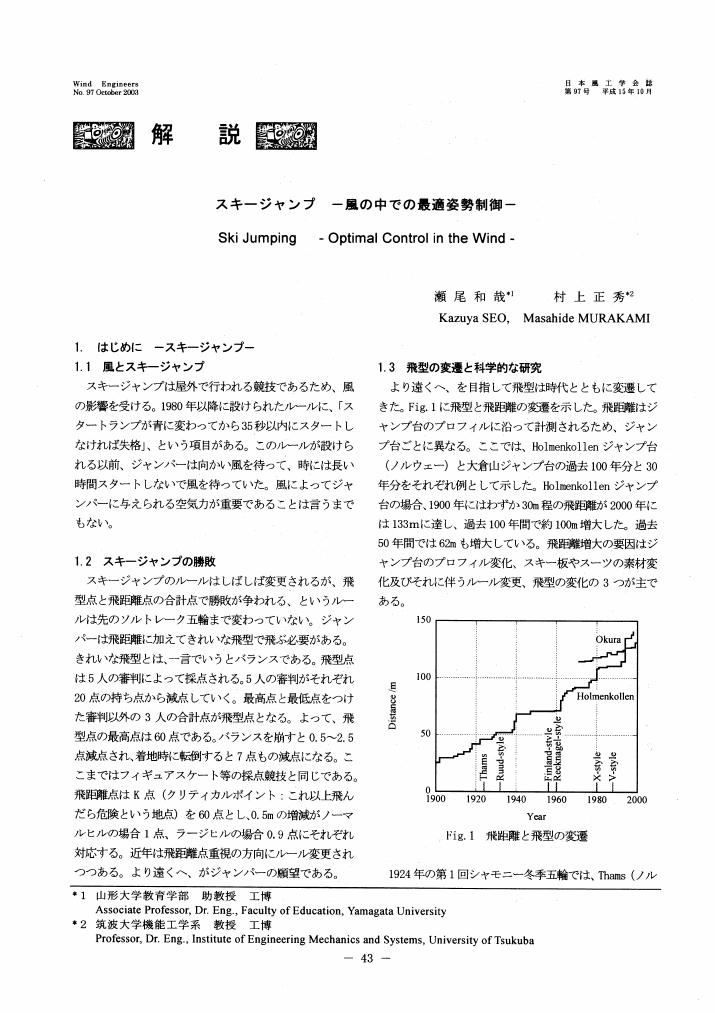
2 0 0 0 OA スキージャンプ
- 著者
- 瀬尾 和哉 村上 正秀
- 出版者
- Japan Association for Wind Engineering
- 雑誌
- 日本風工学会誌 (ISSN:09121935)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2003, no.97, pp.43-48, 2003-10-31 (Released:2010-06-04)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
1 0 0 0 OA 赤外線天文学と極低温工学
- 著者
- 村上 正秀
- 出版者
- CRYOGENICS AND SUPERCONDUCTIVITY SOCIETY OF JAPAN
- 雑誌
- 低温工学 (ISSN:03892441)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.2, pp.65-75, 1982-04-25 (Released:2010-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Considerable astronomical interest has been directed towards the infrared observations in space using cooled telescopes. The design needs the use of advanced technology in many areas, especially in cryogenic.Observations in the infrared from the space environment are free from the absorption and emission by the earth's atmosphere. Telescopes and detectors cooled to a temperature near to absolute zero improve the sensitivity tremendously, because of reduction of the background noise.The use of liquid helium is essential to achieving such temperature level. Superfluid helium may be the best coolant for this purpose, owing to its excellent heat transport capability. On the other hand, several potential difficulties have been pointed out with respect to the containment of superfluid helium in tanks on board. One of such difficulties was the phase separation between vapor and liquid under zero-gravity condition. Now, it seems that this is solved by the use of the porous plug or the active phase separator.More than five space infrared missions have been planned to be launchned in the 80's. Some are presently in preparation and others are under consideration. These missions are expected to reveal stellar and planetary formation in clouds of gas and dust. The dust radiates primarily in the infrared and obscures shorter wavelengths such as the visible radiation. The Galaxy and several external galaxies are important objects which can be well studied in the infrared.We are also proposing an infrared telescope on board a Spacelab (IRTS). Relating fundamental studies and preliminary design consideration are under way.These all missions are ambitious projects and give a challenge to cryogenic physicists and engineers.
1 0 0 0 OA III.宇宙における超電導技術の応用
- 著者
- 村上 正秀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 電気学会
- 雑誌
- 電気学会誌 (ISSN:13405551)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.114, no.4, pp.222-224, 1994-04-20 (Released:2008-04-17)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 著者
- 瀬尾 和哉 渡部 勲 太田 香織 村上 正秀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人日本機械学会
- 雑誌
- ジョイント・シンポジウム講演論文集 : スポーツ工学シンポジウム : シンポジウム:ヒューマン・ダイナミックス : symposium on sports engineering : symposium on human dynamics
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2001, pp.136-140, 2001-11-07
This paper describes the aerodynamic forces acting on the ski jumper during the landing phase as well as the free flight phase. The full size model was employed to measure the lift area, the drag area and the moment volume, which was mounted in a 3-meter low speed wind tunnel. The ground effect plate was set in the test section of the wind tunnel. The clearance between the plate and the center of mass of the body-ski combination was about 1 m. It was found that the difference between the lift area with the ground effect plate and that without the ground effect plate increased with the ski-opening angle, though difference of both lift areas was independent of the angle of attack. The difference of both drag areas was small. The flight distance was estimated about 146 m, which is 6 m longer by taking account of the ground effect.
1 0 0 0 超流動ヘリウムの沸騰熱伝達とそれに伴う振動/カオス現象の研究
実験は、ステンレス薄膜(10ミクロン厚)に細いスリットを入れてジグザグに整形して作った。これは、事実上平面ヒータと見なすことが出来ることが確かめられた。沸騰中のヒーターの平均表面温度はその電気抵抗変化から求めることが出来、これより、周囲のHe IIの温度や圧力等のいろいろな熱力学条件下において、沸騰状態における熱伝達係数を求めることが出来る様になった。同時にヒーターのすぐ上方で、沸騰に誘起されて起こる温度と圧力の変動も測定された。測定データから、上記の温度と圧力の変動は高度な相関をもっており、さらにその変動は可視化画像に見られるほぼ周期的な蒸気泡変形、急激な膨張と収縮の繰り返し、等とも同期していることが確かめられた。その内、大振幅変動については、カオス解析の観点からも解析され、各測定値の相互関係が詳しく調べられた。膜沸騰状態下での熱伝達係数は、ヒーター上方で計られた温度と圧力の変動にも強く依存することが分かった。3種類の膜沸騰状態、ノイジー、遷移状態、サイレントの各膜沸騰、における熱伝達係数の測定からは、沸騰状態はヒータ位置の静圧(液面からの深さに比例)に依存してそのモードが明らかに変わるが、熱伝達係数はそのモードに余り依存せずに大体同一であり、殊にλ点に近い温度では修正されたBreen-Westwater相関式で統一的に良く記述されることが確認された。さらに、これら沸騰モード間の分布マップも、温度-静圧-熱流束からなる、3次元表現として求められた。これら沸騰モードの差異は、その状態、特に蒸気-液界面の安定/不安定性に起因することも分かった。