- 著者
- Yohei Okada Sho Komukai Tetsuhisa Kitamura Takeyuki Kiguchi Taro Irisawa Tomoki Yamada Kazuhisa Yoshiya Changhwi Park Tetsuro Nishimura Takuya Ishibe Yoshiki Yagi Masafumi Kishimoto Toshiya Inoue Yasuyuki Hayashi Taku Sogabe Takaya Morooka Haruko Sakamoto Keitaro Suzuki Fumiko Nakamura Tasuku Matsuyama Norihiro Nishioka Daisuke Kobayashi Satoshi Matsui Atsushi Hirayama Satoshi Yoshimura Shunsuke Kimata Takeshi Shimazu Shigeru Ohtsuru Taku Iwami
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-21-0675, (Released:2021-11-02)
- 参考文献数
- 52
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Background:The hypothesis of this study is that latent class analysis could identify the subphenotypes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients associated with the outcomes and allow us to explore heterogeneity in the effects of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR).Methods and Results:This study was a retrospective analysis of a multicenter prospective observational study (CRITICAL study) of OHCA patients. It included adult OHCA patients with initial shockable rhythm. Patients from 2012 to 2016 (development dataset) were included in the latent class analysis, and those from 2017 (validation dataset) were included for evaluation. The association between subphenotypes and outcomes was investigated. Further, the heterogeneity of the association between ECPR implementation and outcomes was explored. In the study results, a total of 920 patients were included for latent class analysis. Three subphenotypes (Groups 1, 2, and 3) were identified, mainly characterized by the distribution of partial pressure of O2(PO2), partial pressure of CO2(PCO2) value of blood gas assessment, cardiac rhythm on hospital arrival, and estimated glomerular filtration rate. The 30-day survival outcomes were varied across the groups: 15.7% in Group 1; 30.7% in Group 2; and 85.9% in Group 3. Further, the association between ECPR and 30-day survival outcomes by subphenotype groups in the development dataset was as varied. These results were validated using the validation dataset.Conclusions:The latent class analysis identified 3 subphenotypes with different survival outcomes and potential heterogeneity in the effects of ECPR.
- 著者
- Satoshi Yoshimura Atsushi Hirayama Takeyuki Kiguchi Taro Irisawa Tomoki Yamada Kazuhisa Yoshiya Changhwi Park Tetsuro Nishimura Takuya Ishibe Yoshiki Yagi Masafumi Kishimoto Toshiya Inoue Yasuyuki Hayashi Taku Sogabe Takaya Morooka Haruko Sakamoto Keitaro Suzuki Fumiko Nakamura Tasuku Matsuyama Yohei Okada Norihiro Nishioka Daisuke Kobayashi Satoshi Matsui Shunsuke Kimata Takeshi Shimazu Tetsuhisa Kitamura Taku Iwami on behalf of the CRITICAL Study Group Investigators
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-20-1022, (Released:2021-02-02)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Background:The aim of our study was to investigate in detail the temporal trends in in-hospital characteristics, actual management, and survival, including neurological status, among adult out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients in recent years.Methods and Results:From the prospective database of the Comprehensive Registry of Intensive Care for OHCA Survival (CRITICAL) study in Osaka, Japan, we enrolled all OHCA patients aged ≥18 years for whom resuscitation was attempted, and who were transported to participating hospitals between the years 2013 and 2017. The primary outcome measure was 1-month survival with favorable neurological outcome after OHCA. Temporal trends in in-hospital management and favorable neurological outcome among adult OHCA patients were assessed. Of the 11,924 patients in the database, we included a total of 10,228 adult patients from 16 hospitals. As for in-hospital advanced treatments, extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) use increased from 2.4% in 2013 to 4.3% in 2017 (P for trend <0.001). However, the proportion of adult OHCA patients with favorable neurological outcome did not change during the study period (from 5.7% in 2013 to 4.4% in 2017, adjusted odds ratio (OR) for 1-year increment: 0.98 (95% confidence interval: 0.94–1.23)).Conclusions:In this target population, in-hospital management such as ECPR increased slightly between 2013 and 2017, but 1-month survival with favorable neurological outcome after adult OHCA did not improve significantly.
- 著者
- Shunsuke Kawai Daisuke Kobayashi Chika Nishiyama Tomonari Shimamoto Kosuke Kiyohara Tetsuhisa Kitamura Katsuya Tanaka Kouichi Kinashi Naho Koyama Tetsuya Sakamoto Seishiro Marukawa Taku Iwami
- 出版者
- The Japanese Circulation Society
- 雑誌
- Circulation Journal (ISSN:13469843)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.CJ-23-0177, (Released:2023-11-18)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Background: Little is known about how to effectively increase bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), so we evaluated the 10-year trend of the proportion of bystander CPR in an area with wide dissemination of chest compression-only CPR (CCCPR) training combined with conventional CPR training.Methods and Results: We conducted a descriptive study after a community intervention, using a prospective cohort from September 2010 to December 2019. The intervention consisted of disseminating CCCPR training combined with conventional CPR training in Toyonaka City since 2010. We analyzed all non-traumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients resuscitated by emergency medical service personnel. The primary outcome was the trend of the proportion of bystander CPR. We conducted multivariate logistic regression models and assessed the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) using a 95% confidence interval (CI) to determine bystander CPR trends. Since 2010, we have trained 168,053 inhabitants (41.9% of the total population of Toyonaka City). A total of 1,508 OHCA patients were included in the analysis. The proportion of bystander CPR did not change from 2010 (43.3%) to 2019 (40.0%; 1-year incremental AOR 1.02 [95% CI: 0.98–1.05]).Conclusions: The proportion of bystander CPR did not increase even after wider dissemination of CPR training. In addition to continuing wider dissemination of CPR training, other strategies such as the use of technology are necessary to increase bystander CPR.
- 著者
- Mitsuyoshi Okita Yuki Yayoshi Kousuke Ohara Akio Negishi Hayato Akimoto Naoko Inoue Sachihiko Numajiri Shigeru Ohshima Seiichi Honma Shinji Oshima Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.10, pp.1730-1738, 2017-10-01 (Released:2017-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
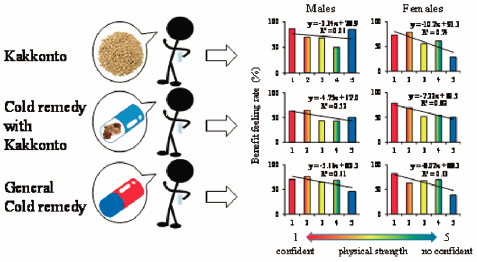
Kakkonto (KK), a traditional Japanese Kampo formulation for cold and flu, is generally sold as an OTC pharmaceuticals used for self-medication. Kampo formulations should be used according to the Sho-symptoms of Kampo medicine. These symptoms refer to the subjective symptoms themselves. Although with OTC pharmaceuticals, this is often not the case. We surveyed the relationship of agreement of Sho with the benefit feeling rate (BFR) of patients who took KK (n=555), cold remedies with KK (CK, n=315), and general cold remedies (GC, n=539) using internet research. BFR of a faster recovery was greater in participants who took the medication early and who had confidence in their physical strength in all treatment groups. BFR was significantly higher in the GC group than in the KK group for patients with headache, runny nose, blocked nose, sneezing, and cough. BFR was also significantly higher in the GC group than in the CK group for headache (males) and cough (females). BFR was the highest in the KK group for stiff shoulders. All cold remedies were more effective when taken early, and the larger the number of Sho that a patient had, the greater the BFR increased. Therefore, a cold remedy is expected to be most effective when there are many cold symptoms and when it is taken at an early stage of the common cold.
- 著者
- Mahitab Elsayed Daisuke Kobayashi Toshio Kubota Naoya Matsunaga Ryusei Murata Yuko Yoshizawa Natsuki Watanabe Tohru Matsuura Yuya Tsurudome Takashi Ogino Shigehiro Ohdo Takao Shimazoe
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.8, pp.1238-1246, 2016-08-01 (Released:2016-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 64
- 被引用文献数
- 2 22
Bisphosphonates and statins are known to have antitumor activities against different types of cancer cell lines. In the present study, we investigated the antiproliferative effects of the combination of zoledronic acid (ZOL), a bisphophosphonate, and fluvastatin (FLU), a statin, in vitro on two types of human pancreatic cancer cell lines, Mia PaCa-2 and Suit-2. The pancreatic cancer cell lines were treated with ZOL and FLU both individually and in combination to evaluate their antiproliferative effects using WST-8 cell proliferation assay. In this study, we demonstrated a potent synergistic antiproliferative effect of both drugs when used in combination in both cell lines. Moreover, we studied the molecular mechanism behind this synergistic effect, which was inhibited by the addition of the mevalonate pathway products, farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Furthermore, we aimed to determine the effect of ZOL and FLU combination on RhoA and Ras guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP)-proteins. The combination induced a marked accumulation in RhoA and unprenylated Ras. GGPP and FPP reversed the increase in the amount of both proteins. These results indicated that the combination treatment impaired RhoA and Ras signaling pathway by the inhibition of geranylgeranylation and/or farnesylation. This study provides a potentially effective approach for the treatment of pancreatic cancer using a combination treatment of ZOL and FLU.
1 0 0 0 OA ダニエル・ベルと消費社会をめぐる論考
- 著者
- 小林 大祐 Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- 同志社社会学研究学会
- 雑誌
- 同志社社会学研究 = The Doshisha Shakaigakukenkyu (Doshisha review of sociology )
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.1, pp.141-147, 1997-03-31
書評論文(Review Article)
- 著者
- Keitaro CHIBA Takashi SUGAWARA Daisuke KOBAYASHI Akihito SATO Yasuhiro MUROTA Taketoshi MAEHARA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.11, pp.647-651, 2021 (Released:2021-11-15)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 3
The significance of atypical histological features (AHF) as risk factors for recurrence in benign meningioma is not well understood. This study examined risk factors of World Health Organization (WHO) Grade I meningioma (GIM) recurrence, focusing on AHF. We investigated 150 consecutive newly diagnosed GIM patients who had more than one year of follow-up after resection in our hospital between January 2007 and March 2018. The following factors were reviewed retrospectively: age, sex, tumor location, extent of resection, MIB-1 index, mitotic figures, number and distribution of AHF, and recurrence. The patients were grouped according to the presence or absence of recurrence and comparatively examined. Recurrence was observed in 10 cases (6.7%). Univariate analysis showed that patients with recurrence had a significantly higher MIB-1 index (2.0 vs. 4.3; p = 0.006) and a significantly higher proportion of male patients (21.4% vs. 70.0%; p = 0.002) and patients with sheet-like growth (6.42% vs. 30.0%; p = 0.04). In multivariate analysis, skull base location (odds ratio [OR] 31.424; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.74–569), gross total resection (OR 0.130; 95% CI 0.0189–0.897), and MIB-1 index (OR 1.939; 95% CI 1.19–3.15) were significantly associated with recurrence. Our study revealed that skull base location, subtotal resection, and high MIB-1 index were independent risk factors for recurrence. Only the presence of sheet-like growth had a significantly higher incidence in patients with recurrence in univariate analysis of AHF. Multivariate analysis found no significant association. Sheet-like growth may be involved in malignancy and recurrence of benign meningioma.
1 0 0 0 OA 名前の社会学的分析に向けて : 漢字がつくる同一性のなかの差異
- 著者
- 小林 大祐 Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- 同志社大学人文学会
- 雑誌
- 評論・社会科学 = Hyoron Shakaikagaku (Social Science Review) (ISSN:02862840)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- no.65, pp.23-41, 2001-03-15
- 著者
- Shinji Oshima Kazuhiko Senoo Akio Negishi Hayato Akimoto Kousuke Ohara Naoko Inoue Shigeru Ohshima Nobuaki Kutsuma Kazuhiko Juni Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.313-322, 2016-03-01 (Released:2016-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 2 6
Article 25-2 of the Japanese Pharmacists’ Act was revised in June 2014, establishing the position of pharmacists as “advisors on the use of pharmaceuticals.” Prior to the Act’s revision, we investigated the perceptions of patients and pharmacists about pharmacists’ roles using a social science methodology. We also examined current opinions and necessary factors for the future growth and development of pharmacists. This questionnaire survey was conducted using an internet method. Patients and pharmacists answered 12 questions. Responses from 529 patients and 338 pharmacists were analyzed. For all items, pharmacists’ awareness of their roles exceeded patients’ awareness of the roles. In this study, the difference between pharmacist and patient awareness was larger than in similar research conducted in the United States. The greatest difference was observed in three items: “Understanding the effects of the drugs the patients are taking” (rate of high ratings: pharmacists 80.2%, patients 37.8%), “Understanding the health changes caused by the drugs dispensed to the patients” (pharmacists 80.2%, patients 28.4%), and “Consciously protecting patients from the adverse effects of drugs” (pharmacists 82.8%, patients 42.2%), indicating role discrepancy. Partition analysis indicated the three factors for a pharmacist to be regarded as a drug therapy or medication specialist: “The patient regards the pharmacist as his/her family or regular pharmacist,” “The pharmacist is making it easy for a patient to talk with him/her” and “The pharmacist is aware of a patient’s use of products other than prescribed drugs, such as over the counter (OTC) medications or health foods and nutritional supplements.” Future efforts are necessary to resolve role discrepancy and implement ongoing monitoring.
- 著者
- Mitsuyoshi Okita Yuki Yayoshi Kousuke Ohara Akio Negishi Hayato Akimoto Naoko Inoue Sachihiko Numajiri Shigeru Ohshima Seiichi Honma Shinji Oshima Daisuke Kobayashi
- 出版者
- 公益社団法人日本薬学会
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b17-00340, (Released:2017-08-04)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Kakkonto (KK), a traditional Japanese Kampo formulation for cold and flu, is generally sold as an over-the-counter (OTC) pharmaceuticals used for self-medication. Kampo formulations should be used according to the Sho-symptoms of Kampo medicine. These symptoms refer to the subjective symptoms themselves. Although with OTC pharmaceuticals, this is often not the case. We surveyed the relationship of agreement of Sho with the benefit feeling rate (BFR) of patients who took KK (n = 555), cold remedies with KK (CK, n = 315), and general cold remedies (GC, n = 539) using internet research. BFR of a faster recovery was greater in participants who took the medication early and who had confidence in their physical strength in all treatment groups. BFR was significantly higher in the GC group than in the KK group for patients with headache, runny nose, blocked nose, sneezing, and cough. BFR was also significantly higher in the GC group than in the CK group for headache (males) and cough (females). BFR was the highest in the KK group for stiff shoulders. All cold remedies were more effective when taken early, and the larger the number of Sho that a patient had, the greater the BFR increased. Therefore, a cold remedy is expected to be most effective when there are many cold symptoms and when it is taken at an early stage of the common cold.