- 著者
- Yong-Gen Yin Atsuko Sanuki Yukihisa Goto Nobuo Suzui Naoki Kawachi Chiaki Matsukura
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.4, pp.345-351, 2023-12-25 (Released:2023-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 32
In early developing tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit, starch accumulates at high levels and is used by various primary metabolites in ripening fruits. ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase is responsible for the first key step of starch biosynthesis. Although it has been reported that AgpL1 and AgpS1 isoforms are mainly expressed in early developing fruit, their regulatory mechanism has not been elucidated. The present study investigated the transcriptional response of AgpL1 and AgpS1 to various metabolizable sugars, nonmetabolizable sugar analogues, hexokinase inhibitors and proline by an experimental system using half-cut fruits. AgpL1 was upregulated in response to sucrose and constituted hexoses such glucose, whereas the AgpS1 gene almost did not exhibit a prominent sugar response. Further analyses revealed that other disaccharides such maltose and trehalose did not show a remarkable effect on both AgpL1 and AgpS1 expressions. These results indicate that there are two distinct regulatory mechanisms, namely, sugar metabolism-dependent and -independent, for the regulation of AGPase gene expression. Interestingly, the ADP treatment, a hexokinase inhibitors, cancelled the sugar response of AgpL1, indicating that hexokinase-mediated sugar signaling should be involved in the sugar response of AgpL1. These results suggest that sugar-dependent (AgpL1) and sugar-independent (AgpS1) pathways coordinatively regulate starch biosynthesis in immature tomato fruit.
1 0 0 0 OA Genome editing and molecular analyses of an Arabidopsis transcription factor, LATE FLOWERING
- 著者
- Yoshimi Nakano Maki Kawai Moeca Arai Sumire Fujiwara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.4, pp.337-344, 2023-12-25 (Released:2023-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 26
Correct flower organ formation at the right timing is one of the most important strategies for plants to achieve reproductive success. Ectopic overexpression of LATE FLOWERING (LATE) is known to induce late flowering, partly through suppressing expression of the florigen-encoding gene FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) in Arabidopsis. LATE is one of the C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors, and it has a canonical transcriptional repression domain called the ethylene-responsive element-binding factor-associated amphiphilic repression (EAR) motif at the end of its C terminus. Therefore, LATE is considered a transcriptional repressor, but its molecular function remains unclear. Our genome-edited late mutants exhibited no distinct phenotype, even in flowering, indicating the presence of redundancy from other factors. To reveal the molecular function of LATE and factors working with it, we investigated its transcriptional activity and interactions with other proteins. Transactivation activity assay showed that LATE possesses transcriptional repression ability, which appears to be attributable to both the EAR motif and other sequences. Yeast two-hybrid assay showed the EAR motif-mediated interaction of LATE with TOPLESS, a transcriptional corepressor. Moreover, LATE could also interact with CRABS CLAW (CRC), one of the most important regulators of floral meristem determinacy, through sequences in LATE other than the EAR motif. Our findings demonstrated the possibility that LATE can form a transcriptional repression complex with CRC for floral meristem determinacy.
1 0 0 0 OA Structural features of T-DNA that induce transcriptional gene silencing during agroinfiltration
- 著者
- Emi Iida Kazunori Kuriyama Midori Tabara Atsushi Takeda Nobuhiro Suzuki Hiromitsu Moriyama Toshiyuki Fukuhara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.4, pp.289-299, 2023-12-25 (Released:2023-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Rhizobium radiobacter) is used for the transient expression of foreign genes by the agroinfiltration method, but the introduction of foreign genes often induces transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional gene silencing (TGS and/or PTGS). In this study, we characterized the structural features of T-DNA that induce TGS during agroinfiltration. When A. tumefaciens cells harboring an empty T-DNA plasmid containing the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter were infiltrated into the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana line 16c with a GFP gene over-expressed under the control of the same promoter, no small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were derived from the GFP sequence. However, siRNAs derived from the CaMV 35S promoter were detected, indicating that TGS against the GFP gene was induced. When the GFP gene was inserted into the T-DNA plasmid, PTGS against the GFP gene was induced whereas TGS against the CaMV 35S promoter was suppressed. We also showed the importance of terminator sequences in T-DNA for gene silencing. Therefore, depending on the combination of promoter, terminator and coding sequences on T-DNA and the host nuclear genome, either or both TGS and/or PTGS could be induced by agroinfiltration. Furthermore, we showed the possible involvement of three siRNA-producing Dicers (DCL2, DCL3 and DCL4) in the induction of TGS by the co-agroinfiltration method. Especially, DCL2 was probably the most important among them in the initial step of TGS induction. These results are valuable for controlling gene expression by agroinfiltration.
- 著者
- Ryszard Zamorski Kei’ichi Baba Takahiro Noda Rimpei Sawada Kana Miyata Takao Itoh Hanae Kaku Naoto Shibuya
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.4, pp.321-336, 2023-12-25 (Released:2023-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 85
Plant cell wall plays important roles in the regulation of plant growth/development and affects the quality of plant-derived food and industrial materials. On the other hand, genetic variability of cell wall structure within a plant species has not been well understood. Here we show that the endosperm cell walls, including both starchy endosperm and aleurone layer, of rice grains with various genetic backgrounds are clearly classified into two groups depending on the presence/absence of β-1,4-linked glucomannan. All-or-none distribution of the glucomannan accumulation among rice varieties is very different from the varietal differences of arabinoxylan content in wheat and barley, which showed continuous distributions. Immunoelectron microscopic observation suggested that the glucomannan was synthesized in the early stage of endosperm development, but the synthesis was down-regulated during the secondary thickening process associated with the differentiation of aleurone layer. Significant amount of glucomannan in the cell walls of the glucomannan-positive varieties, i.e., 10% or more of the starchy endosperm cell walls, and its close association with the cellulose microfibril suggested possible effects on the physicochemical/biochemical properties of these cell walls. Comparative genomic analysis indicated the presence of striking differences between OsCslA12 genes of glucomannan-positive and negative rice varieties, Kitaake and Nipponbare, which seems to explain the all-or-none glucomannan cell wall trait in the rice varieties. Identification of the gene responsible for the glucomannan accumulation could lead the way to clarify the effect of the accumulation of glucomannan on the agronomic traits of rice by using genetic approaches.
- 著者
- Hiroaki Kisaka Dong Poh Chin Tetsuya Miwa Hiroto Hirano Sato Uchiyama Masahiro Mii Mayu Iyo
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.4, pp.311-320, 2023-12-25 (Released:2023-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 35
The biosynthetic pathway of Catharanthus roseus vinca alkaloids has a long research history, including not only identification of metabolic intermediates but also the mechanisms of inter-cellular transport and accumulation of biosynthesized components. Vinca alkaloids pathway begins with strictosidine, which is biosynthesized by condensing tryptamine from the tryptophan pathway and secologanin from the isoprenoid pathway. Therefore, increasing the supply of precursor tryptophan may enhance vinca alkaloid content or their metabolic intermediates. Many reports on the genetic modification of C. roseus use cultured cells or hairy roots, but few reports cover the production of transgenic plants. In this study, we first investigated a method for stably producing transgenic plants of C. roseus, then, using this technique, we modified the tryptophan metabolism system to produce transgenic plants with increased tryptophan content. Transformed plants were obtained by infecting cotyledons two weeks after sowing with Agrobacterium strain A13 containing a plant expression vector, then selecting with 1/2 B5 medium supplemented with 50 mg l−1 kanamycin and 20 mg l−1 meropenem. Sixty-eight regenerated plants were obtained from 4,200 cotyledons infected with Agrobacterium, after which genomic PCR analysis using NPTII-specific primers confirmed gene presence in 24 plants with a transformation rate of 0.6%. Furthermore, we performed transformation into C. roseus using an expression vector to join trpE8 and aroG4 genes, which are feedback-resistant mutant genes derived from Escherichia coli. The resulting transformed plants showed exactly the same morphology as the wild-type, albeit with a marked increase in tryptophan and alkaloids content, especially catharanthine in leaves.
- 著者
- Masahiro Nishihara Toshiya Muranaka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, pp.181-184, 2023-09-25 (Released:2023-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 著者
- Hiroaki Kusano Ami Takeuchi Hiroaki Shimada
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.3, pp.201-209, 2023-09-25 (Released:2023-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 29
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) has a tetraploid genome. To make a mutant lacking a specific gene function, it is necessary to introduce mutations into all four gene alleles. To achieve this goal, we developed a powerful genome editing tool, CRISPR/dMac3-Cas9, which installed the translation enhancer dMac3 that greatly increased the translation of the downstream open reading frame. The CRISPR/dMac3-Cas9 system employing three guide RNAs (gRNAs) greatly elevated the frequency of the generation rate of mutation. This system enabled to create the 4-allele mutants of granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS) and starch branching enzyme (SBE). These mutants indicated functionally defective features, suggesting that we succeeded in efficient genome editing of the potato tetraploid genome. Here, we show the effect of the number of gRNAs for efficient mutagenesis of the target gene using the mutants of the GBSS1 gene. CRISPR/dMac3-Cas9 employing three gRNA genes achieved a higher mutation efficiency than the CRISPR/dMac3-Cas9 with two gRNAs, suggesting being influenced by the dose effect of the number of gRNAs at the target region. The alleles of the SBE3 gene contained SNPs that caused sequence differences in the gRNAs but these gRNAs functioned efficiently. However, many rearrangement events and large deletions were induced. These results support the importance of accurate binding of gRNA to the target sequence, which may lead to a hint to avoid the unexpected mutation on the off-target sites.
- 著者
- Muxiu Tan Fengming Liu Yueying Xie Qiaocheng Mo Fenghua Shi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.167-174, 2023-06-25 (Released:2023-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 34
In this study, the transformed system mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens of Gynostemma pentaphyllum was constructed by using the phosphomannose-isomerase (PMI) gene as a marker. To investigate the cefotaxime sodium salt (Cef) concentration of bacteriostatic medium and the appropriate mannose concentration in the selectable medium, explants of the stems with buds were cultured in a basic medium supplemented with different Cef and mannose concentrations, respectively. After these were optimized, 288 explants were transformed according the protocol described above to verify their availability by using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), reverse transcription-PCR and chlorophenol red. The results showed that the appropriate Cef concentration for bacteriostatic culture and mannose concentration for selectable culture were 150 mg l−1 and 3 g l−1 for stem with buds, respectively. According to the PCR results, the transformation frequency of stems with buds was 20.49% with a regeneration rate of 29.16%. In future, the CPR assay could be the auxiliary method of choice as it is moderately accurate, but it has good maneuverability and is cost effective for large-scale use.
- 著者
- Mitsuko Kishi-Kaboshi Ayako Nishizawa-Yokoi Ichiro Mitsuhara Seiichi Toki Katsutomo Sasaki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.157-165, 2023-06-25 (Released:2023-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Chrysanthemum morifolium is one of the most popular ornamental plants in the world. However, as C. morifolium is a segmental hexaploid, self-incompatible, and has a sizable heterologous genome, it is difficult to modify its trait systematically. Genome editing technology is one of the attractive methods for modifying traits systematically. For the commercial use of genetically modified C. morifolium, rigorous stabilization of its quality is essential. This trait stability can be achieved by avoiding further genome modification after suitable trait modification by genome editing. Since C. morifolium is a vegetatively propagated plant, an approach for removing genome editing tools is required. In this study, we attempted to use the piggyBac transposon system to remove specific DNA sequences from the C. morifolium genome. Using the luminescence as a visible marker, we demonstrated that inoculation of Agrobacterium harboring hyperactive piggyBac transposase removes inserted 2.6 kb DNA, which harbors piggyBac recognition sequences, from the modified Eluc sequence.
1 0 0 0 OA Comparative analysis of endophyte diversity of Dendrobium officinale lived on rock and tree
- 著者
- Xiaolan Li Huan Hu Qunli Ren Miao Wang Yimei Du Yuqi He Qian Wang
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.145-155, 2023-06-25 (Released:2023-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 70
Dendrobium officinale usually lives on rock or tree, but their endophyte diversity has not yet been fully revealed? In this study, high-throughput sequencing technology was used to investigate the endophyte diversity of the roots of D. officinale lived on tree (Group 1–3, arboreal type) and rock (Group 4, lithophytic type). The results showed that their composition of endophytic fungi and bacteria were similar at phylum level, while their relative abundance were different. Their taxa composition and abundance of endophytes differed significantly among groups at the genus level. Alpha diversity of endophytic fungi of lithophytic type was higher than those from arboreal type, while there was no advantage in endophytic bacteria. Beta diversity revealed that the endophytic fungi tended to cluster in each group, but the endophytic bacteria were dispersed among the groups. LEfSe analysis found that the numbers of predicted endophyte biomarkers of lithophytic type were more than arboreal types at genus level, and the biomarkers varied among groups. Microbial network analysis revealed similarities and differences in the taxa composition and abundance of shared and special endophytes in each group. These results suggested that the root endophytes of lithophytic and arboreal D. officinale differed in diversity.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Katsuoka Naoya Hamabe Chiemi Kato Susumu Hisamatsu Fujio Baba Motohiro Taneishi Toshiyuki Sasaki
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.135-143, 2023-06-25 (Released:2023-06-25)
- 参考文献数
- 34
Argyranthemum frutescens (L.) Sch.Bip. and Rhodanthemum gayanum (Coss. & Durieu) B. H. Wilcox, K. Bremer & Humphries are capable of hybridization. To expand flower color variation in this intergeneric hybrid group, we performed crosses using A. frutescens as the seed parent and R. hosmariense (Ball) B. H. Wilcox, K. Bremer & Humphries, R. catananche (Ball) B. H. Wilcox, K. Bremer & Humphries as the pollen parent. One plantlet was obtained from each cross between the white to pale pink-flowered A. frutescens and white-flowered R. hosmariense, and from a cross between the pink-flowered A. frutescens and cream to pale yellow-flowered R. catananche, via ovule culture. The cross with R. hosmariense produced an individual with white to pale pink ray florets, and the cross with R. catananche produced an individual with red ray florets. The flower and leaf shape of the progenies was intermediate between the parents, and other morphological traits were also characterized in the same manner. Morphological observations and a cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence marker-based determination, using the internal transcribed spacer region as a target for amplification and the restriction enzyme Afl II, revealed that both individuals are hybrids between A. frutescens and R. hosmariense, R. catananche. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report that crossbreeding between A. frutescens (seed parent) and R. hosmariense, R. catananche (pollen parent) is possible. Moreover, further development of Argyranthemum breeding, especially that of a series of hybrid cultivars with different flower colors, is expected.
1 0 0 0 OA Lettuce-based production of an oral vaccine against porcine edema disease for the seed lot system
- 著者
- Takeshi Matsui Eiji Takita Seika Oiwa Asuka Yokoyama Ko Kato Kazutoshi Sawada
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.21.0414a, (Released:2021-06-12)
- 参考文献数
- 47
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Plant-made oral vaccines can be a cost-effective method to control infectious diseases of humans and farm animals. Pig edema is a bacterial disease caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli producing the toxin Shiga toxin 2e (Stx2e). In our previous report, we chose the non-toxic B subunit of Stx2e (Stx2eB) as a vaccine antigen, and Stx2eB was expressed in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L., cv. Green wave). We found that a double repeated Stx2eB (2×Stx2eB) accumulates to higher levels than a single Stx2eB. In this study, we analyzed progeny plants introduced with 2×Stx2eB in which the gene was expressed under the control of conventional cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA (CaMV 35S) promoter, and found that the lettuce underwent transgene silencing and bore few seeds. We resolved these problems by using a transgene cassette which harbored a transcriptional promoter derived from the lettuce ubiquitin gene and a longer version of HSPT. The lettuce harboring this expression construct will be valuable in establishing the seed lot system on the basis that thousands of seeds can be obtained from one plant body and the resulting progeny plants accumulate 2×Stx2eB at high levels without the transgene silencing.
- 著者
- Muhammad Fito Bayubaskara Masaru Ohme-Takagi Ming-Tsair Chan
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.117-121, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 21
Piriformospora indica, which is an endophytic fungus that grows on various media in the absence of a host, emits plant growth promoting volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Kaefer medium (KF) has been shown to be the most suitable medium for P. indica growth; however, different media may differentially affect fungal metabolism which may in turn influence the VOC profiles of P. indica. To date, how the VOCs emitted from P. indica cultured on different media affect plant growth has not been well characterized. Here, we show that poor nutrient medium (PNM) promoted the growth of P. indica more effectively than potato dextrose agar (PDA) or KF medium. By contrast, plant total biomass and root fresh weight were increased 1.8-fold and 2.1-fold, when co-cultivated with P. indica cultured on PDA medium in comparison with KF or PNM medium, respectively. Furthermore, sucrose in the plant culture medium downregulated the fold-induction ratio of the plant growth promoted by P. indica VOCs.
- 著者
- Lipeng Zheng Fumitaka Abe Mariko Nonogaki Yuri Kanno Mitsunori Seo Hiroyuki Nonogaki Naoto Kawakami
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.31-41, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 62
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Pre-harvest sprouting of cereals greatly reduces yield and quality of the grains. Abscisic acid (ABA) is an essential phytohormone for the induction and maintenance of seed dormancy. In this study, the ABA responsive promoter-driven ABA biosynthesis gene system was introduced to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to enhance ABA production in the embryos and pre-harvest sprouting tolerance of the grains. This system consists of a wheat ABA responsive element containing Early-Methionine-labelled (EM) promoter and a sorghum 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (SbNCED) gene which encodes an ABA biosynthesis rate-limiting enzyme. Twenty-three independent single-insertion lines were obtained, from which five homozygous lines showing various SbNCED expression levels were selected. Correlations were observed between SbNCED expression, ABA accumulation in the embryos and enhanced dormancy levels of the grains. The engineered wheat grains exhibited a few day-delay in germination, which should be effective in reducing pre-harvest sprouting damage. However, the increase in ABA levels in the recombinant grains was moderate, which explains why germination was not completely suppressed. Further analysis indicated a concomitant increase in the expression of the ABA catabolic enzyme gene TaABA8′OH1 and in the levels of isoleucine-conjugated jasmonic acid, implying the presence of possible negative feedback regulation in the innate system, which should be overcome for future technology development. These findings advance an understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of hormone metabolism in seeds and facilitate the development of pre-harvest sprouting tolerance in cereal grains.
1 0 0 0 OA Isopropylmalate synthase NtIPMS as a potential molecular marker for seed vigor in tobacco
- 著者
- Yongzhi Niu Chengjing Wang Wenlong Suo Guoping Wang Jia Zhao Zhoufei Wang Yunye Zheng
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.43-49, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 22
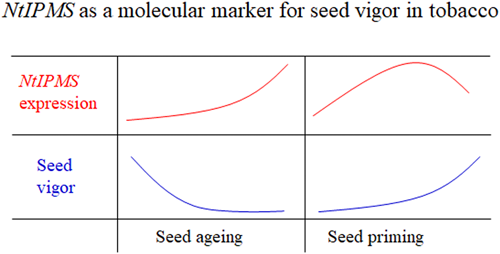
Seed vigor is an important trait for tobacco production. However, the evaluation of seed vigor using molecular biomarkers is scarcely reported in tobacco. In this study, the development of molecular marker isopropylmalate synthase NtIPMS was conducted to detect seed ageing degree and seed priming effect in tobacco. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis showed that the expression of NtIPMS was significantly induced at the initial imbibition stage during seed germination. The NtIPMS expression was positively correlated with the degree of seed ageing in non-pelleted and pelleted seeds. The mRNA level of NtIPMS was gradually increased with the increasing degree of seed ageing. The early best effect of gibberellin priming was observed in 30-h primed seeds, and the highest expression of NtIPMS was observed in 12-h primed seeds. The best stop time-point of seed priming is likely at the time 18 h after the relatively higher NtIPMS expression occurred during seed priming process. The NtIPMS mRNA detection has the potential usage as a potential molecular marker for the evaluation of seed vigor in tobacco.
- 著者
- Nazmul Hasan Naoki Tokuhara Takayuki Noda Nobuhiro Kotoda
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.51-62, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 66
Shortening the juvenility is a burning issue in breeding fruit trees such as Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.). Decreasing the breeding period requires a comprehensive understanding of the flowering process in woody plants. Throughout the Arabidopsis flowering system, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) interacts with other transcription factors (TFs) and functions as a transmissible floral inducer. In a previous study, a VASCULAR PLANT ONE-ZINC FINGER1 (VOZ1)-like TF from the Satsuma mandarin, CuVOZ1, showed protein–protein interaction with two citrus FTs in a yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) system and precocious flowering in Arabidopsis. In this study, another VOZ, CuVOZ2, was isolated from the Satsuma mandarin ‘Aoshima’ and protein–protein interaction was confirmed between CuVOZ2 and CuFTs. No apical meristem (NAM) and zinc coordination motifs were identified within the N-terminal of CuVOZ2. Docking simulation predicted that interactions between CuVOZ2 and CuFTs might occur in domain B of CuVOZ2, which contains a zinc finger motif. According to docking predictions, the distances between the amino acid residues involved ranged from 1.09 to 4.37 Å, indicating weak Van der Waals forces in the interaction. Cys216, Cys221, Cys235, and His239 in CuVOZ2 were suggested to bond with a Zn2+ in the Zn coordination motif. Ectopic expression of 35SΩ:CuVOZ2 in Arabidopsis affected the flowering time, length of inflorescence and internode, and number of siliques, suggesting that CuVOZ2 might regulate both vegetative and reproductive development, act as a trigger for early flowering, and be involved in the elongation of inflorescence possibly in a slightly different way than CuVOZ1.
1 0 0 0 OA Complementation and protein localization analyses of R3 MYBs in an Arabidopsis caprice mutant
- 著者
- Juri Wakamatsu Kosuke Nagao Wakana Tanaka Dong Qin Rumi Tominaga
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.99-103, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 32
Root hairs play vital roles in plant growth since they enable the efficient absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Recent advances in Arabidopsis research have provided a deeper understanding of the molecular genetic mechanisms underlying root hair differentiation. CAPRICE (CPC) and its four homologs, which belong to the CPC gene family and encode R3 MYB transcription factors, play central roles in root hair differentiation. In this study, to better understand the functional specificity and contribution of these five CPC family genes, we conducted phenotypic and expression analyses of the CPC family proteins in a cpc mutant background. As a result, ENHANCER OF TRY AND CPC1 (ETC1) and ETC3 were found to complement the hairless root phenotype of the cpc mutant, as did CPC, whereas TRIPTYCHON (TRY) and ETC2 did not rescue the cpc phenotype. Protein expression analysis revealed that GFP fluorescence was nearly undetectable in pCPC::TRY:GFP/cpc and pCPC::ETC2:GFP/cpc plants, supporting the incapability of root hair formation in these plants. Interestingly, the fluorescence intensity of the CPC:GFP fusion protein was weaker than that of ETC1:GFP and ETC3:GFP fusion proteins. These results were inconsistent with the result of the phenotypic analysis, in which the three genes promoted root hair formation to almost the same degree in the cpc mutant background. We further discuss the discrepancy between the root hair phenotypes and the expression levels of CPC family proteins.
- 著者
- Kai Uchida Masami Yokota Hirai
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.113-116, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
Pea (Pisum sativum) is an agriculturally important leguminous crop cultivated worldwide. It is also the plant from which phytoalexin was isolated for the first time. Several studies have investigated gene functions using pea hairy root culture systems. However, the procedures for producing hairy roots are relatively complicated and only a few pea cultivars and Rhizobium strains have been used. In this study, we established a simple method for generating transgenic hairy roots using a pea cultivar and a Rhizobium strain available in Japan. The transformation efficiency for the transgenic hairy roots (approximately 14%) was calculated on the basis of GFP fluorescence because the binary vector used in this study carried a GFP cassette as a marker. Furthermore, we confirmed that the production of the phytoalexin (+)-pisatin was induced by a copper dichloride treatment, indicating that this system can be used to characterize the biosynthesis of (+)-pisatin, which is a compound with a unique pterocarpan structure. Interestingly, some of the hairy roots turned into crown galls during the culture period. In summary, our simple method enables the production of transgenic pea hairy roots using biological materials accessible in Japan. The generated hairy roots can be used to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying (+)-pisatin biosynthesis as well as hairy root/crown gall formation.
- 著者
- Shun Sasaki Toru Murakami Miharu Yasumuro Ayaka Makita Yutaro Oi Yuta Hiragori Shun Watanabe Rin Kudo Noriya Hayashi Iwai Ohbayashi Munetaka Sugiyama Yui Yamashita Satoshi Naito Hitoshi Onouchi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.21-30, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Perturbations in ribosome biogenesis cause a type of cellular stress called nucleolar or ribosomal stress, which triggers adaptive responses in both animal and plant cells. The Arabidopsis ANAC082 transcription factor has been identified as a key mediator of the plant nucleolar stress response. The 5′-untranslated region (5′-UTR) of ANAC082 mRNA contains an upstream ORF (uORF) encoding an evolutionarily conserved amino acid sequence. Here, we report that this uORF mediates the upregulation of ANAC082 expression in response to nucleolar stress. When transgenic Arabidopsis plants containing a luciferase reporter gene under the control of the ANAC082 promoter and 5′-UTR were treated with reagents that induced nucleolar stress, expression of the reporter gene was enhanced in a uORF sequence-dependent manner. Additionally, we examined the effect of an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-inducing reagent on reporter gene expression because the closest homolog of ANAC082 in Arabidopsis, ANAC103, is involved in the ER stress response. However, the ANAC082 uORF did not respond to ER stress. Interestingly, although ANAC103 has a uORF with an amino acid sequence similar to that of the ANAC082 uORF, the C-terminal sequence critical for regulation is not well conserved among ANAC103 homologs in Brassicaceae. Transient expression assays revealed that unlike the ANAC082 uORF, the ANAC103 uORF does not exert a sequence-dependent repressive effect. Altogether, our findings suggest that the ANAC082 uORF is important for the nucleolar stress response but not for the ER stress response, and that for this reason, the uORF sequence-dependent regulation was lost in ANAC103 during evolution.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Ichida Tomohiko Kazama Shin-ichi Arimura Kinya Toriyama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.109-112, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 11
A highly contiguous mitochondrial and plastid genome sequences of a japonica rice cultivar, Taichung 65, were determined by a hybrid approach with long- and short-read sequences. The assembled mitochondrial genome was 465,453 bases in length with an overall GC content of 43.8%. It was predicted to harbor 62 protein-encoding genes, 16 kinds (33 copies) of transfer RNA, and three kinds (six copies) of ribosomal RNA genes. The mitochondrial genome structure in Taichung 65 is largely the same as that of Nipponbare, but the first ∼9.5 kb sequence in Nipponbare (DQ167400) is replaced with a ∼27 kb sequence duplicated from other parts of the mitochondrial genome. Phylogenetic and sequence polymorphism analysis indicated that Taichung 65 is classified as typical japonica. The assembled plastid genome sequence was 134,551 bases in length and completely identical to the previously reported Nipponbare sequence. These near-complete organelle genome sequences will serve as fundamental resources for investigating alloplasmic cytoplasmic male sterile lines and other organelle-controlled phenomena in rice.