- 著者
- Toshihiro TAKAMI Takeshi HARA Masahito HARA Toshihiko INUI Kiyoshi ITO Izumi KOYANAGI Junichi MIZUNO Masaki MIZUNO Hiroyuki NAKASE Nobuyuki SHIMOKAWA Taku SUGAWARA Shinsuke SUZUKI Toshiyuki TAKAHASHI Masakazu TAKAYASU Satoshi TANI Kazutoshi HIDA Phyo KIM Hajime ARAI Neurospinal Society of Japan The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0148, (Released:2022-10-13)
- 参考文献数
- 74
- 被引用文献数
- 2
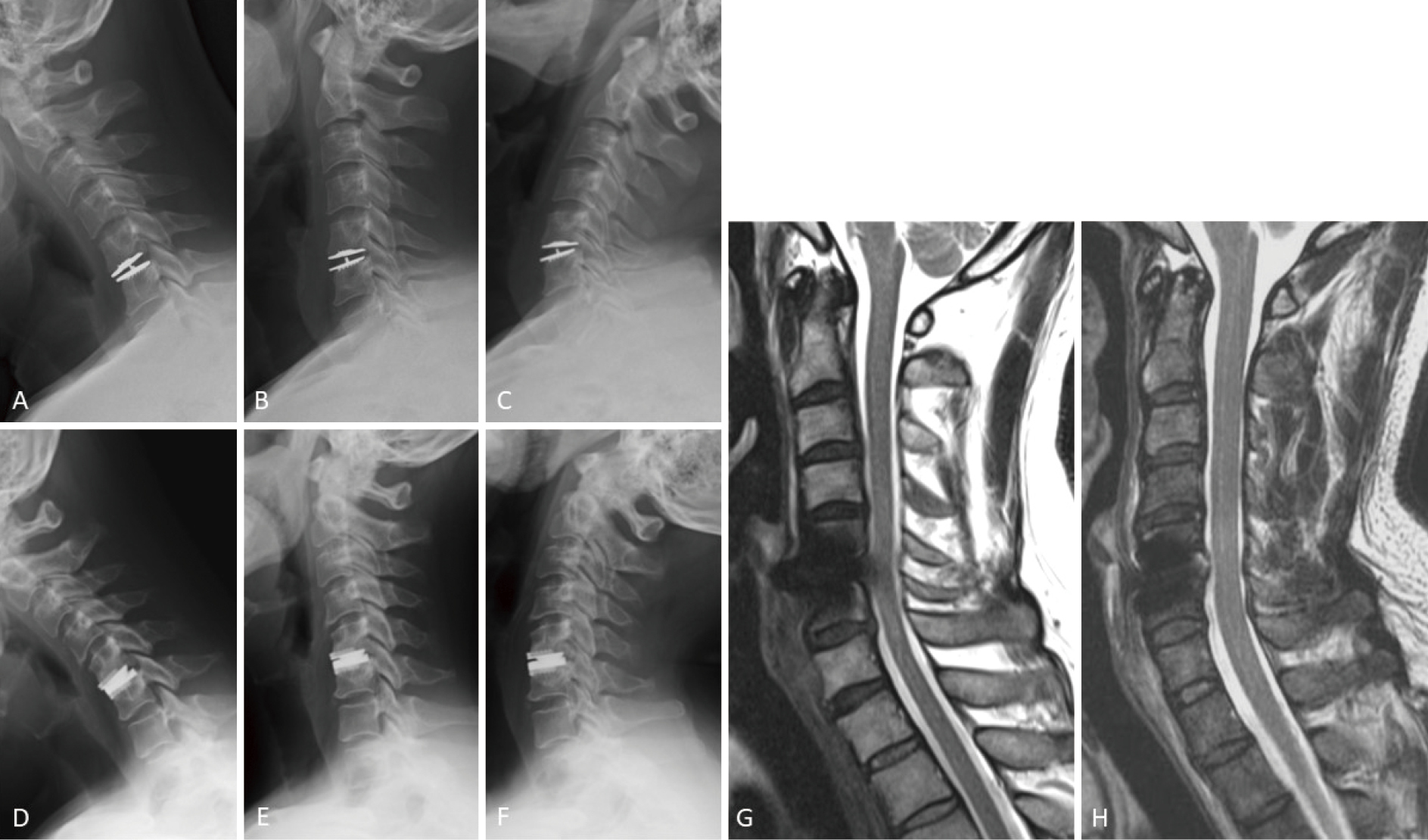
Anterior cervical disc replacement (ACDR) using cervical artificial disc (CAD) has the advantage of maintaining the range of motion (ROM) at the surgical level, subsequently reducing the postoperative risk of adjacent disc disease. Following the approval for the clinical use in Japan, a post-marketing surveillance (PMS) study was conducted for two different types of CAD, namely, Mobi-C (metal-on-plastic design) and Prestige LP (metal-on-metal design). The objective of this prospective observational multicenter study was to analyze the first 2-year surgical results of the PMS study of 1-level ACDR in Japan. A total of 54 patients were registered (Mobi-C, n = 24, MC group; Prestige LP, n = 30, PLP group). Preoperative neurological assessment revealed radiculopathy in 31 patients (57.4%) and myelopathy in 15 patients (27.8%). Preoperative radiological assessment classified the disease category as disc herniation in 15 patients (27.8%), osteophyte in 6 patients (11.1%), and both in 33 patients (61.1%). The postoperative follow-up rates at 6 weeks, 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years after ACDR were 92.6%, 87.0%, 83.3%, and 79.6%, respectively. In both groups, patients' neurological condition improved significantly after surgery. Radiographic assessment revealed loss of mobility at the surgical level in 9.5% of patients in the MC group and in 9.1% of patients in the PLP group. No secondary surgeries at the initial surgical level and no serious adverse events were observed in either group. The present results suggest that 1-level ACDR is safe, although medium- to long-term follow-up is mandatory to further verify the validity of ACDR for Japanese patients.
- 著者
- Daiki Ichikawa Mahiro Sawada Shinsuke Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.MT-M2023055, (Released:2023-07-21)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
The validity of the Tsai-Hill criterion for a porous aluminum alloy with regularly aligned unidirectional pores was investigated experimentally and numerically. The Tsai-Hill criterion predicts failure in different directions in anisotropic composite material. Compression tests of porous aluminum alloy were performed with five different compression angles 0, 30, 45, 60, and 90 deg. The compression angle is the angle between the loading direction and the longitudinal direction of the pore. A numerical analysis of a torsion test of the porous aluminum alloy was also performed to obtain shear strength. Compressive yield strength and equivalent shear strength of the specimen with 0 and 90 deg in compression angle were utilized in the Tsai-Hill criterion. As a result, the yield strength of the specimen with 30, 45, and 60 deg in compression angle was successfully predicted with a maximum relative error of 4 pct. The applicable strain range of the Tsai-Hill criterion was also investigated by altering the yield strength to various offset strengths. The resulted prediction showed a maximum relative error of 10 pct when the offset strain was 40 pct or less. Above that offset strain, densification of the porous structure caused a rapid increase in stress, leading to a drastic decrease in prediction accuracy.
- 著者
- Atsushi SAITO Takashi INOUE Shinsuke SUZUKI Masayuki EZURA Hiroshi UENOHARA Teiji TOMINAGA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.oa.2020-0131, (Released:2021-01-28)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Few studies have reviewed the roles of perfusion magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in the histopathological examination of meningiomas. We analyzed the relationships between radiological findings on perfusion MR imaging and pathological characteristics such as origin of the tumor, mitotic activity, pathological subtype, and perifocal edema formation. The subjects were 21 surgical cases of meningioma preoperatively evaluated by perfusion MR imaging. A region of interest (ROI) was set inside of the tumor, and perifocal edema of the same size, cerebral blood volume (CBV), and cerebral blood flow (CBF) on perfusion MR and diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging were analyzed. These radiological data were evaluated in comparison with histopathological characteristics. On perfusion MR imaging, the average ratio of CBV against the contralateral side was 6.43 (1.13–20.0) and that of CBF was 7.73 (1.34–11.3). There was no significant relationship with perfusion MR imaging data, tumor volume, or perifocal edema volume. However, the large peritumoral edema group often had a higher CBV and CBF than the non-large peritumoral edema group. The skull base group had a significantly higher CBV and lower signal intensity on DW images than the non-skull base group. Signal intensity on DW images was higher in grade II or III than in grade I. Perfusion MR imaging data revealed that the higher ratio of peritumoral edema against tumor size was associated with higher blood flow and blood volume under intratumoral circulatory conditions, and that skull base meningioma had a higher blood volume than non-skull base meningioma.
- 著者
- Mahiro Sawada Daiki Ichikawa Matej Borovinšek Matej Vesenjak Shinsuke Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.9, pp.1782-1789, 2020-09-01 (Released:2020-08-25)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 7
A drop in compressive stress in the plateau region is one of the issues in compressive behavior of porous metals since it has a negative effect on energy absorption efficiency. The compressive deformation behavior of porous aluminum with irregular unidirectional pores was investigated to clarify the mechanism of the drop. Compression tests of cubic specimens with various irregular circular pore geometries were performed. Digital image correlation and finite element analysis were also conducted to obtain strain and stress distribution of the surface perpendicular to the pores. Fracture of the cell walls was observed when the drop occurred. The results show that pore geometry has an effect on the number and the amount of drop in compressive stress. Measurement of an area of two nearest pores of the fractured cell walls suggests that the amount of drop in compressive stress increases as the area increases. Also, a calculation of normalized critical stress for the plastic collapse of the cell walls shows that the fractured cell walls tend to be geometrically weak. Furthermore, stress concentration occurred around the fractured cell walls, which resulted in a secondary fracture of the cell walls.
- 著者
- Kodai Murasawa Masato Takamura Masayoshi Kumagai Yoshimasa Ikeda Hiroshi Suzuki Yoshie Otake Takayuki Hama Shinsuke Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
- 雑誌
- MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS (ISSN:13459678)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.M2017380, (Released:2018-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Neutron diffraction profile analysis using the whole profile fitting method is useful for obtaining microscopic information on metallic materials. To determine an appropriate fitting approach for obtaining reasonable and non-arbitrary results, we applied diffraction line profile analyses using the Convolutional Multiple Whole Profile (CMWP) method to diffraction patterns obtained using the Engineering Materials Diffractometer (TAKUMI, BL19) at the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The tensile specimens of 780 MPa grade bainitic steel were uniaxially stretched until the plastic strain reached a value of 0.05. We performed CMWP analyses on the obtained diffraction patterns during tensile test with various initial parameters of dislocation density and crystallite size. These parameters were optimized in the fitting procedures to minimize the weighted sums of squared residuals (WSSRs). Following this approach, we found that unsuitable initial parameter values resulted in unreasonable convergence. Therefore, initial fitting parameters should be chosen to ensure that the initial profiles are as broad as possible. Reasonable results were obtained following this suggestive approach even when the strain anisotropy parameter is set to arbitrary values.