- 著者
- Britt S.R. Claes Emi Takeo Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma Ron M.A. Heeren
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.A0078, (Released:2019-11-06)
- 参考文献数
- 119
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Mass spectrometry imaging is an imaging technology that allows the localization and identification of molecules on (biological) sample surfaces. Obtaining the localization of a compound in tissue is of great value in biological research. Yet, the identification of compounds remains a challenge. Mass spectrometry alone, even with high-mass resolution, cannot always distinguish between the subtle structural differences of isomeric compounds. This review discusses recent advances in mass spectrometry imaging of lipids, steroid hormones, amino acids and proteins that allow imaging with isomeric resolution. These improvements in detailed identification can give new insights into the local biological activity of isomers.
- 著者
- Britt S. R. Claes Emi Takeo Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma Ron M. A. Heeren
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.8, no.1, pp.A0078, 2019-12-27 (Released:2019-12-28)
- 参考文献数
- 119
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Mass spectrometry imaging is an imaging technology that allows the localization and identification of molecules on (biological) sample surfaces. Obtaining the localization of a compound in tissue is of great value in biological research. Yet, the identification of compounds remains a challenge. Mass spectrometry alone, even with high-mass resolution, cannot always distinguish between the subtle structural differences of isomeric compounds. This review discusses recent advances in mass spectrometry imaging of lipids, steroid hormones, amino acids and proteins that allow imaging with isomeric resolution. These improvements in detailed identification can give new insights into the local biological activity of isomers.
- 著者
- Seitaro OHTSU Masamitsu YAMAGUCHI Hisashi NISHIWAKI Eiichiro FUKUSAKI Shuichi SHIMMA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.9, pp.991-996, 2018-09-10 (Released:2018-09-10)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 12
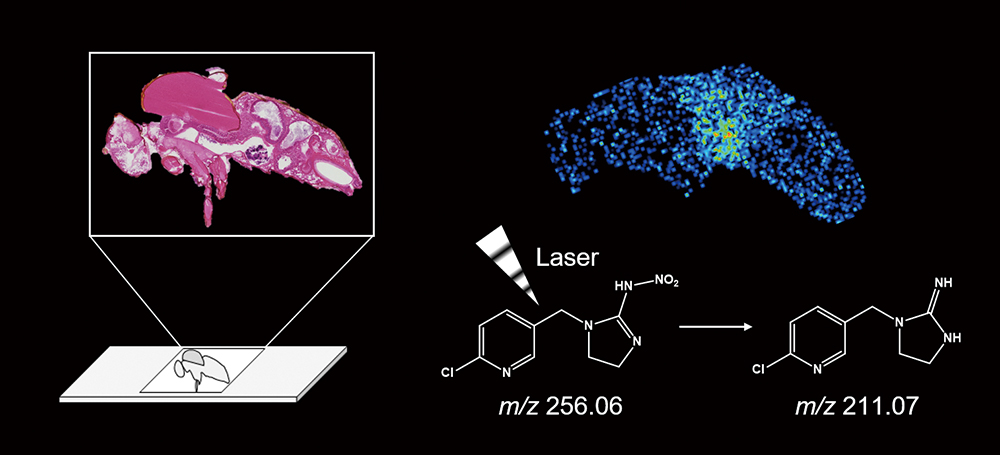
Imidacloprid is widely used for exterminating harmful insects; however, information regarding its distribution in insects is limited. Herein, we developed a visualization method for imidacloprid in Drosophila melanogaster, by using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-IMS). IMS requires sample cryosections; however, certain challenges prevail in retaining fly morphology in sections owing to their small size and heterogeneous components. Therefore, the section preparation method was optimized first, followed by imidacloprid distribution visualized using MALDI-IMS. Using 10% gelatin as an embedding material and 70% ethanol for pretreatment, the gaps between embedding material and D. melanogaster body surface were reduced. The tight adhesion between embedding media and D. melanogaster retains fly morphology in sections. Furthermore, the imidacloprid standard was analyzed separately via MALDI and electrospray ionization (ESI), and imidacloprid was converted to guanidine-imidacloprid via laser irradiation. Consequently, the imidacloprid distribution in D. melanogaster was successfully visualized using guanidine-imidacloprid as the target peak.
- 著者
- Seitaro OHTSU Masamitsu YAMAGUCHI Hisashi NISHIWAKI Eiichiro FUKUSAKI Shuichi SHIMMA
- 出版者
- The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
- 雑誌
- Analytical Sciences (ISSN:09106340)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.18SCP04, (Released:2018-06-29)
- 被引用文献数
- 12
- 著者
- Soichiro Ikuta Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.D22-063, (Released:2023-03-23)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Fungicides must penetrate the internal tissues of plants to kill pathogenic fungi. Mass spectrometers have been used to confirm this penetration, but conventional mass spectrometric methods cannot distinguish the fungicides in different internal tissues owing to the extraction steps. However, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) can detect the penetration of fungicides into leaf sections through direct analysis of the sample surfaces. Therefore, the objective of this study was to establish a method for visualizing fungicide penetration in wheat leaf cross sections using MALDI-MSI. The penetration of azoxystrobin from the epidermal to the internal tissue of the leaves was observed. Moreover, azoxystrobin accumulates in the cells around the vascular bundle. This study suggests that MSI can be useful for the evaluation of fungicide penetration in plant leaves.
2 0 0 0 OA Mass Spectrometry Imaging
- 著者
- Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.11, no.1, pp.A0102, 2022-02-25 (Released:2022-02-25)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) is a technique for obtaining information on the distribution of various molecules by performing mass spectrometry directly on the sample surface. The applications range from small molecules such as lipids to large molecules such as proteins. It is also possible to detect pharmaceuticals and elemental isotopes in interstellar matter. This review will introduce various applications of MSI with examples.
- 著者
- Daisuke Saigusa Ritsumi Saito Komei Kawamoto Akira Uruno Kuniyuki Kano Shuichi Shimma Junken Aoki Masayuki Yamamoto Tadafumi Kawamoto
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.1, pp.A0137, 2023-12-12 (Released:2023-12-12)
- 参考文献数
- 16
The matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) technique was used to obtain the molecular images of cryosections without labeling. Although MALDI-MSI has been widely used to detect small molecules from biological tissues, issues remain due to the technical process of cryosectioning and limited mass spectrometry parameters. The use of a conductive adhesive film is a unique method to obtain high-quality sections from cutting tissue, such as bone, muscle, adipose tissue, and whole body of mice or fish, and we have reported the utilization of the film for MALDI-MSI in previous. However, some signal of the small molecules using the conductive adhesive films was still lower than on the indium tin oxide (ITO) glass slide. Here, the sample preparation and analytical conditions for MALDI-MSI using an advanced conductive adhesive film were optimized to obtain strong signals from whole mice heads. The effects of tissue thickness and laser ionization power on signal intensity were verified using MALDI-MSI. The phospholipid signal intensity was measured for samples with three tissue thicknesses (5, 10, and 20 μm); compared to the signals from the samples on the ITO glass slides, the signals with conductive adhesive films exhibited significantly higher intensities when a laser with a higher range of power was used to ionize the small molecules. Thus, the technique using the advanced conductive adhesive film showed an improvement in MALDI-MSI analysis.
- 著者
- Shuichi Shimma Hiromi Saito Takuya Inoue Fukumatsu Iwahashi
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.1, pp.A0132, 2023-10-12 (Released:2023-10-12)
- 参考文献数
- 26
Pesticide seed treatment provides efficient crop protection in the early season and enables a reduction in the quantity of fungicides used later. Hence, it has been a practical application for crop protection in major crop sectors such as corn, soybean, wheat, and cotton. The chemicals on pesticide-treated seeds may show different distributions depending on the structure of the seeds and the physical properties of the chemicals, but they have not been well studied because of a lack of versatile analytical tools. Here, we used mass spectrometry imaging to visualize the distribution of a fungicide (ethaboxam) in corn and soybean seeds coated with it. Contrasting distribution patterns were noted, which are likely dependent on the seed structure. We also obtained information on fungicide distribution after the seedings, which will contribute to a better understanding of the fungicide delivery pathway within plants. Using this new analytical method, we were able to obtain hitherto unavailable time-dependent, dynamic information on the ethaboxam. We expect that this method will be a useful tool with widespread applications in pesticide development and use.
- 著者
- Erika Nagano Kazuki Odake Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.12, no.1, pp.A0128, 2023-07-25 (Released:2023-07-25)
- 参考文献数
- 27
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) is a well-known method for the ionization of molecules on tissue sections and the visualization of their localization. Recently, different sample preparation methods and new instruments have been used for MSI, and different molecules are becoming visible. On the other hand, although several quantification methods (q-MSI) have been proposed, there is still room for the development of a simplified procedure. Here, we have attempted to develop a reproducible and reliable quantification method using a calibration curve prepared from tissue debris of a frozen section of a sample when we trim the frozen blocks. We discuss the reproducibility of this method across different sample lots and the effect of the biological matrix (ion suppression) on our results. The quantitative performance was evaluated in terms of accuracy and relative standard deviation, and the reliability of the quantitative values obtained by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-MSI was further evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Our q-MSI method for the quantification of dopamine in mouse brain tissue was found to be highly linear, accurate, and precise. The quantitative values obtained by MSI were found to be highly comparable (>85% similarity) to the results obtained by ELISA from the same tissue extracts.
- 著者
- Soichiro Ikuta Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.2, pp.29-34, 2023-05-20 (Released:2023-06-14)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Fungicides must penetrate the internal tissues of plants to kill pathogenic fungi. Mass spectrometers have been used to confirm this penetration, but conventional mass spectrometric methods cannot distinguish the fungicides in different internal tissues owing to the extraction steps. However, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) can detect the penetration of fungicides into leaf sections through direct analysis of the sample surfaces. Therefore, the objective of this study was to establish a method for visualizing fungicide penetration in wheat leaf cross sections using MALDI-MSI. The penetration of azoxystrobin from the epidermal to the internal tissue of the leaves was observed. Moreover, azoxystrobin accumulates in the cells around the vascular bundle. This study suggests that MSI can be useful for the evaluation of fungicide penetration in plant leaves.
- 著者
- Shinnosuke Mori Shuichi Shimma Hiromi Masuko-Suzuki Masao Watanabe Tetsu Nakanishi Junko Tsukioka Katsumi Goto Hiroshi Fukui Nobuhiro Hirai
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.3, pp.355-366, 2021-09-25 (Released:2021-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 65
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We observed trees of the Japanese apricot, Prunus mume ‘Nanko’ (Rosaceae), bearing two types of flowers: 34% had blue fluorescent pollen under UV irradiation, and 66% had non-fluorescent pollen. The fluorescent pollen grains were abnormally crushed, sterile, and devoid of intine and pollenkitt. The development of microspores within anthers was investigated: in the abnormally developed anthers, tapetal cells were vacuolated at the unicellular microspore stage, and fluorescent pollen was produced. Compounds responsible for the blue fluorescence of pollen were identified as chlorogenic acid and 1-O-feruloyl-β-D-glucose. The anthers with fluorescent pollen contained 6.7-fold higher and 3.8-fold lower amounts of chlorogenic acid and N1,N5,N10-tri-p-coumaroylspermidine, respectively, compared to those with non-fluorescent pollen. The tapetal vacuolization, highly accumulated chlorogenic acid, and deficiency of N1,N5,N10-tri-p-coumaroylspermidine imply that low-temperature stress during the early unicellular microspore stage caused a failure in microsporogenesis. Furthermore, potential effects of the visual difference on the bee behavior were also discussed through the colorimetry. The sterility, likely induced by low-temperature stress, and the preference of honeybees for fluorescence may reduce the pollination efficiency of P. mume.
1 0 0 0 OA Metabolic Visualization Reveals the Distinct Distribution of Sugars and Amino Acids in Rice Koji
- 著者
- Adinda Putri Wisman Yoshihiro Tamada Shuji Hirohata Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, no.1, pp.A0089, 2020-08-26 (Released:2020-08-26)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 8
The compounds inside rice koji have been thoroughly investigated as an essential material in making many food-related products, including sake. However, these studies focused only on quantitative aspects, leaving features that can still be uncovered if seen from a new perspective. Visualization of the metabolites inside rice koji may as well be the new angle needed to retrieve more information regarding rice koji making. Here we utilized mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) to visualize the distribution of sugars, sugar alcohols, and amino acids inside rice koji. Imaging results revealed that several sugars alcohols and amino acids were shown to have characteristic distribution near the edges or surface of rice koji. Furthermore, the distribution appears to be correlated with the different structure of rice koji. This study is the first report of using MSI to visualize sugars, sugar alcohols, and amino acids in rice koji.
- 著者
- Shuichi Shimma Yoshiki Makino Kazuto Kojima Takafumi Hirata
- 出版者
- The Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Mass Spectrometry (ISSN:2187137X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, no.1, pp.A0086, 2020-07-13 (Released:2020-07-13)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Platinum, a transition metal that is widely used in anti-cancer agents, also results in the development of nephropathy due to severe adverse reactions caused by platinum-induced nephrotoxicity. Reports on imaging with metals other than platinum remain are limited, even in preclinical studies. Furthermore, most of these are case reports, and the relationship between the distribution of the metal and clinical observations in human samples is not well understood. Here we report on visualizing lanthanum (139La), a component of Fosrenol, which is usually used for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia. Gastric inflammation, also known as hemorrhagic gastritis, is the main adverse event caused by Fosrenol. To conduct this study, 139La was visualized in gastric biopsy samples obtained from a patient using quantitative laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). We also compared the distribution of 139La in tissue and histochemical results. The areas where 139La accumulated corresponded to the macrophage-positive areas observed in immunohistochemistry studies using an anti-CD68 antibody. In contrast, we observed a debris-like crystal morphology in hematoxylin and eosin staining tissues. The debris was also associated with 139La accumulation. The abnormal accumulation of 139La crystals caused the observed inflammation. This phenomenon was previously characterized, but this is the first report in which 139La distribution and histochemical results are compared using LA-ICP-MS.