- 著者
- Yasuhiro HOSAKI Nobuyoshi SHIOZAWA Kozo ASHIDA Satoshi WATANABE Taichi ISHIZAWA Mitsuo TSUNAKAWA Shingo YANO Fumihiro MITSUNOBU
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.5, pp.554-555, 2014-08-29 (Released:2015-01-15)
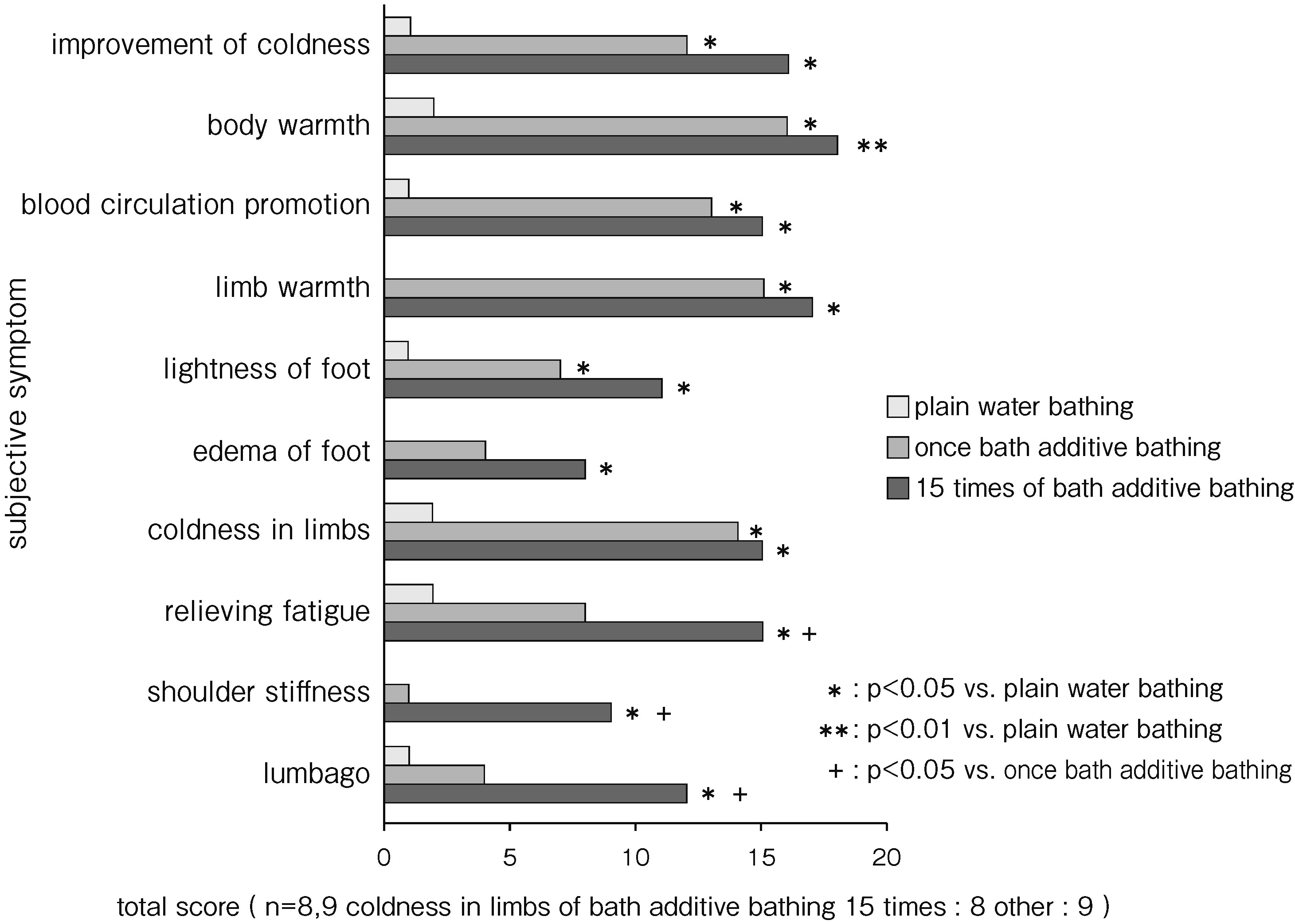
Purpose: We have previously reported the physiological and biochemical effects of bath salts. In this study, we used bath additive containing artificial carbon dioxide and sodium chloride (S bath additive), and the acute effects of bathing once with S bath additive and chronic effects of daily bathing with S bath additive for 15 consecutive days were compared with the effects of bathing once in plain water. Improvement in 10 symptoms was investigated using a 5-point verbal rating scale (VRS).Methods: Nine patients aged 51-82 years (mean, 66.6 years) with cold intolerance and lower leg pain were treated with balneotherapy. Whole-body bathing at 40°C was performed for 10 min daily (day 1, bathing in plain water; days 2-16, bathing with S bath additive). On days 1, 2, and 16, changes in patient’s subjective symptoms were evaluated using a VRS ranging from -1 to +3.Results: Compared with bathing once in plain water, bathing once with S bath additive was improvement of coldness, body warmth, blood circulation promotion, limb warmth, lightness of foot, and coldness in limbs. Daily bathing with S bath additive for 15 days significantly improved all symptoms compared with bathing in plain water. A comparison between single and daily bathing with S bath additive showed that relieving fatigue and lumbago were significantly improved after consecutive bathing, demonstrating the benefits of long-term usage.Discussion: Bathing once with S bath additive had acute effects on symptoms associated with peripheral circulation, such as coldness in limbs, body warmth, and limb warmth. Daily bathing with S bath additive improved bone- and joint-related symptoms, such as lumbago and shoulder stiffness, demonstrating that the chronic effects of S bath additive differ from the acute ones. These results are consistent with previous studies on natural hot springs which found that the efficacy of short-term treatment was distinct from that obtained after >2 weeks of treatment.
- 著者
- Hiroharu Kamioka Kiichiro Tsutani Hiroyasu Okuizumi Yoshiteru Mutoh Miho Ohta Shuichi Handa Shinpei Okada Jun Kitayuguchi Masamitsu Kamada Nobuyoshi Shiozawa Takuya Honda
- 出版者
- 日本疫学会
- 雑誌
- Journal of Epidemiology (ISSN:09175040)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.1, pp.2-12, 2010-01-05 (Released:2010-01-05)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 32 87
Background: The objective of this review was to summarize findings on aquatic exercise and balneotherapy and to assess the quality of systematic reviews based on randomized controlled trials.Methods: Studies were eligible if they were systematic reviews based on randomized clinical trials (with or without a meta-analysis) that included at least 1 treatment group that received aquatic exercise or balneotherapy. We searched the following databases: Cochrane Database Systematic Review, MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, JDream II, and Ichushi-Web for articles published from the year 1990 to August 17, 2008.Results: We found evidence that aquatic exercise had small but statistically significant effects on pain relief and related outcome measures of locomotor diseases (eg, arthritis, rheumatoid diseases, and low back pain). However, long-term effectiveness was unclear. Because evidence was lacking due to the poor methodological quality of balneotherapy studies, we were unable to make any conclusions on the effects of intervention. There were frequent flaws regarding the description of excluded RCTs and the assessment of publication bias in several trials. Two of the present authors independently assessed the quality of articles using the AMSTAR checklist.Conclusions: Aquatic exercise had a small but statistically significant short-term effect on locomotor diseases. However, the effectiveness of balneotherapy in curing disease or improving health remains unclear.
1 0 0 0 IR 足浴における人工芒硝泉が自律神経活動に与える影響
- 著者
- 塩澤 信良 目加田 優子 秋山 嘉子 林 かほり 森 佳子 和田 智史 上岡 洋晴 川野 因 Nobuyoshi SHIOZAWA MEKATA Yuko AKIYAMA Yoshiko HAYASHI Kaori MORI Keiko WADA Satoshi KAMIOKA Hiroharu KAWANO Yukari 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学大学院農学研究科食品栄養学 東京農業大学地域環境科学部教養分野 東京農業大学応用生物科学部栄養科学科 Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Food and Nutritional Science Graduate School of Agriculture Tokyo University of Agriculture Fundamental Arts and Sciences Faculty of Regional Environment Science Tokyo University of Agriculture Department of Nutritional Sciences Faculty of Applied Bio-Science Tokyo University of Agriculture
- 出版者
- 東京農業大学
- 雑誌
- 東京農業大学農学集報 (ISSN:03759202)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.4, pp.185-192,
本研究は人工芒硝泉による足浴が自律神経活動に及ぼす影響について検討することを目的とした。健康な若年男女計6名(男性3名 : 20.7±0.6歳,女性3名 : 21.3±0.6歳)を対象に,人工芒硝泉浴,淡水浴,湯なし条件(対照座位)の足浴条件を1日1条件,ランダムな順序で施行した。対象者には20分間座位安静をとってもらい,引き続き足浴前値の測定を行った。足浴は座位にて41℃(33L)の温湯に両足膝下約10cmまで15分間浸漬して行った。足浴終了後は対象者自身が水分を拭き取り,両足を毛布で覆い,60分間座位安静を保った。その間,心拍数,心拍変動周波数に基づく自律神経活動,鼓膜温を測定するとともに,体感温度,眠気,疲労感などの主観的評価をVisual Analogue Scale(VAS)を用いて記録した。その結果,人工芒硝泉浴及び淡水浴により体感温度は有意に上昇したが,鼓膜温及び心拍数に有意な変動は見られなかった。また淡水浴後は交感神経活動の有意な亢進が認められたが,人工芒硝泉浴後はそれが見られなかった。本結果から人工芒硝泉による足浴は足浴後の交感神経活動の亢進を抑え,疲労感の低減に寄与する可能性が示唆された。This study was conducted to estimate the effect of a footbath with sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) on autonomic nervous system (ANS) activity. Each of three young healthy males (age, 20.7±0.6 years) and females (age, 21.3±0.6 years) participated in 3 conditions in random order, footbaths with or without Na2SO4, and a sitting position without water as a control. Each subject sat on a chair and kept quiet for 20min with heart rate (HR) stabilized, and subsequently basal measurements were conducted. In a sitting position, they dipped their calves 10cm under their knee joints into hot water (41℃, 33L) for 15min. Immediately after the bathing, they removed moisture, covered their knees with a blanket and sat for 60min thereafter. Counts of HR, ANS activity based on frequency of HR variability, and a core temperature using an eardrum thermometer were measured. The degree of thermal comfort such as relatively hot or relatively cool, sleepiness and fatigue were also estimated using visual analogue scales (VAS). As a result, both footbaths with and without Na2SO4 significantly increased the subjective thermal comfort, while the core temperature and HR counts were unaffected. Sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activity was significantly increased by the footbath without Na2SO4, but not with Na2SO4. These observations suggested that in the footbath, Na2SO4 might have an inhibitory effect on increased SNS activity, and induce some depressive effects on feeling of fatigue.