- 著者
- Yuki IWAHANA Atsushi OHBUCHI Yuya KOIKE Masaru KITANO Toshihiro NAKAMURA
- 出版者
- (社)日本分析化学会
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.1, pp.61-66, 2013-01-10 (Released:2013-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 5 19
Radioactive nuclides in the incinerator ashes of municipal solid wastes were determined by γ-ray spectrometry before and after the accident at the Fukushima nuclear power plant (March 11, 2011). Incinerator ash samples were collected in northern Kyushu, Japan, which is located approximately 1200 km west-southwest (WSW) of the Fukushima nuclear power plant, from April 2006 to March 2007 and from March 2011 to October 2011. 40K, 137Cs, 208Tl, 212Pb, 214Pb, 212Bi, 214Bi, and 228Ac were identified in the ashes before the accident (∼February 2011) and 134Cs was identified along with these eight nuclides in the ashes after the accident (March 2011∼). A sequential extraction procedure based on a modified Tessier method with added water extraction was used for 1st fly ash sampled in August 2011 because the highest activity concentrations of 134Cs and 137Cs were observed for this sample. The speciation of radioactive nuclides in the fly ash was achieved by γ-ray spectrometry and powder X-ray diffractometry for the extraction residues. Little variation was observed in the distribution of the chemical forms of 134Cs and 137Cs in 1st fly ash of municipal solid waste; one half of 134Cs existed as water soluble salts and the other half as carbonate compounds, whereas 75% of 137Cs existed as water soluble salts with the remainder as carbonates(10%) and sulfides (15%). These results show that 88% of the total radioactive Cs existed in water soluble and ion extractive forms and might be at risk for elution and diffusion with rain and wind.
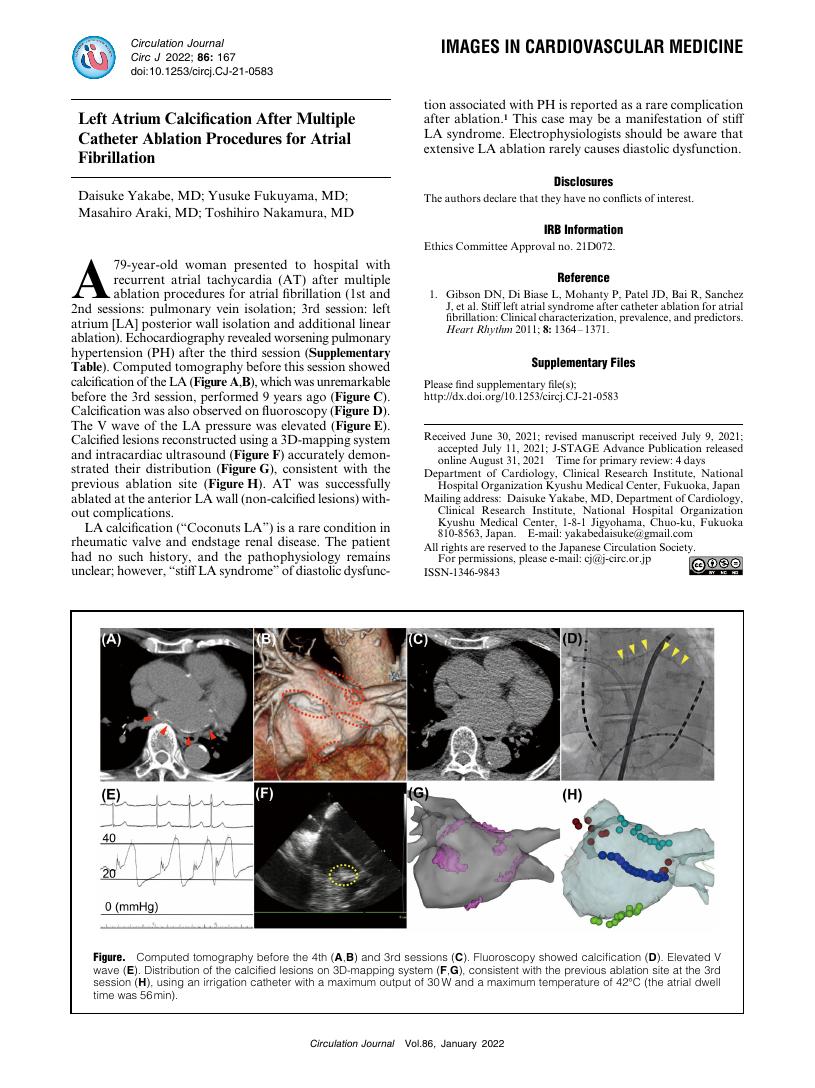
8 0 0 0 OA Left Atrium Calcification After Multiple Catheter Ablation Procedures for Atrial Fibrillation
- 著者
- Daisuke Yakabe Yusuke Fukuyama Masahiro Araki Toshihiro Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.86, no.1, pp.167, 2021-12-24 (Released:2021-12-24)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 2
- 著者
- Mitsuru Takami Koji Fukuzawa Kunihiko Kiuchi Makoto Takemoto Toshihiro Nakamura Jun Sakai Atsusuke Yatomi Kazutaka Nakasone Yusuke Sonoda Kyoko Yamamoto Hiroyuki Takahara Yuya Suzuki Kenichi Tani Ken-ichi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.3, no.5, pp.294-299, 2021-05-10 (Released:2021-05-10)
- 参考文献数
- 10
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Background:Demand is growing for remote electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring systems in the COVID-19 era in Japan. This study describes initial experiences with a small wireless ECG monitoring device and the utility of delivery via the postal service for outpatient care in Japan.Methods and Results:Long-term ECG monitoring following postal delivery of the small ECG device was evaluated in 25 patients. The patients had no difficulties with either the postal delivery or self-fitting and wearing the devices. A median of 57 h monitoring per patient was performed. Arrhythmic events were detected in 8 patients. Most patients were satisfied with both the ECG devices and postal delivery.Conclusions:Postal delivery of ECG devices could be used in clinical practice to achieve less or no in-person contact during the COVID-19 era.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Takami Koji Fukuzawa Kunihiko Kiuchi Hiroyuki Takahara Kimitake Imamura Toshihiro Nakamura Yusuke Sonoda Kazutaka Nakasone Kyoko Yamamoto Yuya Suzuki Kenichi Tani Hidehiro Iwai Yusuke Nakanishi Mitsuhiko Shoda Atsushi Murakami Shogo Yonehara Ken-ichi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CR-23-0083, (Released:2023-10-28)
- 参考文献数
- 11
Background: There is a strong demand for remote monitoring systems to gather health data. This study investigated the safety, usefulness, and patient satisfaction in outpatient care using telehealth with real-time electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring after catheter ablation.Methods and Results: In all, 38 patients who underwent catheter ablation were followed up using telehealth. At the 3- and 6-month follow-up, a self-fitted Duranta ECG monitoring device was sent to the patient’s home before the online consultation. Patients attached the devices themselves, and the doctors viewed the patients by video chat and performed real-time ECG monitoring. The frequency of hospital visits and the ECG monitoring duration were compared with conventional in-person follow-up data (n=102). The completion rate for telehealth follow-up was 32 of 38 patients (84%). The number of hospital visits during the 6 months was significantly lower with telehealth follow-up than with conventional follow-up (median [interquartile range] 1 [1–1] vs. 5 [3–5]; P<0.0001). However, the ECG monitoring duration was approximately 4-fold longer for the telehealth follow-up (median [interquartile range] 89 [64–117] vs. 24 [0.1–24] h; P<0.0001). No major adverse events were observed during the telehealth follow-up. Patient surveys showed high satisfaction with telehealth follow-up due to reduced hospital visits.Conclusions: A combination of telehealth follow-up with real-time ECG monitoring increased the ECG monitoring duration and patient satisfaction without any adverse events.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Takami Koji Fukuzawa Kunihiko Kiuchi Hiroyuki Takahara Kimitake Imamura Toshihiro Nakamura Yusuke Sonoda Kazutaka Nakasone Kyoko Yamamoto Yuya Suzuki Kenichi Tani Hidehiro Iwai Yusuke Nakanishi Mitsuhiko Shoda Atsushi Murakami Shogo Yonehara Ken-ichi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Reports (ISSN:24340790)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.5, no.11, pp.415-423, 2023-11-10 (Released:2023-11-10)
- 参考文献数
- 11
Background: There is a strong demand for remote monitoring systems to gather health data. This study investigated the safety, usefulness, and patient satisfaction in outpatient care using telehealth with real-time electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring after catheter ablation.Methods and Results: In all, 38 patients who underwent catheter ablation were followed up using telehealth. At the 3- and 6-month follow-up, a self-fitted Duranta ECG monitoring device was sent to the patient’s home before the online consultation. Patients attached the devices themselves, and the doctors viewed the patients by video chat and performed real-time ECG monitoring. The frequency of hospital visits and the ECG monitoring duration were compared with conventional in-person follow-up data (n=102). The completion rate for telehealth follow-up was 32 of 38 patients (84%). The number of hospital visits during the 6 months was significantly lower with telehealth follow-up than with conventional follow-up (median [interquartile range] 1 [1–1] vs. 5 [3–5]; P<0.0001). However, the ECG monitoring duration was approximately 4-fold longer for the telehealth follow-up (median [interquartile range] 89 [64–117] vs. 24 [0.1–24] h; P<0.0001). No major adverse events were observed during the telehealth follow-up. Patient surveys showed high satisfaction with telehealth follow-up due to reduced hospital visits.Conclusions: A combination of telehealth follow-up with real-time ECG monitoring increased the ECG monitoring duration and patient satisfaction without any adverse events.
1 0 0 0 OA Clinical Significance of the Insulin Resistance Index as Assessed by Homeostasis Model Assessment
- 著者
- YUKIO IKEDA TADASHI SUEHIRO TOSHIHIRO NAKAMURA YOSHITAKA KUMON KOZO HASHIMOTO
- 出版者
- The Japan Endocrine Society
- 雑誌
- Endocrine Journal (ISSN:09188959)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.1, pp.81-86, 2001 (Released:2006-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 91 94
To examine the clinical significance of the insulin resistance index as determined by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR), we investigated the relationship between HOMA-IR and the insulin resistance estimated by the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp method in various subgroups and compared the significance of HOMA-IR with that of fasting plasma insulin levels (FIRI). HOMA-IR was significantly correlated to the inverse of the glucose infusion rate (1/GIR) in both diabetic and non-diabetic subjects (r=0.747, P<0.0001 and r=0.419, P<0.002, respectively). In the diabetic patients, treatment with sulfonylureas did not weaken this correlation (r=0.833, P<0.0001). HOMA-IR was found to be closely related to FIRI (r=0.932, P<0.0001), but HOMA-IR was more closely associated with 1/GIR than FIRI was. HOMA-IR as well as 1/GIR was correlated with the visceral fat area (VFA) more closely than with the subcutaneous fat area (SFA), while FIRI was correlated almost equally with both of them. In conclusion, HOMA-IR is a convenient and beneficial method for evaluating insulin resistance, especially in subjects with visceral fat accumulation, and reflects insulin resistance obtained by euglycemic clamp more accurately than FIRI alone.
1 0 0 0 OA Left Atrium Calcification After Multiple Catheter Ablation Procedures for Atrial Fibrillation
- 著者
- Daisuke Yakabe Yusuke Fukuyama Masahiro Araki Toshihiro Nakamura
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0583, (Released:2021-08-31)
- 参考文献数
- 1
- 被引用文献数
- 2