2 0 0 0 外性器形成過程の解析;細胞増殖因子群による陰茎、陰核形成制御
我々は本研究によって、哺乳類の外性器形成の特徴である陰茎および陰核形成メカニズムに迫った。哺乳類は脊権動物の中でも、良く発達した外性器を有している。高等哺乳類の外性器形成過程は、これまで分子発生学的に全く解明されておらず、そもそも如何なるメカニズムで胎生期に外性器原基(一種の突起構造)が伸長するのか、如何にそれが分化して外性器となるか殆ど理解されていない。陰茎および陰核はアダルトにおいてはその形態は大きく異なるものの、胎生期形態は後期に至るまで両性で類似した形を有している。ここでは体幹部から伸長、分化するメカニズムが雌雄で類似しており、さらに胎生末期から生後に到るホルモン影響下の分化の違いが出るという興味ある現象がある。我々は胎生期における陰核および陰茎形成プログラムとして間葉性のFGF遺伝子、および尿道上皮に発現するShh(ソニックヘッジホッグ)遺伝子が近接した状態で(尿道上皮のShhが中央に、両側にFGF10遺伝子が)発現し、それら相互作用が陰茎、陰核形成にとって、最も重要な尿道板/尿道形成に作用していることを世界で初めて見い出した。さらにこうしたShhおよびFGF遺伝子群が陰核、陰茎形態が顕著な哺乳類ばかりでなく、烏類胚(ヒダ状のものから突出した交接器を有するものまである)においてもこれら遺伝子発現が興味ある相関を示している事を見い出した。このようなメカニズムが今後さらに胎生後期から新生児期にホルモンの制御を受けるかに関して、これら細胞増殖因子群の遺伝子発現変化、及び形態変化を今後解析していく予定である。
1 0 0 0 脩身唱歌 : 教育勅語 : 全
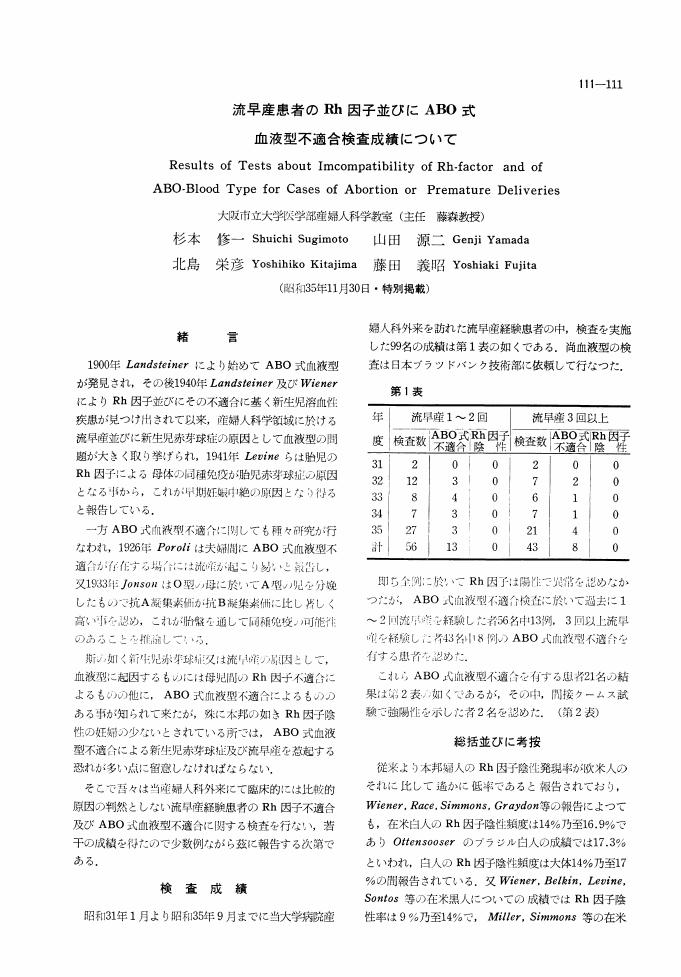
1 0 0 0 OA 流早産患者のRh因子並びにABO式血液型不適合検査成績について
1 0 0 0 眼窩底骨折を併発した頬骨・類骨弓骨折の2症例
- 著者
- 千野 武広 佐野 雄三 山田 源一郎 中川 喬
- 出版者
- Japanese Society of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
- 雑誌
- 日本口腔外科学会雑誌 (ISSN:00215163)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.21, no.3, pp.354-361, 1975
- 著者
- Suzuki Kentaro Daniel Bachiller Chen YiPing P. Kamikawa Mami Ogi Hidenao Haraguchi Ryuma Ogino Yukiko Minami Yasuhiro Mishina Yuji Ahn Kyung Crenshaw III E. Bryan Yamada Gen オギ ヒデナオ ハラグチ リュウマ オギノ ユキコ ヤマダ ゲン 尾木 秀直 原口 竜摩 荻野 由紀子 山田 源
- 出版者
- Company of Biologists
- 雑誌
- Development
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.130, no.25, pp.6209-6220, 2003-12
- 被引用文献数
- 3 111
Extra-corporal fertilization depends on the formation of copulatory organs: the external genitalia. Coordinated growth and differentiation of the genital tubercle (GT), an embryonic anlage of external genitalia, generates a proximodistally elongated structure suitable for copulation, erection, uresis and ejaculation. Despite recent progress in molecular embryology, few attempts have been made to elucidate the molecular developmental processes of external genitalia formation. Bone morphogenetic protein genes (Bmp genes) and their antagonists were spatiotemporally expressed during GT development. Exogenously applied BMP increased apoptosis of GT and inhibited its outgrowth. It has been shown that the distal urethral epithelium (DUE), distal epithelia marked by the Fgf8 expression, may control the initial GT outgrowth. Exogenously applied BMP4 downregulated the expression of Fgf8 and Wnt5a, concomitant with increased apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation of the GT mesenchyme. Furthermore, noggin mutants and Bmpr1a conditional mutant mice displayed hypoplasia and hyperplasia of the external genitalia respectively. noggin mutant mice exhibited downregulation of Wnt5a and Fgf8 expression with decreased cell proliferation. Consistent with such findings, Wnt5a mutant mice displayed GT agenesis with decreased cell proliferation. By contrast, Bmpr1a mutant mice displayed decreased apoptosis and augmented Fgf8 expression in the DUE associated with GT hyperplasia. These results suggest that some of the Bmp genes could negatively affect proximodistally oriented outgrowth of GT with regulatory functions on cell proliferation and apoptosis. The DUE region can be marked only until 14.0 dpc (days post coitum) in mouse development, while GT outgrowth continues thereafter. Possible signaling crosstalk among the whole distal GT regions were also investigated.