本基盤研究では、船舶及び海洋構造物を対象とした防食、特にSUS304ステンレス材料のすきま腐食の防止に必要な放射線誘起表面活性(RISA)のメカニズムの解明、すきま腐食に対する適切な皮膜の基礎開発及び、人工海水中のRISAの効果の確認を行い、以下の結果を得た。1)試験片に小型密封放射線源^<60>Coを密着させ、その裏面から照射されるγ線を利用した実験により、ステンレス鋼の不動態皮膜をより強固にすることで局部腐食の発生を抑制し、RISA防食法が放射線照射施設外においても応用できることがわかった。2)放射化試験片自らが発するγ線を利用した実験により、中・強放射化試験片では安定した不動態皮膜を保ち、厳しい腐食環境下でも耐食性が維持できることがわかった。3)腐食電位の卑化は密封放射線源の有無に対応しており、微弱放射線環境においてもRISA効果によりすきま腐食の抑制効果が得られる。4)SUS304鋼の腐食電位をカソード防食電位まで卑化させずとも、不動態皮膜を保持し、すきま腐食を防止することを確認した。5)放射化試験片自らが発する放射線を利用した実験により、66μGy/h以上の照射積算線量で安定した不動態皮膜を保ち、厳しい腐食環境下でも耐食性が維持できることを確認した。6)試験片の照射積算線量を変化させた場合、その積算線量の増加により防食効果が増大することを確認した。これまで防食亜鉛や防食塗料などの鉄鋼構造物腐食防止法の多くはいずれも海外先進国によって開発されており、船舶・海洋構造物の腐食制御技術は国外技術に依存しているが、この新しい船舶・海洋構造物の腐食制御方法は、エネルギー環境技術として、我が国の技術水準を向上させ世界に貢献する重要な手段になると期待される。
3 0 0 0 OA 炭素鋼の腐食速度と海塩を含む水膜の厚さの関係
- 著者
- 細矢 雄司 篠原 正 押川 渡 元田 慎一
- 出版者
- Japan Society of Corrosion Engineering
- 雑誌
- Zairyo-to-Kankyo (ISSN:09170480)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.54, no.8, pp.391-395, 2005-08-15 (Released:2011-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 6 17
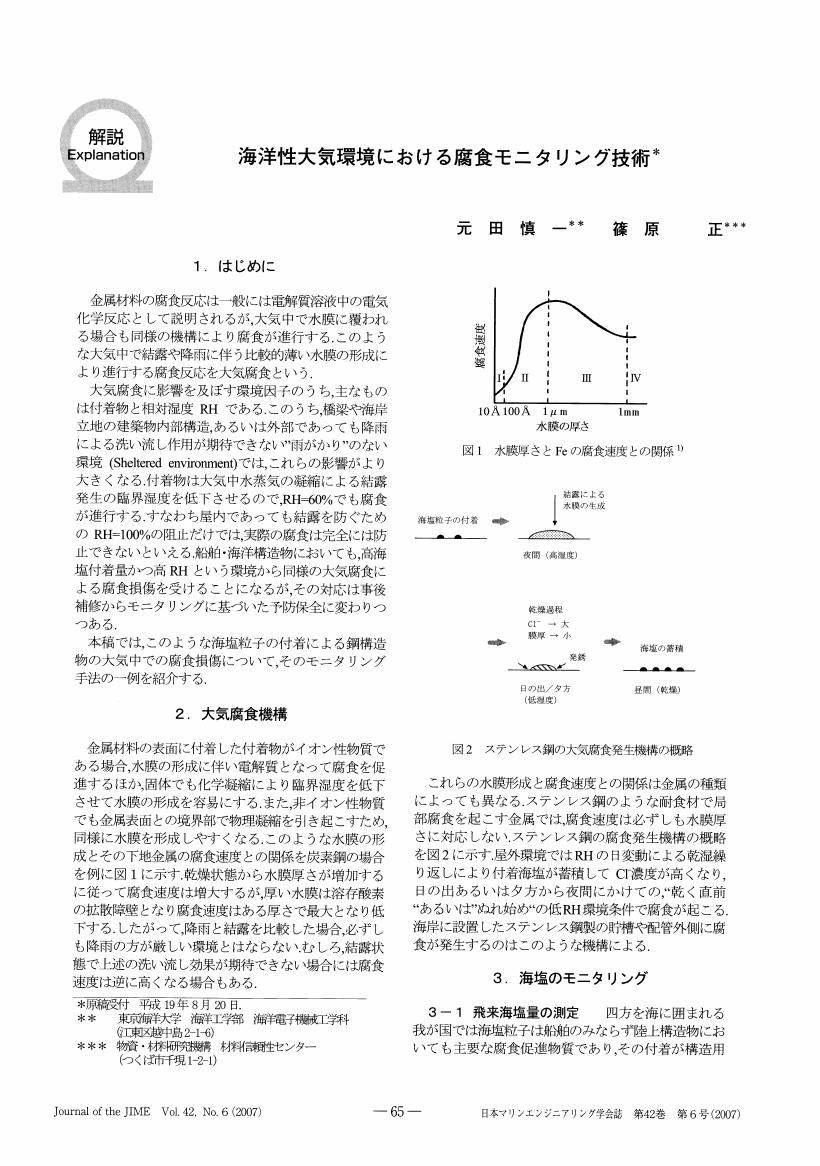
炭素鋼の大気腐食における環境の腐食性について, 付着海塩が吸水することによって表面に形成される水膜の厚さの影響を中心に検討した.付着海塩への吸着水量を種々の条件下で実測し, 形成された液膜の濃度を計算値と比較して熱力学計算が実験結果をよく再現する条件を得た. また種々の条件下で炭素鋼の腐食試験を行い, 熱力学計算で導出される水膜の厚さdと腐食速度CRとの関係について調べた. d=50μm近傍においてCRは最大値約0.07mgm-2s-1を取ることを見い出した.
3 0 0 0 OA 海洋性大気環境における腐食モニタリング技術
- 著者
- 元田 慎一 篠原 正
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 日本マリンエンジニアリング学会
- 雑誌
- マリンエンジニアリング (ISSN:13461427)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.6, pp.993-998, 2007-11-01 (Released:2010-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 12
1 0 0 0 OA Ⅲ.腐食の電気化学測定法の応用―ACM型腐食センサ―
- 著者
- 元田 慎一
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人 腐食防食学会
- 雑誌
- Zairyo-to-Kankyo (ISSN:09170480)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.4, pp.150-155, 2018-04-15 (Released:2018-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 28
本稿ではACMセンサの出力原理と基本的特性,および再現性に優れる作製プロセスを解説した.これによりACMによる大気腐食モニタリングを理解する一助としたい.
1 0 0 0 OA 強電解質が吸水してできる水膜組成と水膜厚さの推定
- 著者
- 押川 渡 篠原 正 元田 慎一
- 出版者
- Japan Society of Corrosion Engineering
- 雑誌
- Zairyo-to-Kankyo (ISSN:09170480)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.6, pp.293-298, 2003-06-15 (Released:2011-12-15)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 18 35
To estimate concentration and thickness of water film formed on metal surface in atmospheric environment, relative humidity (RH) data in equilibrium with various concentrations of strong electrolyte solutions were calculated with available thermodynamic data. The activity coefficient of water (fw(X)) for the solution with molar fraction of water (X) could be given as a function of ionic strength of the solution, which was determined by mean activity coefficient data in literatures for electrolytes in the solution. RH values obtained as RH(%)=100×fw(X)·X were fitted well with measured values of these solutions in each literatures, for example NaCl, MgCl2, Na2SO4, Mg(NO3)2 and so on. RH values for solutions with various contents of Na-MgCl ternary system were also calculated as NaCl-MgCl2 mixed solution. The calculated RH values were also fitted well with measured data. Using the relationship between density and concentration of the solution, the thickness of water film was also calculated. When the sea salt is put on 1g/m2, while the thickness of water film reaches 3-30μm in the range of relative humidity is larger than 75%, it remains 0.3-0.7μm in the range of relative humidity is smaller than 75% where NaCl solid state deposition occurs.