- 著者
- Ryuta NAKAE Yasuo MURAI Yasuhiro TAKAYAMA Kaoru NAMATAME Yoshiyuki MATSUMOTO Takahiro KANAYA Yu FUJIKI Hidetaka ONDA Go SUZUKI Junya KANEKO Takashi ARAKI Yasutaka NAOE Hidetaka SATO Kyoko UNEMOTO Akio MORITA Hiroyuki YOKOTA Shoji YOKOBORI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0226, (Released:2022-10-13)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Coagulopathy, a common complication of traumatic brain injury (TBI), is characterized by a hypercoagulable state developing immediately after injury, with hyperfibrinolysis and bleeding tendency peaking 3 h after injury, followed by fibrinolysis shutdown. Reflecting this timeframe, the coagulation factor fibrinogen is first consumed and then degraded after TBI, its concentration rapidly decreasing by 3 h post-TBI. The fibrinolytic marker D-dimer reaches its maximum concentration at the same time. Hyperfibrinolysis in the acute phase of TBI is associated with poor prognosis via hematoma expansion. In the acute phase, the coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters must be monitored to determine the treatment strategy. The combination of D-dimer plasma level at admission and the level of consciousness upon arrival at the hospital can be used to predict the patients who will "talk and deteriorate." Fibrinogen and D-dimer levels should determine case selection and the amount of fresh frozen plasma required for transfusion. Surgery around 3 h after injury, when fibrinolysis and bleeding diathesis peak, should be avoided if possible. In recent years, attempts have been made to estimate the time of injury from the time course of coagulation and fibrinolysis parameter levels, which has been particularly useful in some cases of pediatric abusive head trauma patients.
- 著者
- Masaaki UNO
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0207, (Released:2022-10-25)
- 参考文献数
- 78
- 被引用文献数
- 8
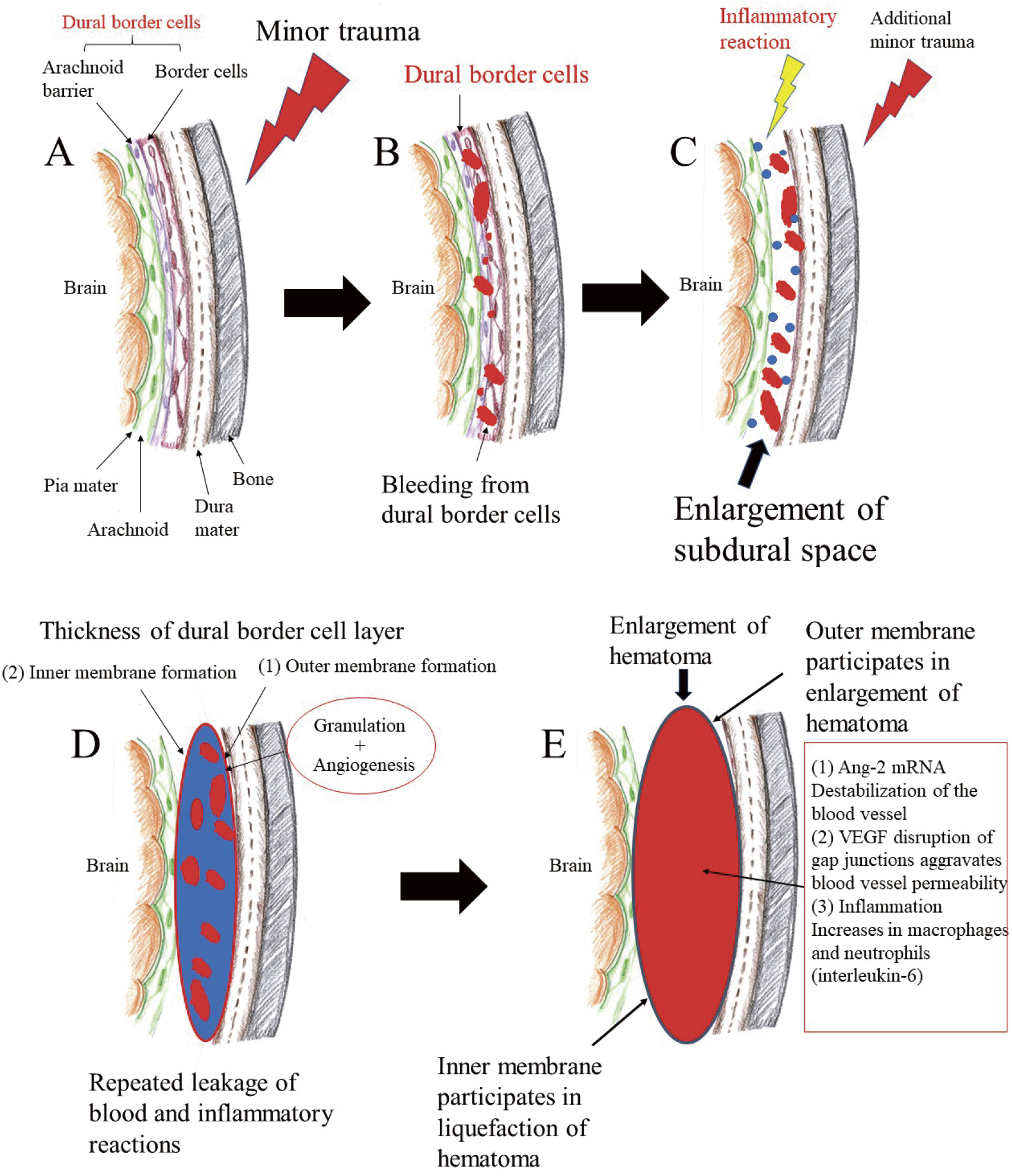
In this paper, I review the historical changes in the etiological concepts and surgical treatments for chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) across the world and in Japan. I also examine future problems associated with its surgical procedures and medical costs. CSDH was first reported by Wepfer in 1657 as "delayed apoplexy." In 1857, Virchow described the famous concept of so-called "pachymeningitis hemorrhagica interna." He considered that the etiology of CSDH involved inflammation. In 1914, Trotter described the origin of CSDH as traumatic. Currently, CSDH is considered to arise with a first leak of blood from dural border cells after mild trauma. Inflammatory cells are then drawn to the border cell layer. At this point, new membranes form from activated inflammation; then, the hematoma enlarges, promoted by angiogenic factors and new capillaries. In 1883, Hulke reported successful trepanning of a patient with CSDH. Burr holes and craniotomy for removal of the hematoma were subsequently reported, and new methods were developed over the course of several decades around the world. In Japan, after the first report by Nakada in 1938, many Japanese pioneering figures of neurological surgery have studied CSDH. After Mandai reported the middle meningeal artery embolization in 2000, this method is now considered useful as an initial or second treatment for CSDH. However, the age of patients is increasing, so more minimally invasive surgeries and useful pharmacotherapies are needed. We must also consider the costs for treating CSDH, because of the increasing numbers of surgical cases.
- 著者
- Arata NAGAI Yasuhiro SUZUKI Tomohisa ISHIDA Yoshimichi SATO Tomoo INOUE Teiji TOMINAGA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0155, (Released:2022-10-13)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 1
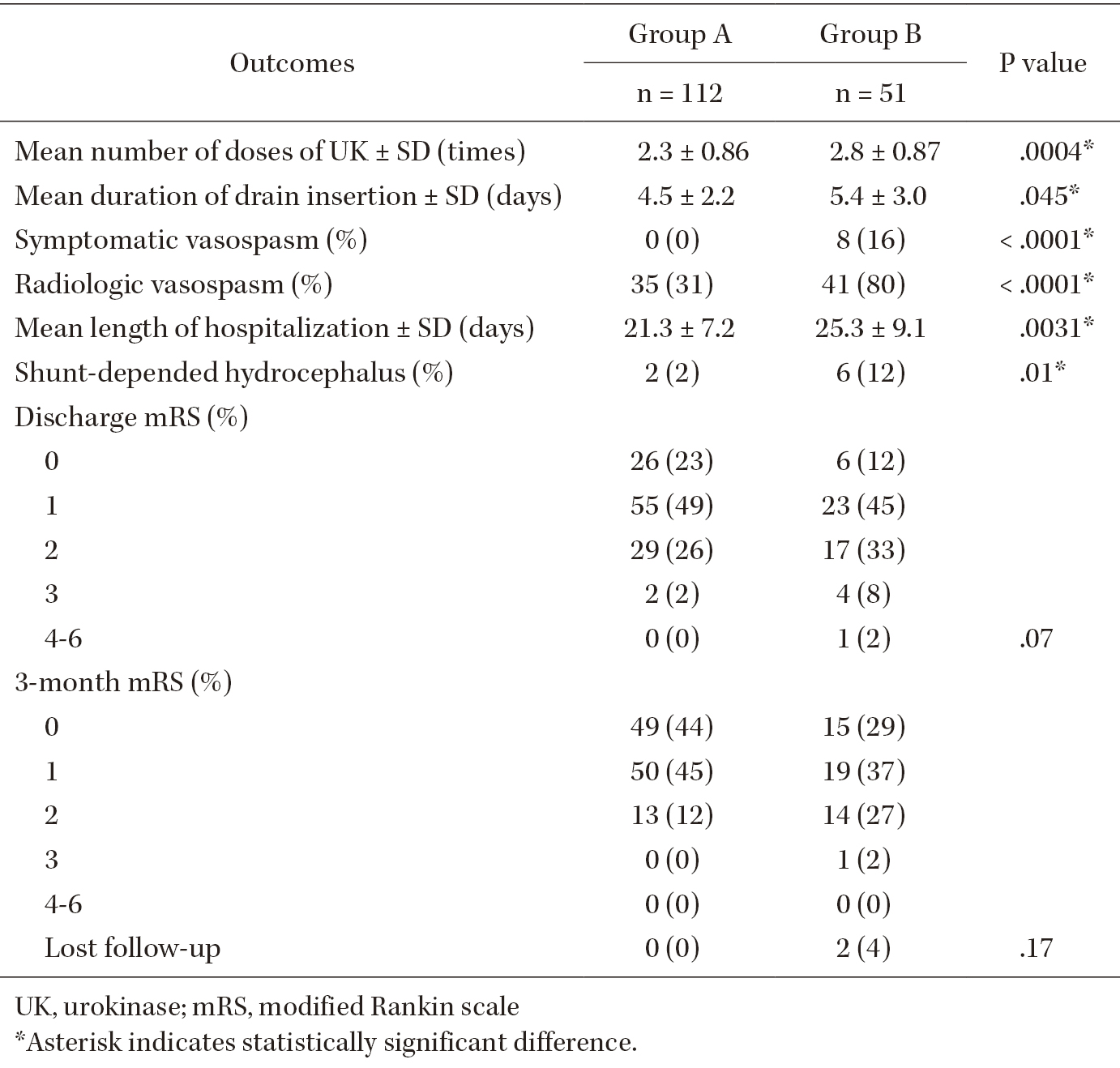
Delayed cerebral vasospasms after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) are a risk factor for poor prognosis after successful treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Different strategies to remove clots from the subarachnoid space and prevent vasospasms have different outcomes. Intrathecal urokinase infusion therapy combined with endovascular treatment (EVT) can reduce the incidence of symptomatic vasospasms. To analyze the relationship between symptomatic vasospasms and residual SAHs after urokinase infusion therapy, we retrospectively reviewed the records of 348 consecutive patients managed with EVT and intrathecal urokinase infusion therapy for aneurysmal SAH at our institution between 2010 and 2021. Among them, 163 patients met the study criteria and were classified into two groups according to the presence of residual SAH in the cisterns, Sylvian fissures, and frontal interhemispheric fissure. The incidence of symptomatic vasospasms and the clinical outcomes were assessed. In total, eight (5.0%) patients developed symptomatic vasospasms. Patients with symptomatic vasospasms had a significantly higher incidence of residual SAH in the Sylvian or frontal interhemispheric fissures than those without (P <.0001). No patient with SAHs resolved by urokinase infusion therapy developed symptomatic vasospasms. However, the two groups did not differ significantly in terms of modified Rankin scale scores at discharge. Treatment with intrathecal urokinase infusion after EVT for aneurysmal SAH can substantially reduce the risk of clinically evident vasospasms.
- 著者
- Satoru YABUNO Takao YASUHARA Satoshi MURAI Tetsuya YUMOTO Hiromichi NAITO Atsunori NAKAO Isao DATE
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.10, pp.465-474, 2022-10-15 (Released:2022-10-15)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Intensive care unit (ICU) survivors after traumatic brain injury (TBI) frequently have serious disabilities with subsequent difficulty in reintegration into society. We aimed to investigate outcomes for ICU survivors after moderate to severe TBI (msTBI) and to identify predictive factors of return home (RH) and return to work (RTW). This single-center retrospective cohort study was conducted on all trauma patients admitted to the emergency ICU of our hospital between 2013 and 2017. Of these patients, adult (age ≥ 18 years) msTBI patients with head Abbreviated Injury Scale ≥ 3 were extracted. We performed univariate/multivariate logistic regression analyses to explore the predictive factors of RH and RTW. Among a total of 146 ICU survivors after msTBI, 107 were included (median follow-up period: 26 months). The RH and RTW rates were 78% and 35%, respectively. Multivariate analyses revealed that the predictive factors of RH were age < 65 years (P < 0.001), HR < 76 bpm (P = 0.015), platelet count ≥ 19× 104/μL (P = 0.0037), D-dimer < 26 μg/mL (P = 0.034), and Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score > 8 (P = 0.0015). Similarly, the predictive factors of RTW were age < 65 years (P < 0.001) and GCS score > 8 (P = 0.0039). This study revealed that "age" and "GCS score on admission" affected RH and RTW for ICU survivors after msTBI.
- 著者
- Asuka FUJINO Yoji TANAKA Daisu ABE Yosuke ARIIZUMI Motoki INAJI Taketoshi MAEHARA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.10, pp.483-487, 2022-10-15 (Released:2022-10-15)
- 参考文献数
- 13
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage is a major complication following endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery. Various skull base reconstruction methods are available, and the use of a vascularized nasoseptal flap (NSF) in skull base reconstruction has greatly contributed to a decrease in the CSF leak rate. A balloon catheter such as a sinus balloon or a Foley catheter is often used to support an NSF; however, in cases wherein nasal and/or paranasal structures supporting the balloon are lacking following the surgery, the NSF is not properly fixed and postoperative CSF leak may occur. Here we introduce a new technique of using multiple-balloon catheters to fix an NSF in such cases and provide the results of our analysis of the new technique's efficacy. Eight patients who underwent endonasal endoscopic surgery for the following cases were included: olfactory neuroblastoma (n = 6), recurrent craniofacial meningioma (n = 1), and recurrent chordoma (n = 1). After tumor resection, multilayered reconstruction with vascularized NSF was performed. Given that the Foley catheter was not stable to fix the flap in each case, we used an additional nasal catheter to support the Foley catheter. No complications such as postoperative CSF leak and necrosis of the vascularized flap were observed. These results suggest that the multiple-balloon catheter technique is a useful method for fixing the NSF to the skull base even when nasal cavity structures are missing due to surgical removal.
- 著者
- Kentaro NAITO Yuta NAKANISHI Toshihiro TAKAMI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0172, (Released:2022-09-30)
- 参考文献数
- 26
Although reconstructive laminoplasty is commonly performed after resection of spinal intramedullary tumors of the cervical spine, its biomechanical rigidity of laminoplasty framework remains unclear. The objective of this study was to examine the structural reliability of our unique method of cervical lift-up basket laminoplasty by using computed tomography (CT)-based finite element analysis (FEA) and clinical radiological evaluation. A finite element model of cervical laminoplasty was created based on CT images using FEA software. Cervical lift-up basket laminoplasty (Basket) was compared with the standard style of open-door basket laminoplasty (Open-door). Clinical subjects for radiological evaluation comprised 33 patients who underwent cervical lift-up basket laminoplasty after resection of spinal intramedullary tumors. An FEA-equivalent stress histogram showed that stress was moderately dispersed around the basket. Virtual displacement of the spinous process of the Basket model was equivalent to that of the Open-door model in any direction of posterior-to-anterior, right-to-left, or top-to-bottom force. In the clinical analysis, radiological data with a minimum postoperative period of 6 months were obtained in a total of 28 out of 33 patients. No patients underwent revision surgery because of implant-related complications. No significant differences in C2-C7 angle or cervical tilt angle were observed between pre- and postoperatively. The structural rigidity of cervical lift-up basket laminoplasty was equivalent to the open-door style on the FEA. Clinical radiological evaluation suggested that there were no serious adverse events associated with cervical laminoplasty, although the longer postoperative follow-up is mandatory.
- 著者
- Koreaki IRIE Yuichi MURAYAMA Mitsuyoshi URASHIMA Fusao IKAWA Hirotoshi SANO Akira SATO
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-0249, (Released:2022-04-07)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
This is a post hoc multivariate analysis of the modified World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies (WFNS) grading project, multicenter prospective observational study including 38 neurosurgical institutions across Japan. Japan Neurosurgical Society WFNS grading committee conducted a modified WFNS grading project as a nationwide prospective registry study. We investigate the clinical outcome of both surgical and endovascular interventions after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) in Japan. A total of 792 patients received surgical intervention and 417 patients received endovascular treatment. Eight hundred patients were female, and 409 patients were male. The mean age was 61.5 ± 13.7 years. At 3 month follow-up, there was no statistically significant difference in good clinical outcome between surgical (68.2%) and endovascular (60.9%) group (odds ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.68-1.16; p = 0.381). Unfavorable outcome rate was 31.8% (238 patients) in the surgical group and 39.1% (154 patients) in the endovascular group. Male, elderly people, modified Rankin scale condition before onset, high-grade modified WFNS clinical grading scale, intracerebral hematoma, posttreatment normal pressure hydrocephalus, and neurological deficit due to symptomatic vasospasm were risk factors for the clinical outcome. Treatment modality was not a statistical factor for clinical outcomes. Surgical clipping has still a major role in the management of SAH in Japan. The present study was not a randomized controlled study, but clinical outcome is not influenced by treatment modalities.
1 0 0 0 OA Coagulopathy and Traumatic Brain Injury: Overview of New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies
- 著者
- Ryuta NAKAE Yasuo MURAI Akio MORITA Shoji YOKOBORI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0018, (Released:2022-04-22)
- 参考文献数
- 72
- 被引用文献数
- 11
Coagulopathy is a common sequela of traumatic brain injury. Consumptive coagulopathy and secondary hyperfibrinolysis are associated with hypercoagulability. In addition, fibrinolytic pathways are hyperactivated as a result of vascular endothelial cell damage in the injured brain. Coagulation and fibrinolytic parameters change dynamically to reflect these pathologies. Fibrinogen is consumed and degraded after injury, with fibrinogen concentrations at their lowest 3-6 h after injury. Hypercoagulability causes increased fibrinolytic activity, and plasma levels of D-dimer increase immediately after traumatic brain injury, reaching a maximum at 3 h. Owing to disseminated intravascular coagulation in the presence of fibrinolysis, the bleeding tendency is highest within the first 3 h after injury, and often a condition called "talk and deteriorate" occurs. In neurointensive care, it is necessary to measure coagulation and fibrinolytic parameters such as fibrinogen and D-dimer routinely to predict and prevent the development of coagulopathy and its negative outcomes. Currently, the only evidence-based treatment for traumatic brain injury with coagulopathy is tranexamic acid in the subset of patients with mild-to-moderate traumatic brain injury. Coagulation and fibrinolytic parameters should be closely monitored, and treatment should be considered on a patient-by-patient basis.
- 著者
- Hayato KOBAYASHI Jun HARA Yoshihiro KITAHAMA Junya HANAKITA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.10, pp.508-511, 2006 (Released:2006-10-25)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 3 4
A 57-year-old man presented with an extremely rare osteoma originating from the left L-5 inferior articular process and causing lumbo-crural sciatica. Postmyelography computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging showed an osteoma compressing the spinal nerve root at the lateral recess. Decompression facetectomy and excision of the lesion followed by transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion between L-5 and S-1 provided complete relief from the symptoms. Histological examination confirmed the diagnosis of benign osteoma. The previous seven cases of spinal osteoma involved the vertebral body, pedicle and posterior elements. Spinal osteomas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of benign lesion originating from the articular process.
- 著者
- Shusuke YAMAMOTO Daina KASHIWAZAKI Haruto UCHINO Hisayasu SAITO Naoki AKIOKA Naoya KUWAYAMA Satoshi KURODA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.60, no.7, pp.360-367, 2020 (Released:2020-07-15)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 5 11
Some of the pediatric moyamoya patients spend their childhood without diagnosed as moyamoya disease (MMD) because of their mild ischemic attacks and emerge again with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke in their adulthood. This study was aimed to clarify the clinical characteristics of adult moyamoya patients with childhood onset and elucidate the impact of long disease period on their clinical features. Present study included 116 untreated hemispheres of 69 adult patients with MMD. They were divided into two groups: childhood onset group (26 hemispheres of 14 patients) and adult onset group (90 hemispheres of 55 patients). Clinical features were compared between the two groups. The incidence of hemorrhagic stroke was significantly higher in childhood onset group (P = 0.0091). Lenticulostriate and choroidal channels were more developed in childhood onset group (P = 0.044 and P <0.001, respectively). Vault moyamoya was more frequently observed in childhood onset group (P <0.001). The development of surgical collaterals through indirect bypass was more marked in childhood onset group (P = 0.0019). Multivariate analysis revealed that childhood onset and developed choroidal channels were significantly associated with the occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke (OR 4.31 [95% CI 1.21–15.4], P = 0.025 and OR 6.78 [95% CI 1.78–25.8], P = 0.0050, respectively). This study clearly shows that adult moyamoya patients with childhood onset have more developed spontaneous collaterals, which may, in turn, highly causes hemorrhagic stroke. Adult moyamoya patients with “childhood onset” should be recognized as a novel and important concept when elucidating the underlying mechanisms of hemorrhagic stroke in MMD.
- 著者
- Seiichiro IMATAKA Rei ENATSU Tsukasa HIRANO Ayaka SASAGAWA Masayasu ARIHARA Tomoyoshi KURIBARA Satoko OCHI Nobuhiro MIKUNI
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.5, pp.215-222, 2022-05-15 (Released:2022-05-15)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The aim of the present study was to evaluate motor area mapping using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) compared with electrical cortical stimulation (ECS). Motor mapping with fMRI and ECS were retrospectively compared in seven patients with refractory epilepsy in which the primary motor (M1) areas were identified by fMRI and ECS mapping between 2012 and 2019. A right finger tapping task was used for fMRI motor mapping. Blood oxygen level-dependent activation was detected in the left precentral gyrus (PreCG)/postcentral gyrus (PostCG) along the "hand knob" of the central sulcus in all seven patients. Bilateral supplementary motor areas (SMAs) were also activated (n = 6), and the cerebellar hemisphere showed activation on the right side (n = 3) and bilateral side (n = 4). Furthermore, the premotor area (PM) and posterior parietal cortex (PPC) were also activated on the left side (n = 1) and bilateral sides (n = 2). The M1 and sensory area (S1) detected by ECS included fMRI-activated PreCG/PostCG areas with broader extent. This study showed that fMRI motor mapping was locationally well correlated to the activation of M1/S1 by ECS, but the spatial extent was not concordant. In addition, the involvement of SMA, PM/PPC, and the cerebellum in simple voluntary movement was also suggested. Combination analysis of fMRI and ECS motor mapping contributes to precise localization of M1/S1.
- 著者
- Satoshi MAESAWA Epifanio BAGARINAO Daisuke NAKATSUBO Tomotaka ISHIZAKI Sou TAKAI Jun TORII Sachiko KATO Masashi SHIBATA Toshihiko WAKABAYASHI Ryuta SAITO
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.62, no.1, pp.45-55, 2022 (Released:2022-01-15)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI) has been utilized to visualize large-scale brain networks. We evaluated the usefulness of multitier network analysis using rs-fMRI in patients with focal epilepsy. Structural and rs-fMRI data were retrospectively evaluated in 20 cases with medically refractory focal epilepsy, who subsequently underwent surgery. First, structural changes were examined using voxel-based morphometry analysis. Second, alterations in large-scale networks were evaluated using dual-regression analysis. Third, changes in cortical hubs were analyzed and the relationship between aberrant hubs and the epileptogenic zone (EZ) was evaluated. Finally, the relationship between the hubs and the default mode network (DMN) was examined using spectral dynamic causal modeling (spDCM). Dual-regression analysis revealed significant decrease in functional connectivity in several networks including DMN in patients, although no structural difference was seen between groups. Aberrant cortical hubs were observed in and around the EZ (EZ hubs) in 85% of the patients, and a strong degree of EZ hubs correlated to good seizure outcomes postoperatively. In spDCM analysis, facilitation was often seen from the EZ hub to the contralateral side, while inhibition was seen from the EZ hub to nodes of the DMN. Some cognition-related networks were impaired in patients with focal epilepsy. The EZ hub appeared in the vicinity of EZ facilitating connections to distant regions in the early phase, which may eventually generate secondary focus, while inhibiting connections to the DMN, which may cause cognitive deterioration. Our results demonstrate pathological network alterations in epilepsy and suggest that earlier surgical intervention may be more effective.
- 著者
- Keitaro CHIBA Takashi SUGAWARA Daisuke KOBAYASHI Akihito SATO Yasuhiro MUROTA Taketoshi MAEHARA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.61, no.11, pp.647-651, 2021 (Released:2021-11-15)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 3
The significance of atypical histological features (AHF) as risk factors for recurrence in benign meningioma is not well understood. This study examined risk factors of World Health Organization (WHO) Grade I meningioma (GIM) recurrence, focusing on AHF. We investigated 150 consecutive newly diagnosed GIM patients who had more than one year of follow-up after resection in our hospital between January 2007 and March 2018. The following factors were reviewed retrospectively: age, sex, tumor location, extent of resection, MIB-1 index, mitotic figures, number and distribution of AHF, and recurrence. The patients were grouped according to the presence or absence of recurrence and comparatively examined. Recurrence was observed in 10 cases (6.7%). Univariate analysis showed that patients with recurrence had a significantly higher MIB-1 index (2.0 vs. 4.3; p = 0.006) and a significantly higher proportion of male patients (21.4% vs. 70.0%; p = 0.002) and patients with sheet-like growth (6.42% vs. 30.0%; p = 0.04). In multivariate analysis, skull base location (odds ratio [OR] 31.424; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.74–569), gross total resection (OR 0.130; 95% CI 0.0189–0.897), and MIB-1 index (OR 1.939; 95% CI 1.19–3.15) were significantly associated with recurrence. Our study revealed that skull base location, subtotal resection, and high MIB-1 index were independent risk factors for recurrence. Only the presence of sheet-like growth had a significantly higher incidence in patients with recurrence in univariate analysis of AHF. Multivariate analysis found no significant association. Sheet-like growth may be involved in malignancy and recurrence of benign meningioma.
- 著者
- Masaki IWAKURA Tetsuro KAWAGUCHI Kohkichi HOSODA Yuji SHIBATA Hideki KOMATSU Akira YANAGISAWA Eiji KOHMURA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.3, pp.172-175, 2005 (Released:2005-03-22)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 20 22
A 28-year-old man attempted to kill himself with a knife stab into the parietal area. Neuroimaging showed no vascular impairment except slow venous flow around the knife due to tamponading. After obtaining informed consent, the knife was removed through a craniotomy without new brain injury. Postoperative neurological findings showed no deficit. Follow-up angiography revealed no vascular impairment. No infection occurred. Brain stab wounds cause numerous complications, such as intracranial hemorrhage, injury of important vessels, and infections. Minimal blade movement during removal and precautions to prevent massive hemorrhage are essential.
- 著者
- Masazumi FUJII Satoshi MAESAWA Sumio ISHIAI Kenichiro IWAMI Miyako FUTAMURA Kiyoshi SAITO
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.56, no.7, pp.379-386, 2016 (Released:2016-07-15)
- 参考文献数
- 57
- 被引用文献数
- 24 41
The neural basis of language had been considered as a simple model consisting of the Broca’s area, the Wernicke’s area, and the arcuate fasciculus (AF) connecting the above two cortical areas. However, it has grown to a larger and more complex model based upon recent advancements in neuroscience such as precise imaging studies of aphasic patients, diffusion tensor imaging studies, functional magnetic resonance imaging studies, and electrophysiological studies with cortical and subcortical stimulation during awake surgery. In the present model, language is considered to be processed through two distinct pathways, the dorsal stream and the ventral stream. The core of the dorsal stream is the superior longitudinal fasciculus/AF, which is mainly associated with phonological processing. On the other hand, semantic processing is done mainly with the ventral stream consisting of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and the intratemporal networks. The frontal aslant tract has recently been named the deep frontal tract connecting the supplementary motor area and the Broca’s area and it plays an important role in driving and initiating speech. It is necessary for every neurosurgeon to have basic knowledge of the neural basis of language. This knowledge is essential to plan safer surgery and preserve the above neural structures during surgery.
- 著者
- Sosho KAJIWARA Yu HASEGAWA Tetsuya NEGOTO Kimihiko ORITO Takayuki KAWANO Munetake YOSHITOMI Kiyohiko SAKATA Nobuyuki TAKESHIGE Yukako YAMAKAWA Hirofumi JONO Hideyuki SAITO Nobuhisa HIRAYU Osamu TAKASU Masaru HIROHATA Motohiro MORIOKA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.oa.2021-0097, (Released:2021-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 4
This study aimed to examine the beneficial effects of a novel prophylactic barbiturate therapy, step-down infusion of barbiturates, using thiamylal with normothermia (NOR+sdB), on the poor outcome in the patients with severe traumatic brain injuries (sTBI), in comparison with mild hypothermia (MD-HYPO). From January 2000 to March 2019, 4133 patients with TBI were admitted to our hospital. The inclusion criteria were: a Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score of ≤8 on admission, age between 20 and 80 years, intracranial hematoma requiring surgical evacuation of the hematoma with craniotomy and/or external decompression, and patients who underwent management of body temperature and assessed their outcome at 6–12 months. Finally, 43 patients were included in the MD-HYPO (n = 29) and NOR+sdB (n = 14) groups. sdB was initiated intraoperatively or immediately after the surgical treatment. There were no significant differences in patient characteristics, including age, sex, past medical history, GCS on admission, type of intracranial hematoma, and length of hospitalization between the two groups. Although NOR+sdB could not improve the patient’s poor outcome either at discharge from the intensive care unit (ICU) or at 6–12 months after admission, the treatment inhibited composite death at discharge from the ICU. The mean value of the maximum intracranial pressure (ICP) in the NOR+sdB group was <20 mmHg throughout the first 120 h. NOR+sdB prevented composite death in the ICU in patients with sTBI, and we may obtain novel insights into the beneficial role of prophylactic barbiturate therapy from suppression of the elevated ICP during the first 120 h.
1 0 0 0 OA 視床出血の診断と治療に対する考察
- 著者
- 香川 泰生 神野 哲夫 佐野 公俊 片田 和広 MOHAMAD YUSUF SHAH 藤本 和夫 戸田 孝
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17pt2, no.3, pp.243-251, 1977 (Released:2006-12-28)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Diagnosis of thalamic hemorrhage has become more accurate by CT scan, and the precise location and extent of hematoma can be visualized preoperatively, as well as postoperatively, i.e. the follow-up study showing the outcome of hematoma and secondary changes of the brain is more readily available. Operative procedure for such a lesion should be reevaluated. Thalamic hemorrhage constituted 27% of all hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhages in our series (the reported incidence was not so high). According to CT findings (except for 3 cases with giant hematoma), we could classify their main locations into 3 types as follows; —1) anterior type — located in the anterior nuclear group of the thalamus — 2 cases, 2) medial type located in the medial nuclear group of the thalamus — 2 cases, 3) posterolateral type located in the lateral nuclear group of the thalamus — 5 cases. As to the extention of hematoma, we devided all cases into the following 5 types; Type I — localized in the thalamus, Type II — medially extending & perforating into the third ventricle, Type III — laterally extending into the internal capsule and the basal ganglia, Type IV — spreading into all directions, Type V giant hematoma. This classification was found useful in relation to the clinical picture, the operative decision, the choice of operative method and the postoperative prognosis. The onset of the clinical picture was always sudden and included disturbance of consciousness and hemiparesis or hemiplegia. Of 8 cases which allowed a satisfactory clinical examination of sensory and motor function, only few cases showed signs of the thalamic syndrome. In 2 cases of giant hematoma with extensive spread, downward deviation of the eyeballs was noticed. Surgery should be performed; with exceptions to the following conditions — 1) no agreement of family, 2) over 75 years of age, 3) already representing the symptoms of brain stem, 4) severe associated deseases, 5) mild case (mainly level of consciousness). Based on CT findings the most suitable operative procedure should be adopted, — that is, only unilateral C.V.D. (continuous ventricular drainage) on localized type, bilateral or unilateral C.V.D. on medial type, trans-paracallosal approach on anterior type and posterolateral type, trans-temporal approach on lateral extention type, trans-paracallosal or trans-temporal approach combining irrigation-evacuation of the intraventricular clots on giant hematoma type and all extention type. Out of 12 cases six survived, and 3 cases have useful life. Relatively better prognosis was obtained in medial type, and in posterolateral type, but giant hematoma type and all extention type resulted in the worst outcome. In marked lateral extention type of posterolateral type improvement of hemiplegia was not good. Except for the massive intraventricular hemorrhage, the prognosis was dependent on the grade of deterioration of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and the midbrain rather than the ventricular perforation. Even if hematoma was not so large, delayed surgical treatment for C.S.F. obstruction due to ventricular perforation carried the poor prognosis on mortality and morbidity.
- 著者
- OI Shizuo YAMADA Hiroshi KIMURA Mitsuru EHARA Kazuo MATSUMOTO Satoshi KATAYAMA Kazuaki MOCHIZUKI Matsuto UETANI Yoshiyuki NAKAMURA Hajime
- 出版者
- 日本脳神経外科学会
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.7, pp.456-461, 1990
- 被引用文献数
- 2 14
Twenty hydrocephalic patients diagnosed in the third trimester of fetal life were evaluated and followed during a 7-year period. The factors affecting the prognosis, including the type of hydrocephalus, underlying conditions, associated anomalies, time of diagnosis and delivery, fetal period after diagnosis, head circumference and degree of ventriculomegaly at birth, and age at treatment, were comprehensively analyzed. The difference between final outcomes as assessed by developmental quotient (DQ) or intelligence quotient (IQ) were statistically tested with computation by means of STAX packages in an NEC 9801 VX. Hydrocephalus as an isolated defect occurred in six cases (30%), was associated with other central nervous system anomalies in nine (45%), and was secondary to intrauterine intraventricular hemorrhage or brain tumor in five (25%). The average age at the time of diagnosis was 33.9 weeks of gestation (range, 27-40 weeks). One fetus was treated by transabdominal cephalocentesis, but the majority of patients underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt postnatally. The final IQ or DQ scores ranged from 20 to 120 (mean score, 50.6). The data analyses revealed that the only significant factor affecting outcome was the fetal period after diagnosis of hydrocephalus (r = -0.5076, p < 0.01). Our data supports the fact that the results of an on-going hydrocephalic state may become irreversible during fetal life. It is emphasized that establishment of a more precise pathophysiological evaluation, and a less invasive but more reliable decompressive technique for fetal hydrocephalus, is urgent.
- 著者
- Shingo MATSUDA Fusao IKAWA Hideo OHBA Michitsura YOSHIYAMA Toshikazu HIDAKA Kaoru KURISU Susumu MIYAMOTO Isao DATE Hiroyuki NAKASE
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.6, pp.197-203, 2019 (Released:2019-06-15)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 1 7
Various guidelines regarding surgical site infection (SSI) have recently been established. However, perioperative management of the wound and use of antibiotics have never been standardized completely in departments of neurosurgery in Japan. This survey investigated current perioperative management and administration of surgical antibiotic prophylaxis (SAP) and compared with guidelines intended to reduce SSI associated with neurosurgery in Japan. Questionnaires were distributed to members of the conference on Neurosurgical Techniques and Tools and the Japan Society of Aesthetic Neurosurgery via internet. The questionnaires asked about methods of perioperative management. A total of 255 members returned answers to the questionnaires. The questionnaires revealed that partial or no removal of the hair and hair shampooing at the day before surgery were performed in 96.1% and 88.1% of each institute following the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines. Use of SAP at just before, during, and after surgery were 65.0%, 86.2%, and 63.0%, respectively. The postoperative period of use of intravenous SAP prolonged beyond 24 h in 80.0% against the recommendation of WHO. Perioperative management of wounds and use of SAP varies in institutes in Japan and some procedures were far different from the WHO guidelines. Japanese neurosurgeons should notice the prolonged SAP and comply with the WHO guidelines.
- 著者
- Totaro TAKEUCHI Kozo YAJIMA
- 出版者
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- 雑誌
- Neurologia medico-chirurgica (ISSN:04708105)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.59, no.7, pp.281-286, 2019 (Released:2019-07-15)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 5 19
A total of 482 operated idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) patients were divided into those aged <80 years at the time of surgery (group A: 400 cases; and male-to-female ratio, 259:141) and ≥80 years (group B: 82 cases; male-to-female ratio, 43:39) and comparatively investigated based on the following variables: (1) temporal changes in shunt efficacy rates, and (2) temporal changes in each symptom, including the patient’s fall frequency and preoperative modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score and during follow-up at 3, 6 months, 1–4 years postoperatively. (1) The shunt efficacy rates at 3 months and 4 years postoperatively were 93% and 82%, respectively, in group A and 92.3% and 70.7%, respectively, in group B. This demonstrates a decrease in shunt efficacy at 4 years postoperatively, regardless of the persistence of shunt function or adjustments in setting pressure. This trend was particularly observed in group B. In group A, 41 (9.8%) cases had decreased efficacy rate, compared with 21 (25.6%) cases in group B, which occurred due to complications with an extracranial or intracranial disease. (2) Gait disturbance (G) and urinary incontinence (U) showed signs of improvement in the early postoperative stage, while dementia (D) and mRS score began to gradually improve from 6 months postoperatively. Patient’s fall frequency tended to become higher until 6 months postoperatively than the preoperative rate. In group A, symptom improvement was comparatively maintained until 4 years postoperatively, while in group B, all symptoms and mRS tended to gradually deteriorate beginning at 3 years postoperatively.