33 0 0 0 OA 高齢者の浴槽入浴頻度と抑うつ発症との関連:JAGESプロジェクトによる6年間のコホート研究
- 著者
- 早坂 信哉 尾島 俊之 八木 明男 近藤 克則
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2359, (Released:2023-07-24)
- 参考文献数
- 17
【背景・目的】高齢者において抑うつの発症は様々な疾患のリスクとなり,要介護状態に陥るきっかけとなる.一方,日本においては浴槽の湯につかる特有の入浴法が多くの国民の生活習慣となっているが,この生活習慣としての浴槽入浴と長期的な抑うつ発症との関連は明らかではなかった.本研究は,大規模な6年間にわたる縦断研究によって生活習慣としての浴槽入浴が長期的な抑うつ発症との関連を明らかにすることを目的とした. 【方法】Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study(以下,JAGES)の一環として2010年,2016年に調査対象となった11,882人のうち,自立しておりかつGeriatric Depression Scale (以下,GDS)4点以下で抑うつがなく,夏の入浴頻度の情報のある6,452人,および冬の入浴頻度の情報がある6,465人をそれぞれ解析した.コホート研究として週0~6回の浴槽入浴と週7回以上の浴槽入浴の各群の6年後のGDSによる抑うつ発症割合を求め,浴槽入浴との関連をロジスティック回帰分析によって年齢,性別,治療中の病気の有無,飲酒の有無,喫煙の有無,婚姻状況,教育年数,等価所得を調整して多変量解析を行いオッズ比を求めた. 【結果】週0~6回の浴槽入浴に対する週7回以上の浴槽入浴の抑うつ発症の,調整後の多変量解析によるオッズ比は夏の入浴頻度0.84(95%信頼区間:0.64~1.10),冬の入浴頻度0.76(95%信頼区間:0.59~0.98)であり,冬に週7回以上浴槽入浴することは抑うつを発症するリスクが有意に低かった. 【結論】習慣的な浴槽入浴の温熱作用を介した自律神経のバランス調整などによる抑うつ予防作用による結果の可能性があり,健康維持のため高齢者へ浴槽入浴が勧められることが示唆された.
2 0 0 0 森林浴効果の生理・心理学的研究
- 著者
- 近藤 照彦 武田 淳史 武田 信彬 下村 洋之助 谷田貝 光克 小林 功
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.71, no.2, pp.131-138, 2008-02-01
- 被引用文献数
- 3 2
We performed a physio-psychological research on the mental, physical relaxation and health-keeping effect of <i>Shinrin-yoku</i> (forest walking) in Kawaba village. Eleven male and 8 female healthy elderly residents in Kawaba village, whose average age was 74.0±3.5 years old for male and 74.9±2.9 years old for females volunteered for this experiment. All members walked for one hour in the Kawaba Forest on August 17 under cloudy skies, 30-32°C temperature, 58-60% humidity, and, 0-2m/sec wind condition and walked again for another one hour in a non-forest rural agricultural area on August 21 under almost the same weather conditions. Phytoncides in the air, Profile of Mood State (POMS) test, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), fasting levels of serum natural killer cell activity (NK), plasma catecholamine (adrenaline, noradrenalin and dopamine), plasma cortisol, and serum adiponectin were measured before and after walking. Phytoncides were detected in the forest and non-forest, all members showed a decrease of POMS total scale, BP, adrenalin and serum cortisol. Six (3 male and 3 female subjects) of them expressed an increase of serum NK cell activity after the forest-walking. One female showed a high serum NK cell activity after both forest and non-forest rural walking.<br>Our experiment on the forest-walking in Kawaba village indicated that its relaxation and health-keeping effects, probably due to walking in the fresh forest air.
2 0 0 0 慢性関節リウマチに対する高濃度炭酸ガス浴の効果
- 著者
- 前田 真治 山北 秀香 佐々木 麗 田中 裕美子 後出 秀聡 木村 広 井上 市郎
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.4, pp.187-194, 1998-08-01
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 1
慢性関節リウマチ (RA) 患者を対象に組織循環改善作用と新陳代謝亢進による疼痛の軽減を目的に90%以上になる高濃度炭酸ガス浴装置を用い効果を調べた。<br>気体としての炭酸ガス浴は更衣動作の障害されているRA患者にとって, 衣服のまま入浴できる画期的な入浴法である。血圧・脈拍の大きな変化なく, 循環機能の影響の少ない入浴法と考えられた。表面皮膚温も前値に比べ入浴後期に1℃以上の上昇がみられ, 局所の血液循環の改善が示唆され, 老廃物・疼痛物質などの除去・新陳代謝改善の効果が期待できると考えられた。ADL得点 (平均67→75/96), Visual Analogue Pain Scale (5.3→2.7/10), Face Scale (9.4→5.4/20), AIMS変法 (身体的要素28.5→30.1, 社会的25.2→27.3, 精神的26.2→29.9/36) と入浴前に比べ有意に改善しており, 高濃度炭酸ガス浴がRA患者のADL・QOLの改善に効果があると思われた。
2 0 0 0 ラットのアキレス腱修復に与える鍼通電刺激の効果
- 著者
- 大井 優紀 井上 基浩 中島 美和 糸井 恵 北小路 博司
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.75, no.2, pp.112-123, 2012-02-29
目的:鍼通電刺激の腱修復能に及ぼす影響について調査する目的で、アキレス腱断裂モデルラットを用いて、組織学的、および力学的に検討した。<br>方法:Wistar系ラット(雄性、12週齢)60匹を用いて、アキレス腱断裂モデルを作成し、無作為に鍼通電刺激群(EA群)と無処置群(Control群)の 2群に分けた。EA 群は、軽度麻酔拘束下にアキレス腱断裂部の内外側に先端部が腱断裂部に接触するようにそれぞれ鍼を刺入し、内側部を陰極、外側部を陽極として間欠的直流鍼通電刺激(刺激条件:刺激幅 5 ms、刺激頻度 50 Hz、刺激強度 20 μA、刺激時間 20分間)をモデル作成日の翌日から各評価日まで連日行った。Control群は麻酔拘束処置のみ行った。評価として、モデル作成後 7日と 10日に修復腱を採取し、設定した関心領域内の全細胞数(HE染色)、TGF-<i>β</i>1、および b-FGF の陽性細胞数(免疫組織化学染色)の計測とそれぞれの染色による組織像の観察を行った。また、モデル作成後 10日には、引張試験による修復腱の最大破断強度を測定した。<br>結果:HE染色では、各評価日とも群間に有意差を認め、EA群で明らかな細胞数の増加を認めた(7日:p<0.05、10日:p<0.001)。免疫染色においては、TGF-<i>β</i>1、b-FGFともにモデル作成後7日のEA群で最も強い発現を認め、他との間に有意差を認めた[(TGF-<i>β</i>1:7日 EA群vs. 10日 EA群:p<0.001、vs. 7日 Control群:p<0.0001、vs. 10日 Control群:p<0.0001)(b-FGF:7日 EA群vs. 10日 EA群:p<0.001、vs. 7日 Control群:p<0.0001、vs. 10日 Control群:p<0.0001)]。モデル作成後 10日における修復腱の最大破断強度は EA群で有意に高い値を示した(pp<0.01)。<br>考察・結語:アキレス腱断裂後早期の検討において、EA群では細胞数の増加と成長因子の発現量増加、さらに腱強度の増大を認めた。これらの結果から、直流鍼通電刺激は腱修復部における細胞増殖と成長因子の発現に有益に作用し、修復腱の力学的強度を高めることが示唆され、腱修復能に促進的に作用する有用な方法となる可能性が考えられた。
- 著者
- Motohiro INOUE Miwa NAKAJIMA Megumi ITOI
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.3, pp.187-194, 2015-05-13 (Released:2015-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: The relaxing phenomenon induced by acupuncture on hypertonic muscle has not clearly been demonstrated. We studied whether acupuncture stimulation on the hypertonic muscle model induce relaxation. Methods: A rat model of hypertonia was created by inducing tetanic contraction in the triceps surae muscles of 21 Wistar rats (male, 12 weeks) with four electrical stimulations (80 Hz, 5 mA, 5 min.), with a 2 min. interval between each stimulation. The rats were randomly divided into two test groups: 1. Untreated group (N = 12), 2. Group treated with acupuncture stimulation of the triceps surae muscle (N = 9). Rats in the untreated group received no therapeutic treatment after the model was created. Acupuncture was performed within 5 min. after the model was created. Evaluations were taken before and 5 min., 1, 2 and 3 days after tetanic contraction was induced. The rats were anaesthetized and a tension sensor for measuring static and dynamic muscle tension was used to determine triceps surae muscle stretching tension during passive dorsal flexion of the foot (30°, 40°, 50°).Results: In both groups, at each of the angles of passive dorsal flexion, there was a significant increase in stretching tension 5 min. after inducing tetanic contraction compared to before induction, and statistics showed recovery to pre-induced tetanic contraction values after 1 day and thereafter. Compared to the untreated group, however, values 5 min. after induced tetanic contraction tended to be lower in the group treated with acupuncture stimulation.Conclusions: Compared to the untreated group, stretching tension values 5 min. after inducing tetanic contraction tended to be lower in the acupuncture group. This could be due to acupuncture stimulation causing changes in blood flow in the lower leg, including muscle tissue, resulting in reuptake of calcium by the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and/or the influence acupuncture on reducing lower leg edema. Acupuncture stimulation could also have an action on the γ fibers and Ib fibers associated with continuous muscle tonus and muscle relaxation.
- 著者
- Yasuhiro HOSAKI Nobuyoshi SHIOZAWA Kozo ASHIDA Satoshi WATANABE Taichi ISHIZAWA Mitsuo TSUNAKAWA Shingo YANO Fumihiro MITSUNOBU
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.5, pp.554-555, 2014-08-29 (Released:2015-01-15)
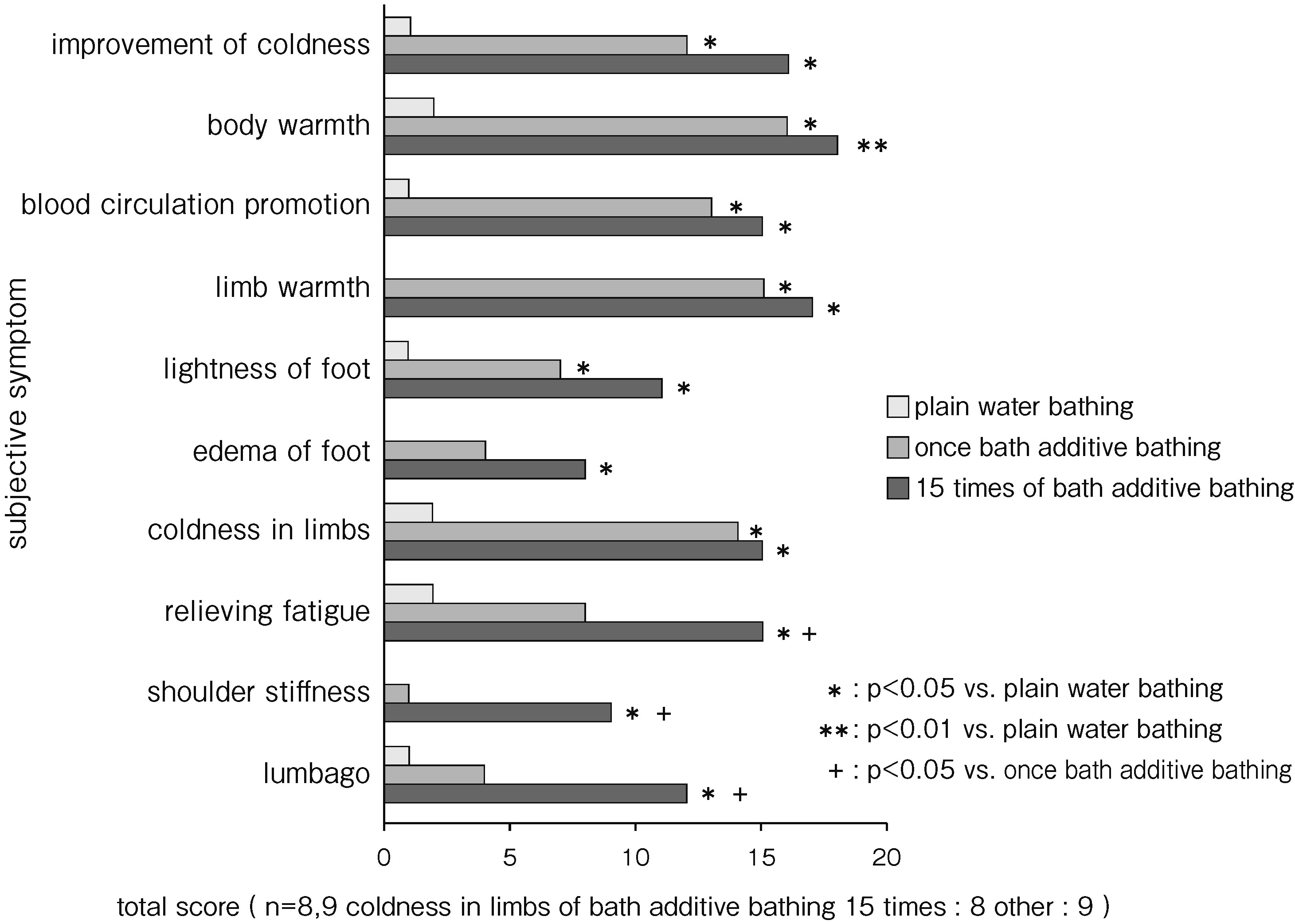
Purpose: We have previously reported the physiological and biochemical effects of bath salts. In this study, we used bath additive containing artificial carbon dioxide and sodium chloride (S bath additive), and the acute effects of bathing once with S bath additive and chronic effects of daily bathing with S bath additive for 15 consecutive days were compared with the effects of bathing once in plain water. Improvement in 10 symptoms was investigated using a 5-point verbal rating scale (VRS).Methods: Nine patients aged 51-82 years (mean, 66.6 years) with cold intolerance and lower leg pain were treated with balneotherapy. Whole-body bathing at 40°C was performed for 10 min daily (day 1, bathing in plain water; days 2-16, bathing with S bath additive). On days 1, 2, and 16, changes in patient’s subjective symptoms were evaluated using a VRS ranging from -1 to +3.Results: Compared with bathing once in plain water, bathing once with S bath additive was improvement of coldness, body warmth, blood circulation promotion, limb warmth, lightness of foot, and coldness in limbs. Daily bathing with S bath additive for 15 days significantly improved all symptoms compared with bathing in plain water. A comparison between single and daily bathing with S bath additive showed that relieving fatigue and lumbago were significantly improved after consecutive bathing, demonstrating the benefits of long-term usage.Discussion: Bathing once with S bath additive had acute effects on symptoms associated with peripheral circulation, such as coldness in limbs, body warmth, and limb warmth. Daily bathing with S bath additive improved bone- and joint-related symptoms, such as lumbago and shoulder stiffness, demonstrating that the chronic effects of S bath additive differ from the acute ones. These results are consistent with previous studies on natural hot springs which found that the efficacy of short-term treatment was distinct from that obtained after >2 weeks of treatment.
1 0 0 0 OA 人の体温調節における飲水温度の影響
- 著者
- 美和 千尋 島崎 博也 出口 晃 森 康則 前田 一範 水谷 真康 浜口 均
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.2, pp.78-85, 2019-05-31 (Released:2019-06-19)
- 参考文献数
- 23
人は環境の温度変化に対して,身体の外部や内部から熱の出し入れをして調節する.身体の内部からの熱の出し入れの一つに温度の異なる水を飲むことが挙げられる.しかし,温度の異なる飲水に伴う人体作用の変化の詳細は明らかになっていない.そこで,この研究では,異なる温度の水を飲むことで,どのような体温応答があるのかを明らかにする.健常な若年男性13名(平均年齢21.3±0.8歳)を対象とし,3℃,室温,60℃Cの水を飲んだときと水を飲まないときの体温応答について検討した.測定項目は鼓膜温,皮膚血流量,発汗量,平均皮膚温である.鼓膜温はサーミスターにより,皮膚血流量はレーザードップラー血流計で,発汗量はカプセル換気法で測定した.平均皮膚温は,身体の7点をサーミスターで測定し,算出した.鼓膜温は水温3℃と60℃の飲水時に他の条件と比べ有意に変化した.皮膚血流量は水温60℃と3℃の間で,発汗量は水温60℃と他の条件の間で,平均皮膚温は水温3°Cと他の条件の間で有意差が認められた.飲水初期の変化は,飲水時の温度による温度受容器の反応で起こり,その後は飲んだ水の温度が持つ熱エネルギーが関与していると考えられた.
1 0 0 0 高血圧症のハリ治療
- 著者
- 高島 文一
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.1, pp.35-36, 1979
- 著者
- 岩下 佳弘 渡 孝輔 前田 曙 杉本 和樹 山田 しょうこ 飯山 準一
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2345, (Released:2021-10-14)
- 参考文献数
- 40
温熱治療によって増加する熱ショックタンパク質(heat shock protein, Hsp)は,アポトーシスを阻害し,尿細管の生存能力を維持し,腎保護に作用する.その一方で,近年,嚢胞性腎疾患においてHspが治療ターゲットとなり得ることが示された.そこで,我々は,多発性嚢胞腎(autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, ADPKD)モデル動物を用いて,サウナ介入を反復させたときのADPKDへの影響について調査した.我々は,DBA/2FG-pcy(pcy)マウスを用い,サウナ介入を実施し,脱水予防のために4%スクロース水を摂水させた(TS)群,4%スクロース水のみを摂水させた(SW)群,および,サウナ介入を行わないコントロール群の3群(各n = 3)で実験を行った.熱負荷には遠赤外線サウナ装置を用い,マウス直腸温を約39°Cに上昇させ30分程度維持した.1週間に2回のサウナ介入を4週間実施した. 実験終了時のクレアチニンやBUN値に有意差は認められなかったが,TS群は他よりもわずかに高い値を示した.しかしながら,TS群とSW群の嚢胞の成長はcontrolに比して軽減しており,Hsp90の発現は有意な減少を示した(p < 0.01 or p < 0.001, vs. control).またTS群では,嚢胞形成や増殖に関与するErkの有意な減少が認められた(p < 0.05, vs. control).Hsp27の発現およびリン酸化はTS群で増加し,caspase-3の発現は減少傾向であったが,活性化に差は認められなかった. 4週間のサウナ介入は,一時的な脱水とそれに伴う腎機能低下のリスクや熱負荷に伴うHsp27の発現増加による嚢胞形成や増殖を刺激するリスクを示唆するものであった.その一方で,熱負荷直後に適切な水分多量摂取を実施すれば,脱水予防と同時に嚢胞成長の抑制が期待できると考えられた.
- 著者
- Shigeaki IWANAGA
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.1, pp.12, 2020-02-29 (Released:2020-05-22)
1 0 0 0 OA PT1-4 Balneotherapy research in France: the AFRETH (French Association for Balneotherapy Research)
- 著者
- Christian François ROQUES Claude Eugene BOUVIER
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.5, pp.386-387, 2014-08-29 (Released:2015-01-15)
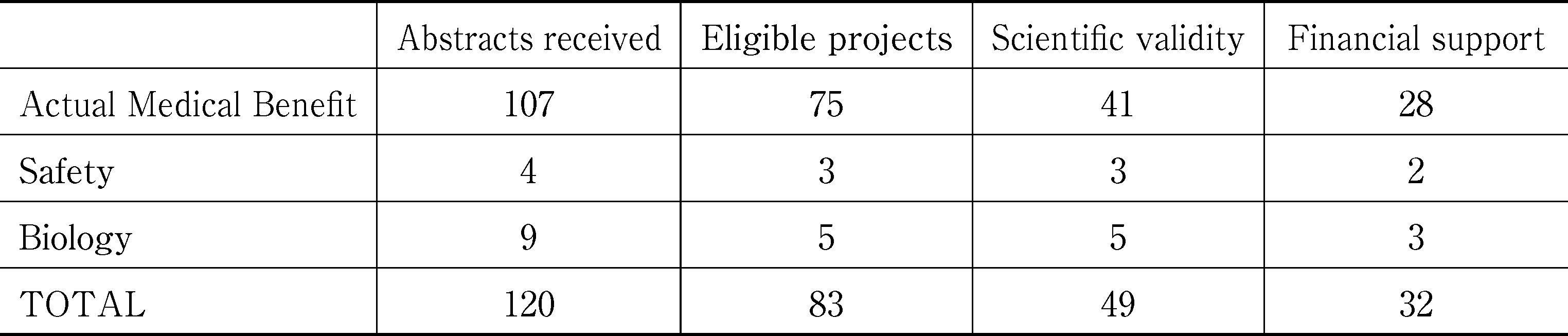
In France, several public and or private scientific investigation bodies are involved in medical balneological scientific investigation (academic or university-linked institutes in Paris, Nancy, Bordeaux, Grenoble, Clermont-Ferrand; private structures in Paris, Aix les Bains, Saujon). However, these last 10 years, the important development in medical balneology investigation could be related to the French Association for Balneotherapy Research (AFRETH). The Afreth has been created in 2004 by the French Union of SPA Contractors, the Union of the mayors of spa resorts and the French branch of the FEMTEC. The AFRETH provides every year a budget of 1 M€ for scientific investigation in balneology. The founders’ representatives, who constitute the association’s administrative committee, take the decision of supporting financially the scientifically validated projects. The scientific validity is pronounced by the scientific committee (12 independent and acknowledged doctors and scientists) on the basis of external independent experts’ advices (methodological, clinical and biological sciences from French academic institutions). 10 calls for projects have been launched and fully implemented. They concerned mainly the actual medical benefit (cf. Table below). A global budget of 11 M€ has been engaged. Regarding the medical benefit have been implemented and published: STOP-TAG (treatment of generalised anxiety, 237 patients); Thermarthrose (knee osteo-arthritis, 462 patients); Maathermes (obesity and overweight, 257 patients); Pacthe (treated breast cancer patients, 250 patients) Thermes & veines (chronic venous insufficiency, 425 patients). These different randomised controlled trials have demonstrated significant results in favour of balneotherapy. Publication is in progress for Rotatherm (a RCT concerning shoulder cuff tendinitis, 186 patients). Are in progress a RCT on COPD (BPCeaux), a RCT on subacute lumbar pain (ITILO). Pilot investigations have been implemented concerning the metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease and other ageing problems, psychotropic drugs withdrawal, therapeutic education of patients with chronic venous insufficiency. So scientific investigation has to come with usual balneotherapy but also with the development of new trends which have to be scientifically assessed from their initiation.From our experience, we have to emphasize the difficulties related to the patients’ enrolment and the need of new methodological designs, alternative to usual RCT to investigate such a complex therapeutic intervention.
- 著者
- Shinichi ICHIKAWA
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.1, pp.4, 2019-02-28 (Released:2019-04-03)
1 0 0 0 OA Special Topics from Japan Thrombotic and Hematostatic Reactions to Bathing in Very Hot Hot-Spring
- 著者
- Hitoshi KURABAYASHI
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.78, no.3, pp.177-186, 2015-05-13 (Released:2015-05-26)
- 参考文献数
- 23
Very hot hot-spring is loved by the Japanese, although it might cause thrombotic events. It causes addiction to hyperthermia possibly because of an increase in the production of morphine-like substance. Increases in platelet activation, adhesion molecules on the platelet surface, platelet-derived microparticles, and blood viscosity as well as decreases in fibrinolytic capacity and blood pressure were observed after bathing in very hot hot-spring. Bathing in very hot hot-spring is not recommended for the elderly in view of age-related changes in endothelial function, fibrinolytic capacity, dehydration, and dysregulation of blood pressure. Instead, hydrotherapy or bathing in hot-spring in temperatures under 42°C is beneficial with little risk regarding hemostasis and thrombosis.
- 著者
- 武田 泉
- 出版者
- THE JAPANESE SOCIETY OF BALNEOLOGY, CLIMATOLOGY AND PHYSICAL MEDICINE
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候学会雑誌 (ISSN:03694240)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.20, no.4, pp.305-320, 1957
The author prescribed experimental bathing in Genzo-yu and the Hot-spring of Narugo-Branch Hospital in the Tohoku University, all in Narugo Spa, Miyagi-ken, to study the effect of the bathing on the serum Ch-E values of children, as well as the bearing they have on the liver function, and arrived at the following conclusion:<br>1) The effect of once bathing on the serum Ch-E, values was most marked directly after the bath, falling in some cases and rising in others, thus revealing individual differences, but returned to the pre-bath values in 3 hours. The rise or fall was found widest upon bathing in Genzo-yu. No change was seen in the liver function before and after once bathing.<br>2) During continuous bathing, the serum Ch-E values decreased on the 3rd-7th but reincreased by the 14th day. This fluctuation of the values also was day the most manifest upon bathing in Genzo-yu. The change in the values ran parallel with anomalies appearing in the liver function.<br>3) The fluctuation of the serum Ch-E values following once bathing became narrowed down in scope by continuous bathing.<br>4) As symptoms of bathing reaction in children, accentuated 2nd pulmonary sounds, audible femoral sounds, a slight reduction of the serum Ch-E values and a very mild dysfunction of the liver were observed. All these were transient and could be attributed to an anomaly in the function of the liver. In particular, the symptoms could be detected in sucklings on earlier dates of the continuous bathing than in adults, and were apparently more prevalent in the cases with lowered nutrition.<br>5) The change of the serum Ch-E values following hot-spring bathing seems to be induced by the general and non-specific stimulative exerted by the hot-spring bathing.
1 0 0 0 OA 自律神経機能と感情尺度に着目したヒノキ浴槽の入浴に伴うリラックス効果
- 著者
- 森 康則 犬飼 健自 一色 博 今井 奈妙
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.80, no.2, pp.66-72, 2016 (Released:2017-05-30)
- 参考文献数
- 13
目的:ヒノキに代表される木質の建築資材は,利用者のリラックス感を促進すると考えられている.本研究では,三重県産ヒノキで作られた浴槽に入浴する者の自律神経機能と感情尺度の変化に着目して,その仮説の科学的な検証を試みた.方法:被験者には,健常成年16名を選定した.被験者1人につき,入浴介入を2回行った.1回の入浴は通常のユニットバスでの入浴とし(対照実験),もう1回の入浴はユニットバスと同一形状に設計されたヒノキで作られた浴槽での入浴とした.入浴介入前に唾液の採取と主観的感情尺度(MCL-S.2)の測定,入浴介入後にも唾液の採取と主観的感情尺度(MCL-S.2, VAS)の測定をそれぞれ行った.また実験を通じて,胸部に防水機構付きのホルター心電計を装着し,データを採取した.結果および考察:MCL-S.2による感情尺度評価の結果,ヒノキ製浴槽への入浴前後の「快感情」で,有意なスコア上昇が認められた.加えて,VASによる感情尺度評価の結果,ヒノキ製浴槽の入浴後の方が,対照実験後のそれに比べて,「疲労感」のスコアが有意に低い値が得られた.このことから,ヒノキ浴槽における入浴の「快感情」の促進効果と,「疲労感」の軽減効果が示唆された.また,唾液中コルチゾールの各入浴介入前後の比較の結果,いずれの入浴介入においても入浴後の有意な濃度低下が認められた.また,入浴直前と入浴後安静における副交感神経指標である√HFの比較を行ったところ,いずれの入浴介入においても,有意に高い値に推移していることが明らかになった.これらの結果から,いずれの浴槽材質の入浴であっても,本研究で設定した入浴条件(38~39℃15分間)であれば,入浴行為そのものによっても副交感神経が優位となる傾向が示された.
1 0 0 0 アトピー性皮膚炎のかゆみに対する草津温泉療法の効果
- 著者
- 田村 耕成 久保田 一雄
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.1, pp.19-19, 2001
- 著者
- 石井 敦子 石井 正三 石井 匡
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.2, pp.117-122, 2011-01-01
The experience of the thermal spa lake "Blue Lagoon" in Iceland was reported. The plenty of geothermal seawater was supplied from the Svartsengi geothermal power plant to the Blue Lagoon. It was utilized not only as the spa for the public but also for the treatment of psoriasis at the annex clinic. The well-organized project supplying electric power to the community and hot water for the heating system of the public and home use was supposed to be the advanced model to answer to the increasing demand for carbon offset with ecological purposes.
1 0 0 0 西郷隆盛:そして大久保利通と島津斉彬
- 著者
- 原口 泉
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.1, pp.9-10, 2004
1 0 0 0 空気中のマイナスイオンが脳波に与える影響
- 著者
- 渡部 一郎 真野 行生 野呂 浩史
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.3, pp.121-126, 1998-05
- 被引用文献数
- 3
High levels of negative ions have been detected in the air in forests, at spas, near waterfalls, and so forth, and there have been reported that they have a favorable effect on human beings' feeling of comfort and their feeling of fatigue. In this study we prepared an experimental room in which it was possible to maintain temperature constant at 25°C and constant humidity, and turn the supply of negative ions on and off, and in addition to assessing comfort level and fatigue level subjectively, we assessed them by means of the -wave component of the EEG, which indicates the degree of relaxation, and by auditory evoked potential P300, which reflects attentiveness and degree of fatigue.<br>Methods: The subjects were 15 healthy physicians and nurses. The experiment was conducted in a room maintained at a constant temperature of 25°C and a constant humidity of 50% during a 2-hour period on different days without informing the subjects of whether the air was loaded with negative ions or not. Constant temperature and humidity were maintained, and the level of negative ions was adjusted by using a shinki genertor (Geochto Ltd.). The parameters measured were determined with a flicker test and P300 (auditory evoked) test, and the α-wave ratio was calculated from the 60-minute closed-eye resting EEG.<br>Results: A higher percentage of subjects reported subjective comfort when the air was loaded with neagtive ions (6/15, 40%) than when it was not (4/15, 27%).<br>Significant difference was not observed in the P300 tests, but the α<sub>2</sub> (10-13Hz) ratio of the EEG and flicker test tended to be higher with negative ion-air than without nagative ion-air.
- 著者
- 白倉 卓夫 田村 耕成
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society of Balneology, Climatology and Physical Medicine
- 雑誌
- 日本温泉気候物理医学会雑誌 (ISSN:00290343)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.58, no.2, pp.121-126, 1995-02
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Effect of carbon dioxide bath on cardiovascular functions and peripheral circulation were studied using a new system of carbon dioxide bath. The subjects consisted of 13 males and 17 females, ranging from 50 to 84 years old, 67.4±8.3 in average, having the complaints resulting mainly from arteriosclerosis such as coldness on extremities or exertional pains of lower extremities. Each subject took a bath in plain water (PW) on the first experimental day and then a bath in carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>) at the same time on the second experimental day. Both baths were done for 10min. at 39°C of water temperature. The results obtained were as follows.<br>1) Mean blood pressure (MBP) was elevating during bath and lowered below prebath level immediately after bath in both PW and CO<sub>2</sub> groups. However, MBP in CO<sub>2</sub> group was lower significantly (p<0.05) than in PW group 20 and 30min after bath.<br>2) Both body and skin temperatures were similarly elevated at all points to be measured directly after bath, and then lowerd gradually thereafter. There was no significance in changes between both groups.<br>4) An increase in cutaneous blood flow was observed at the same grade in both groups during and after bath, though no showing significant difference between both groups.<br>5) PO<sub>2</sub> in venous blood increased after bath, while PCO<sub>2</sub> decreased. However, no significant difference in these changes was observed between both groups.<br>6) Tendency to increase in CV R-R was observed during and after bath, though no significant difference was showed between both groups.<br>7) Relating to the feeling to bath, all subjects had the feeling of "warmness" at the beginning of bath and also of comfortableness during and after bath in both PW and CO<sub>2</sub> groups. However, there was no difference in the intensity of these feelings between both groups.<br>8) No side reaction due to an inhalation of carbon dioxide during bath was observed in all subjects.<br>From these results, it is expected that a new carbon dioxide bath results in benefit for patients with disturbance of peripheral circulation.