- 著者
- 山崎 詩郎
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.4, pp.189-190, 2021
1 0 0 0 近代五種とオリンピック精神
- 著者
- 泉川 寛晃
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.2, pp.74-76, 2020
- 著者
- 清水 亮太
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面科学会 / 一般社団法人 日本真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.2, pp.100-101, 2018
1 0 0 0 OA Van der Waals結晶原子層におけるモアレ模様と電子構造
- 著者
- 越野 幹人
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.11, pp.706-711, 2018-11-10 (Released:2018-11-10)
- 参考文献数
- 26
We present an overview of recent studies on the moiré superlattices in Van der Waals atomic layer materials. We first introduce typical moiré superlattices such as twisted bilayer graphene and graphene h-BN superlattice. We also argue about the Hofstadter fractal energy spectrum in magnetic fields, the strain effect and domain formation, and the graphene quasicrystals.
1 0 0 0 OA モントレー湾水族館研究所MBARIの日々
- 著者
- 中山 典子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.11, pp.745-746, 2018-11-10 (Released:2018-11-10)
1 0 0 0 量子アニーリングのための超伝導パラメトロン素子
- 著者
- 白根 昌之 山本 剛
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.63, no.3, pp.112-116, 2020-03-10 (Released:2020-03-10)
- 参考文献数
- 36
Quantum annealing is a method for finding the global minimum of a given objective function by using quantum fluctuations and is used mainly for combinatorial optimization problems where the search space is discrete. For ideal quantum annealing quantum bits which have long coherence time and scalability are necessary, and superconducting circuits are promising candidates for them. This is because high coherence is expected due to superconducting phenomena and high integration is realized by solid-state devices. In this paper quantum annealing based on superconducting parametric oscillators and related technology are introduced.
1 0 0 0 OA 周波数変調原子間力顕微鏡で測定するエネルギー散逸
- 著者
- 新井 豊子
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.10, pp.632-638, 2018-10-10 (Released:2018-10-10)
- 参考文献数
- 25
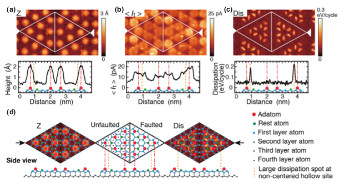
Frequency modulation atomic force microscopy (FM-AFM) can simultaneously detect the conservative and non-conservative force interactions between a tip and a sample, based on the resonance frequency shift (Δf) and the mechanical energy dissipation of an oscillating cantilever, respectively. Here, we outline the energy dissipation measured by FM-AFM and introduce our recent results obtained through measurement of the energy dissipation. First, surface resistances can be evaluated in non-contact using the proportional relationship between the energy dissipation due to Joule heat and Δf due to the electrostatic attractive force. Second, Si adatoms on a Si(111)-(7×7) surface, which are observed to be static by FM-AFM, can move back and force between their stable sites and their neighboring quasi-stable sites, detected by measuring of the energy dissipation.
1 0 0 0 OA 合併による大いなる飛躍の年
- 著者
- 大門 寛
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.1, pp.1-2, 2018-01-10 (Released:2018-01-24)
1 0 0 0 OA 第1回日本表面真空学会若手研究会
- 著者
- 國貞 雄治
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.4, pp.229, 2019-04-10 (Released:2019-04-10)
1 0 0 0 グラフェン上での金属原子吸着状態の理論的研究
- 著者
- 長谷川 瞬 國貞 雄治 坂口 紀史
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.6, pp.344-349, 2019-06-10 (Released:2019-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1
We investigated the adsorption states and diffusion behavior of Pt and Fe atoms on pristine and various light-element-doped graphene using first-principle calculations based on density functional theory to reveal the support that can keep particle size of metal clusters for a long time. We show a weak interaction between Pt, Fe atoms and pristine graphene. The corresponding diffusion barrier for a Pt atom on pristine graphene is only 0.14 eV, which causes rapid agglomeration of Pt clusters. However, light-element-doped graphene shows large diffusion barrier for metal atoms. Notably, O, Si and P doped graphene show large diffusion barrier for both Pt and Fe atoms. Therefore, these light-element-doped graphene is a promising support for Pt and Fe clusters.
- 著者
- 伝宝 一樹
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.6, pp.318-323, 2019-06-10 (Released:2019-06-10)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We have successfully created a Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) model on a commercial FEM software COMSOL Multiphysics (COMSOL). As far as we know, this is the first DSMC model developed on COMSOL. Since two particles as a colliding pair cannot be sampled simultaneously from the same population in the Particle-tracing module of COMSOL, a new inter-molecular collision scheme named “quasi-Nanbu scheme” has been introduced to the model. The results obtained for benchmark problems using the present DSMC model agree well with those from a theory and other DSMC codes.
1 0 0 0 OA 海の向こうで暮らしてみれば
- 著者
- 持箸 晃
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.5, pp.304-305, 2019-05-10 (Released:2019-05-10)
1 0 0 0 カーボンナノチューブのオゾンによる損傷の評価
- 著者
- 石川 諒 中野 尭雄 島 龍之介 清水 麻希 本間 芳和
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.12, pp.797-801, 2018-12-10 (Released:2018-12-10)
- 参考文献数
- 19
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are light and highly tensile, which makes them a candidate material for space elevator. However, CNTs are not resistant to oxidant. We studied the damage of CNTs caused by exposure to ozone using several kinds of single-walled CNTs with varying crystallinity and morphology. We found a correlation between the initial crystallinity and resistance to ozone : high-crystallinity CNTs with a small number of defects were lightly damaged by ozone exposure, while highly-defective CNTs were further damaged. The thickness of bundling also affected the resistance to ozone. High-crystallinity CNTs forming a thick bundle were most resistant to ozone.
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.54, 2019
- 著者
- 中野 武雄 小森 文夫 福谷 克之 谷本 育律
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.48-50, 2019-01-10 (Released:2019-01-10)
- 参考文献数
- 3
- 著者
- 高草木 達 朝倉 清高
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本表面真空学会
- 雑誌
- 表面と真空 (ISSN:24335835)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.5, pp.309-314, 2018-05-10 (Released:2018-05-10)
- 参考文献数
- 25
3D structures of evaporated metals onto a TiO2(110) surface premodified with ortho-mercaptobenzoic acid (o-MBA) were studied using polarization-dependent total reflection fluorescence X-ray absorption fine structure (PTRF-XAFS) technique to determine the effects of the premodification on the dispersion of the metal atoms over the TiO2(110) surface. Cu, Au and Ni were found to be atomically dispersed, with the formation of S-metal-O bonds (where the S is provided by the o-MBA and the O is present in the TiO2 lattice) on the surface. In contrast, Pt underwent aggregation to form small clusters. The varying behavior of these metals on the o-MBA-modified TiO2(110) surface can be explained based on the energy difference between sulfur-metal-oxygen and metal-metal bond formations, and we propose a new indicator for single metal dispersion on the TiO2(110) surface.