- 著者
- Ki-Bae Hong Sung Hee Han Yooheon Park Hyung Joo Suh Hyeon-Son Choi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.8, pp.1269-1276, 2018-08-01 (Released:2018-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 7
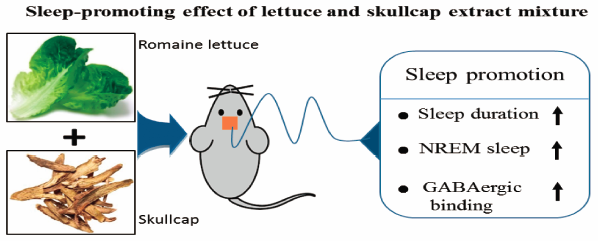
The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of romaine lettuce leaves extract (RE), skullcap root extract (SE) and their mixture on sleep behaviors in vertebrate models. HPLC analysis showed that RE contains lactucopicrin (0.02±0.01 mg/g extract), chlorogenic acid (4.05±0.03 mg/g extract), caffeic acid (2.38±0.03 mg/g extract), and chicoric acid (7.02±0.32 mg/g extract) as main phenolic compounds, while SE includes baicalin (99.4±0.5 mg/g extract), baicalein (8.28±0.21 mg/g extract), and wogonin (3.09±0.32 mg/g extract). The mixture of RE (100 mg/g extract) and SE (40 mg/g extract) increased total sleep time by 50.9% compared with the control in pentobarbital-induced sleep model. In electroencephalography (EEG) analysis, RE/SE mixture significantly increased Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM), in which delta wave was enhanced by around 40% compared with normal control, leading to the increase of sleep time. In caffeine-induced wake model, RE/SE mixture greatly decreased (53%) caffeine-induced wake time, showing a similar level to normal control. In addition, caffeine-induced decreased of NREM and delta wave effectively increased with RE/SE mixture; NREM and delta wave increased by 85% and 108%, respectively. Furthermore, RE/SE mixture was shown to bind to a gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA)-benzodiazepine (BZD) receptor stronger than RE or SE single extract. Taken together, RE/SE mixture effectively improved sleep behavior with the increase of NREM via GABAA-BZD receptor binding. RE/SE mixture can be used as an herbal agent for sleep disorders.
1 0 0 0 OA Lipid Bilayers Manipulated through Monolayer Technologies for Studies of Channel-Membrane Interplay
- 著者
- Shigetoshi Oiki Masayuki Iwamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.3, pp.303-311, 2018-03-01 (Released:2018-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 82
- 被引用文献数
- 12
Fluidity and mosaicity are two critical features of biomembranes, by which membrane proteins function through chemical and physical interactions within a bilayer. To understand this complex and dynamic system, artificial lipid bilayer membranes have served as unprecedented tools for experimental examination, in which some aspects of biomembrane features have been extracted, and to which various methodologies have been applied. Among the lipid bilayers involving liposomes, planar lipid bilayers and nanodiscs, recent developments of lipid bilayer methods and the results of our channel studies are reviewed herein. Principles and techniques of bilayer formation are summarized, which have been extended to the current techniques, where a bilayer is formed from lipid-coated water-in-oil droplets (water-in-oil bilayer). In our newly developed method, termed the contact bubble bilayer (CBB) method, a water bubble is blown from a pipette into a bulk oil phase, and monolayer-lined bubbles are docked to form a bilayer through manipulation by pipette. An asymmetric bilayer can be readily formed, and changes in composition in one leaflet were possible. Taking advantage of the topological configuration of the CBB, such that the membrane’s hydrophobic interior is contiguous with the surrounding bulk organic phase, oil-dissolved substances such as cholesterol were delivered directly to the bilayer interior to perfuse around the membrane-embedded channels (membrane perfusion), and current recordings in the single-channel allowed detection of immediate changes in the channels’ response to cholesterol. Chemical and mechanical manipulation in each monolayer (monolayer technology) allows the examination of dynamic channel-membrane interplay.
- 著者
- Jun Ho Kim Jin Hyup Lee Young Jun Kim
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b15-00585, (Released:2015-11-06)
- 参考文献数
- 14
This article has been retracted by the Editorial Committee of The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan because it contains scientific misconduct. Although the data published in this article were generated in part by the first author, the authors violated authorship and sponsorship protocol.
- 著者
- Kazuaki Matsumoto Akari Shigemi Kazuro Ikawa Naoko Kanazawa Yuko Fujisaki Norifumi Morikawa Yasuo Takeda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.2, pp.235-238, 2015-02-01 (Released:2015-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 5 22
Ganciclovir is a nucleoside guanosine analogue that exhibits therapeutic activity against human cytomegalovirus infection, and is primarily excreted via glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion. The adverse effects induced by ganciclovir therapy are generally of a hematological nature and include thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Low marrow cellularity and elevated serum creatinine have been identified as risk factors for ganciclovir-induced neutropenia. However, the risk factors for thrombocytopenia have yet to be determined. Therefore, this study investigated patients administered ganciclovir to determine the risk factors for thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 41 of these patients (30.6%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified three independent risk factors for thrombocytopenia: cancer chemotherapy (odds ratio (OR)=3.1), creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) (OR=12.8), and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=15.1). Leukopenia occurred in 36 patients (28.6%), and white blood cell count (<6000 cells/mm3) (OR=3.7) and the ganciclovir dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) (OR=7.8) were identified as risk factors. These results demonstrated that several factors influenced the occurrence of ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, and suggest that special attention should be paid to patients receiving cancer chemotherapy with a low creatinine clearance (<20 mL/min) and high dose (≥12 mg/kg/d) in order to avoid ganciclovir-induced thrombocytopenia.
- 著者
- Shuichi Fujimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.10, pp.1923-1929, 2007-10-01 (Released:2007-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 12 22
TAS-103, 6-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno-[2,1-c]quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride, is a dual topoisomerases I and II inhibitor. Antitumor activities of TAS-103 against fresh surgical specimens resected from 525 patients (32 types of tumors) were examined by flow cytometric (FCM) analysis of DNA integrity of tumor cells, and compared with those of five other investigational new drugs and 31 clinically available anticancer agents. Concentrations of clinically available anticancer agents were set at one-tenth of the peak plasma concentration (PPC) of the clinically recommended doses. On the other hand, since PPCs of investigational new drugs in humans were frequently unknown, these were estimated by a method that determines the theoretically achievable concentration in body fluid (TAC method). Correlations between TAC and PPC were examined for 16 clinically available anticancer agents, and it was found that TAC at 7n (the modified Fibonacci's dose-escalation scheme) of 14 drugs corresponded well with each one-tenth of PPC. By defining a 30% or more reduction in the integrated diploid peak as effective and a 60% or more reduction as definitely effective, TAS-103 at 5 μg/ml (7n) showed significantly higher effective rates and definitely effective rates than those of all other investigational new drugs, as well as almost all clinically available anticancer agents, against various malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer, brain tumor and renal cancer. These results strongly suggest that TAS-103 will be expected to show excellent antitumor activities against a wide range of human tumors.
- 著者
- Kosuke Shimizu Miki Takada Tomohiro Asai Koichi Kuromi Kazuhiko Baba Naoto Oku
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.25, no.10, pp.1385-1387, 2002 (Released:2002-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 6 8
A novel anti-tumor agent, 6-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-7H-indeno[2,1-c]quinolin-7-one dihydrochloride (TAS-103), effectively inhibits both topoisomerase I and II activities. To enhance anti-tumor efficacy and to reduce the side effects of the agent, liposomalization of TAS-103 was performed. TAS-103 was effectively entrapped in liposomes by a remote-loading method, and was stable at 4 °C and in the presence of 50% serum. To evaluate the anti-tumor efficacy of liposomal TAS-103, the growth inhibition against Lewis lung carcinoma cells in vitro and the therapeutic efficacy against solid tumor-bearing mice in vivo were examined. Liposomal TAS-103 showed strong cytotoxic effect against Lewis lung carcinoma cells in a dose dependent manner and effectively suppressed solid tumor growth accompanying longer survival time of tumor-bearing mice in comparison with the mice treated with free TAS-103. These results suggest that liposomal TAS-103 is useful for cancer therapy.
- 著者
- Jin Sun Lee Myung Sun Lee Won Keun Oh Ji Young Sul
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.8, pp.1427-1432, 2009-08-01 (Released:2009-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 26 53
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is highly expressed in breast carcinomas to support their continuous growth and proliferation, but has low expression level in normal tissues. Considerable interest has been developed in searching for novel FASN inhibitors as a therapeutic target for breast cancer. In present study, amentoflavone was isolated from Selaginella tamariscina, a traditional oriental medicine that has been used to treat cancer for many years, and was found to significantly inhibit the in vitro enzymatic activity of FASN at concentrations above 50 μM. Amentoflavone was also found to decrease fatty acid synthesis by the reduction of [3H]acetyl-CoA incorporation into lipids in FASN-overexpressed SK-BR-3 human breast cancer cells. Furthermore, this study showed that amentoflavone, at a concentration greater than 75 μM, increased the cleavage-activity of caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and administration of pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK completely rescued the SK-BR-3 cells from PARP cleavages. The sequential internucleosomal DNA fragmentation in SK-BR-3 cells was observed at a concentration of 100 μM. A decrease in breast cancer cell growth was observed in SK-BR-3 cells at 12 and 24 h post treatment with 100 μM of amentoflavone, followed by a dramatic suppression after 48 h. The inhibition of cancer-growth by amentoflavone was dose-dependent, showing a slight reduction at 50 μM and significant reduction at concentrations of 75 and 100 μM. FASN-nonexpressed NIH-3T3 normal cell growth was not decreased by amentoflavone-treatment, both in time- and dose-dependent manners. These data provide evidence that amentoflavone isolated from S. tamariscina induced breast cancer apoptosis through blockade of fatty acid synthesis.
- 著者
- Zhihua Yue Jinhai Shi Haona Li Huiyi Li
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.2, pp.158-162, 2018-02-01 (Released:2018-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are likely to be used concomitantly with acyclovir or valacyclovir in clinical practice, but the study on the safety of such combinations was seldom reported. The objective of the study was to investigate reports of acute kidney injury (AKI) events associated with the concomitant use of oral acyclovir or valacyclovir with an NSAID by using the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS) database between January 2004 and June 2012. The frequency of AKI events in patients while simultaneously taking either acyclovir or valacyclovir and an NSAID was compared using the Chi-square test. The effect of concomitant use of acyclovir or valacyclovir and individual NSAIDs on AKI was analyzed by the reporting odds ratio (ROR). The results showed that AKI was reported as the adverse event in 8.6% of the 10923 patients taking valacyclovir compared with 8.7% of the 2556 patients taking acyclovir (p=NS). However, AKI was significantly more frequently reported in patients simultaneously taking valacyclovir and an NSAID (19.4%) than in patients simultaneously taking acyclovir and an NSAID (10.5%) (p<0.01). The results also suggested that increased risk of AKI was likely associated with the concomitant use of valacyclovir and some NSAIDs such as loxoprofen, diclofenac, etodolac, ketorolac, piroxicam or lornoxicam. The case series from the AERS indicated that compared with acyclovir, valacyclovir is more likely to be affected by NSAIDs, and the concomitant use of valacyclovir with some NSAIDs might be associated with increased risk of AKI. The drug interactions with this specific combination of medications are worth exploring further.
1 0 0 0 OA Mechanism of the Tissue-Specific Action of the Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator S-101479
- 著者
- Kazuyuki Furuya Noriko Yamamoto Yuki Ohyabu Teruyuki Morikyu Hirohide Ishige Michael Albers Yasuhisa Endo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.3, pp.442-451, 2013-03-01 (Released:2013-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 56
- 被引用文献数
- 8 26
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) comprise a new class of molecules that induce anabolic effects with fewer side effects than those of other anabolic agents. We previously reported that the novel SARM S-101479 had a tissue-selective bone anabolic effect with diminished side effects in female animals. However, the mechanism of its tissue selectivity is not well known. In this report, we show that S-101479 increased alkaline phosphatase activity and androgen receptor (AR) transcriptional activity in osteoblastic cell lines in the same manner as the natural androgen ligand dihydrotestosterone (DHT); conversely, stimulation of AR dimerization was very low compared with that of DHT (34.4%). S-101479 increased bone mineral content in ovariectomized rats without promoting endometrial proliferation. Yeast two-hybrid interaction assays revealed that DHT promoted recruitment of numerous cofactors to AR such as TIF2, SRC1, β-catenin, NCoA3, gelsolin and PROX1 in a dose-dependent manner. SARMs induced recruitment of fewer cofactors than DHT; in particular, S-101479 failed to induce recruitment of canonical p160 coactivators such as SRC1, TIF2 and notably NCoA3 but only stimulated binding of AR to gelsolin and PROX1. The results suggest that a full capability of the AR to dimerize and to effectively and unselectively recruit all canonical cofactors is not a prerequisite for transcriptional activity in osteoblastic cells and resulting anabolic effects in bone tissues. Instead, few relevant cofactors might be sufficient to promote AR activity in these tissues.
- 著者
- Ha Jeoung-Hee Lee Maan-Gee Chang Soo-Min LEE Jae-Tae
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.29, no.7, pp.1414-1417, 2006-07-01
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Fossilia Mastodi Ossis, which is a skeletal fossil of a Mastodon, an ancient mammal, has been found to have anxiolytic, sedative and anticonvulsant activities in Oriental medicine. In this study, in vivo characterization of the sedative activities of Fossilia Mastodi OSSIS was performed in order to obtain basic information for the development of a putative natural sedative. The 80% methanol extract of Fossilia Mastodi OSSIS given per os at a dose of 3g/kg in mice showed anxiolysis, potentiation of pentobarbital sleeping time, reduced locomotor activity, and anticonvulsive activity. Fossilia elicited GABA_A receptor-mediated anxiolysis. The data obtained suggest that the 80% methanol extract of Fossilia Mastodi OSSIS contains some biologically active principles with sedative activity.
- 著者
- Sandoval Moises Burgos Johanna Sepulveda Francisco V. Cid L. Pablo
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.6, pp.803-809, 2011
- 被引用文献数
- 10
The importance of intracellular pH (pH<sub>i</sub>) in the regulation of diverse cellular activities ranging from cell proliferation and differentiation to cell cycle, migration and apoptosis has long been recognised. More recently, extracellular pH (pH<sub>o</sub>), in particular that of relatively inaccessible compartments or domains that occur between cells in tissues, has begun to be acknowledged as a relevant signal in cell regulation. This should not be surprising given the abundant reports highlighting the pH<sub>o</sub>-dependence of the activity of membrane proteins facing the extracellular space such as receptors, transporters, ion channels and enzymes. Changes in pH affect the ionisation state of proteins through the effect on their titratable groups. There are proteins, however, which respond to pH shifts with conformational changes that are crucial for catalysis or transport activity. In such cases protons act as signalling molecules capable of eliciting fast and localised responses. We provide examples of ion channels that appear fastidiously designed to respond to extracellular pH in a manner that suggests specific functions in transporting epithelia. We shall also present ideas as to how these channels participate in complex transepithelial transport processes and provide preliminary experiments illustrating a new way to gauge pH<sub>o</sub> in confined spaces of native epithelial tissue.
- 著者
- Yuki Hasebe Kiyoshi Egawa Yoko Yamazaki Setsuko Kunimoto Yasuaki Hirai Yoshiteru Ida Kiyoshi Nose
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, no.10, pp.1379-1383, 2003 (Released:2003-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 35
- 被引用文献数
- 30 41
Screening using a reporter under the control of the hypoxia-response element (HRE) identified several flavonoids and homoisoflavonoids that inhibit the activation of HRE under hypoxic conditions. Among various compounds, isorhamnetin, luteolin, quercetin, and methyl ophiopogonanone B (MOB) were effective at 3 to 9 μg/ml in inhibiting the reporter activity. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA during hypoxia was also inhibited by MOB in HepG2 cells, but the effective doses were 10 to 20 μg/ml. MOB caused destabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, as revealed by Western blotting, that was dependent on proteasome activity and the tumor suppressor, p53. The tubular formation and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells was also inhibited by MOB. MOB is expected to act as an inhibitor of angiogenesis.
1 0 0 0 OA Temporal Kinetics of Microgliosis in the Spinal Dorsal Horn after Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rodents
- 著者
- Keita Kohno Junko Kitano Yuta Kohro Hidetoshi Tozaki-Saitoh Kazuhide Inoue Makoto Tsuda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1096-1102, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 33
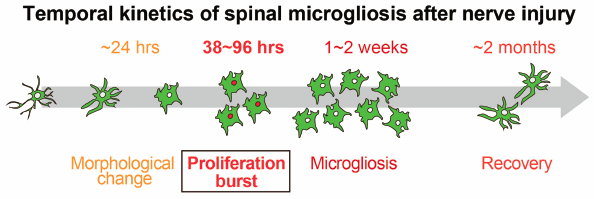
Neuropathic pain, a highly debilitating chronic pain following nerve damage, is a reflection of the aberrant functioning of a pathologically altered nervous system. Previous studies have implicated activated microglia in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) as key cellular intermediaries in neuropathic pain. Microgliosis is among the dramatic cellular alterations that occur in the SDH in models of neuropathic pain established by peripheral nerve injury (PNI), but detailed characterization of SDH microgliosis has yet to be realized. In the present study, we performed a short-pulse labeling of proliferating cells with ethynyldeoxyuridine (EdU), a marker of the cell cycle S-phase, and found that EdU+ microglia in the SDH were rarely observed 32 h after PNI, but rapidly increased to the peak level at 40 h post-PNI. Numerous EdU+ microglia persisted for the next 20 h (60 h post-PNI) and decreased to the baseline on day 7. These results demonstrate a narrow time window for rapidly inducing a proliferation burst of SDH microglia after PNI, and these temporally restricted kinetics of microglial proliferation may help identify the molecule that causes microglial activation in the SDH, which is crucial for understanding and managing neuropathic pain.
- 著者
- Guo-dong Xu Lei Cai Yi-shu Ni Shi-yi Tian Ying-qi Lu Li-na Wang Lian-lian Chen Wen-ya Ma Shao-ping Deng
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.7, pp.1024-1033, 2018-07-01 (Released:2018-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 54
- 被引用文献数
- 16
Acarbose and voglibose are the most widely used diabetes drugs as glycosidase inhibitors. In this study, the use of these two inhibitors significantly increased the content of starch in large intestine, and altered the concentration of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) by affecting the intestinal microbiota. However, there are some differences in the intestinal microbiome of the two groups of mice, mainly in bacteria such as Bacteroidaceae bacteroides and Desulfovibrionaceae desulfovibrio. The productions of acetate and propionate in caecum in voglibose group were significantly higher than those in acarbose group and two kinds of glycosidase inhibitors were close in the production of butyrate in caecum. The Tax4Fun analysis based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) data indicated that different productions of acetate and propionate between acarbose group and voglibose group may be related to 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase and pyruvate oxidase. In addition, in-vitro experiments suggested that voglibose had less effect on epithelial cells than acarbose after direct stimulation. According to the recent researches of SCFAs produced by intestinal microbiota, our comparative study shown higher concentration of these beneficial fatty acids in the lumen of voglibose-treated mice, which implied a lower level of inflammation.
- 著者
- Nobuyoshi Kobayashi Koichi Seto Yuki Orikawa Hiroki Hamano Koji Yoshinaga Mineo Takei
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.33, no.2, pp.216-222, 2010-02-01 (Released:2010-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 6 10
Z-360 is a novel cholecystokinin (CCK)-2/gastrin receptor antagonist that is being developed for the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in combination with gemcitabine. A previous study shows that the co-administration of Z-360 with gemcitabine significantly prolonged the survival of mice with orthotopically implanted human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. To clarify the therapeutic effects of Z-360 in combined with gemcitabine, we analyzed gene expression. When gemcitabine was administered, CCK-2/gastrin receptor expression was induced in an orthotropic xenograft model; the result indicating that Z-360 could act on gemcitabine-sensitive cells. Both in vitro and in vivo studies showed that gemcitabine increased the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), a prognostic factor for survival in pancreatic cancer, while Z-360 suppressed this induction of VEGFA gene expression. These results help to explain how Z-360 prolongs survival when used in combination with gemcitabine.
1 0 0 0 OA The Involvement of the Oxidative Stress in Murine Blue LED Light-Induced Retinal Damage Model
- 著者
- Maho Nakamura Yoshiki Kuse Kazuhiro Tsuruma Masamitsu Shimazawa Hideaki Hara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.8, pp.1219-1225, 2017-08-01 (Released:2017-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 1 43
The aim of study was to establish a mouse model of blue light emitting diode (LED) light-induced retinal damage and to evaluate the effects of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Mice were exposed to 400 or 800 lx blue LED light for 2 h, and were evaluated for retinal damage 5 d later by electroretinogram amplitude and outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness. Additionally, we investigated the effect of blue LED light exposure on shorts-wave-sensitive opsin (S-opsin), and rhodopsin expression by immunohistochemistry. Blue LED light induced light intensity dependent retinal damage and led to collapse of S-opsin and altered rhodopsin localization from inner and outer segments to ONL. Conversely, NAC administered at 100 or 250 mg/kg intraperitoneally twice a day, before dark adaptation and before light exposure. NAC protected the blue LED light-induced retinal damage in a dose-dependent manner. Further, blue LED light-induced decreasing of S-opsin levels and altered rhodopsin localization, which were suppressed by NAC. We established a mouse model of blue LED light-induced retinal damage and these findings indicated that oxidative stress was partially involved in blue LED light-induced retinal damage.
- 著者
- Miwa NISHIDA Ayako HINO Kazushige MORI Takehisa MATSUMOTO Takashi YOSHIKUBO Hideo ISHITSUKA
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.19, no.11, pp.1407-1411, 1996-11-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 87 100
The antitumor activity of cytostatic 5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine (5'-dFUrd) depends on its being converted to 5-fluorouracil (5-FUra) by the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase (dThdPase, EC 2.4.2.4). We prepared mouse anti-human dThdPase monoclonal antibodies to serve as tools for clinical studies with this drug. Partially purified dThdPase obtained from HCT116 human colon cancer cells grown in athymic mice was used as an antigen for the immunization of mice. Six hydridomas were cloned which produced anti-human dThdPase antibodies, as detected by Western blot analysis with human dThdPase. With these antibodies, we developed an ELISA method sensitive enough to measure dThdPase levels, even in tumor tissue samples weighing as little as 10 mg. In addition, one monoclonal antibody was suitable for immunologically staining the enzyme in tumor tissues. Thus, these anti-human dThdPase monoclonal antibodies could be used to measure levels of the enzyme in tumor cells, which is essential for the activation of 5'-dFUrd.
- 著者
- Tohru ISHIKAWA Yu FUKASE Taeko YAMAMOTO Fumiko SEKIGUCHI Hideo ISHITSUKA
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.21, no.7, pp.713-717, 1998-07-15 (Released:2008-04-10)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 28 39
Capecitabine (N4-pentyloxycarbonyl-5'-fluorocytidine) is a novel fluoropyrimidine carbamate that was synthesized for the purpose of finding antitumor drugs with improved safety and efficacy profiles compared with those of 5-fluorouracil (5-FUra) and doxifluridine (5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine, 5'-dFUrd). The present study compared the antitumor activities of the compound with those of other fluoropyrimidines in 12 human cancer xenograft models and their antimetastatic activities in murine tumor models. The antitumor efficacy of capecitabine was greater than those of 5'-dFUrd, UFT (a mixture of tegafur and uracil) and 5FUra. Capecitabine was also much safer, particularly much less toxic to the intestinal tract, than the other compounds, indicating higher therapeutic indices. The therapeutic indices. The therapeutic indices of capecitabine, 5'-dFUrd and 5-FUra were >40, >20 and 2.0 against the human CXF280 colon cancer xenograft, the most sensitive line to the fluoropyrimidines so far tested, and 5.1, 1.5, and <1.5 against the human HCT116 colon cancer xenograft with ordinary sensitivity, respectively. In addition, capecitabine, as well as 5'-dFUrd, selectively suppressed the spontaneous metastasis of mouse Lewis lung carcinoma in mice at extremely low doses, 32-64 fold lower than their minimum effective dose (MED) against the primary tumor growth. Capecitabine was even more antimetastatic than 5'-dFUrd. These results indicate that dapecitabine has high therapeutic potential.
1 0 0 0 Effects of Fatty Acid Glycerol Esters on Intestinal Absorptive and Secretory Transport of Ceftibuten
- 著者
- Koga Kenjiro Murakami Masahiro Kawashima Susumu
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.22, no.4, pp.402-406, 1999-04-15
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The effects of fatty acid glycerol esters and Tweens on the intestinal transport of ceftibuten were studied using a diffusion chamber system. The apparent permeation coefficient (P<SUB>app</SUB>) was used as an index of the mucosal permeability to ceftibuten. The P<SUB>app</SUB> markedly increased by the addition of hexaglycerol monostearate (HGMS) or hexaglycerol sesquistearate (HGSS) under an H<SUP>+</SUP>-gradient condition, while hexaglycerol tristearate (HGTS) and Tweens showed no effect on the absorptive ceftibuten permeability. These result are in agreement with those obtained in the previous study in the brush-border membrane vesicles. On the other hand, in the absence of an H<SUP>+</SUP>-gradient, the S-to-M transport of ceftibuten was proven to be significantly higher than the M-to-S one. In addition, either ATP-depletion of the mucosa or the addition of probenecid proved to enhance significantly the permeability of ceftibuten. These findings suggest the existence of an active secretory transport system for ceftibuten in the jejunal mucosa. To estimate potential effects of glycerol esters on efflux pumps as well as peptide transporters, the mucosal-to-serosal (M-to-S) and serosal-to-mucosal (S-to-M) permeability in the presence of the esters was further examined. HGMS, HGSS and HGTS markedly enhanced the M-to-S but not the S-to-M transport in the ATP-depleted jejunum without an H<SUP>+</SUP>-gradient, in which conditions contributions of both peptide transporter and efflux pump should be substantially small. HGMS and HGSS significantly enhanced the M-to-S ceftibuten transport in the ATP-depleted jejunum with an H<SUP>+</SUP>-gradient (p<0.01 vs. M-to-S transport without surfactant under the same conditions). Whereas, these glycerol esters were fround hardly to affect the P<app> of the S-to-M transport. These results indicate that the enhanced intestinal transport of ceftibuten due to the glycerol esters may be based on their effects on peptide transporters but neither on efflux pumps nor on the passive permeation routes.
- 著者
- Maya Fujita Takaki Yagi Umi Okura Jun’ichi Tanaka Naohide Hirashima Masahiko Tanaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.5, pp.786-796, 2018-05-01 (Released:2018-05-01)
- 参考文献数
- 49
- 被引用文献数
- 9
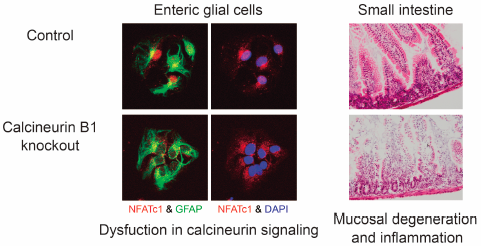
Although calcineurin is abundantly expressed in the nervous system and involved in neurite extension and synaptic plasticity in neurons, little is known about its roles in glial cells. To investigate the roles of calcineurin in glial cells, we generated glial calcineurin B1-conditional knockout (CKO) mice and analyzed the abnormalities in the small intestine. The CKO mice were generated by crossing floxed calcineurin B1 mice with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-Cre mice. The CKO mice exhibited growth retardation approximately from the third postnatal week and died mostly within the fourth postnatal week. The small intestine of the CKO mice was thin and hemorrhagic. The mucosal layer was degenerated and GFAP expression was reduced in the CKO small intestine. These pathological changes were associated with inflammation and increased intestinal permeability. In contrast, no apparent abnormalities were observed in the large intestine of the CKO mice. Nuclear factor of activated T cells failed to translocate into the nucleus after stimulation in enteric glial cells of the CKO small intestine. In conclusion, the calcineurin B1 deficiency in glial cells impairs the small intestine and leads to malnutrition and eventual death in mice, suggesting that calcineurin plays a novel and important role in enteric glial cells.