238 0 0 0 OA ゴム技術者のための入門講座〔III〕わかりやすいゴムの物性(12)
- 著者
- 剣菱 浩
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.53, no.12, pp.719-727, 1980 (Released:2008-04-16)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 3 2 3
80 0 0 0 OA 効果的な研究発表のコツ
- 著者
- 鈴木 喬
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.41, no.3, pp.219-226, 1968-03-15 (Released:2009-10-16)
- 参考文献数
- 8
25 0 0 0 OA ゴムの耐放射線性
- 著者
- 町 末男
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.2, pp.115-121, 1979-02-15 (Released:2013-03-05)
- 参考文献数
- 13
- 被引用文献数
- 3 1
10 0 0 0 OA コンドームで培ったラテックスの製膜技術
- 著者
- 対馬 恭吾
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.9, pp.358-362, 2015 (Released:2015-11-25)
- 参考文献数
- 7
Condoms, which are controlled medical devices, are easily utilized as they are low cost and cause no side effects. Condoms are increasingly used as one of the most effective means of birth control and prevention of sexually trans-mitted diseases. When producing condoms, the dipping/drying processes are repeated twice during the molding. After being released from the mold, post-vulcanization is applied. The quality inspection of the finished products includes a bursting test which is used as a substitute for the “no tearing during use” test. Japanese condoms of a thickness of 0.03mm had been used successfully in the past. After introducing the bursting test into ISO 4074, the condoms being 0.03mm in thickness became problematic to produce. However, the subsequent development of new technologies again enabled the production of the condoms with a thickness of 0.03mm. These are more suitable to new competitive rules, and the production of the condoms continues to this day.
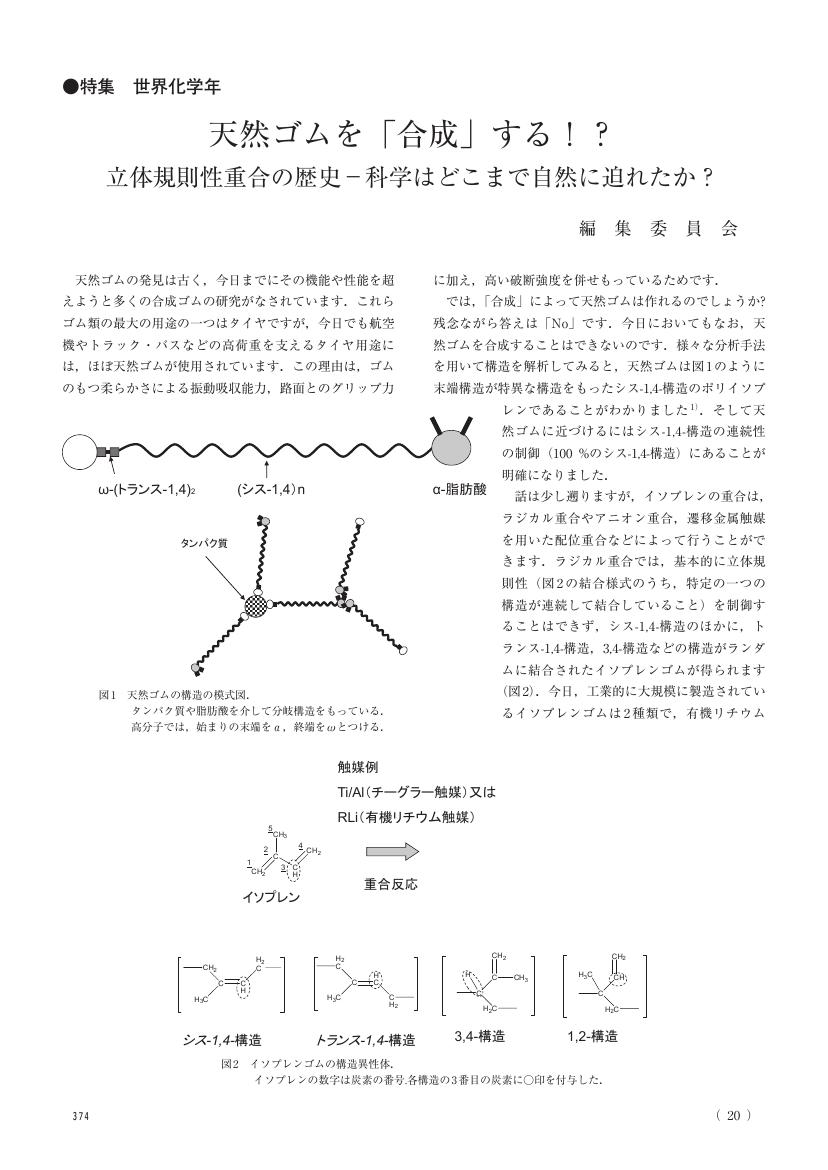
10 0 0 0 OA 天然ゴムを「合成」する!?
- 著者
- 編集委員会
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.84, no.12, pp.374-375, 2011 (Released:2012-03-27)
- 参考文献数
- 2
9 0 0 0 OA 補講(4)
- 著者
- 編集委員会
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.83, no.4, pp.109-116, 2010 (Released:2010-08-25)
- 参考文献数
- 9
9 0 0 0 OA タイヤの力学的特性について
- 著者
- 酒井 秀男
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.1, pp.19-33, 1979-01-15 (Released:2013-03-05)
- 参考文献数
- 10
8 0 0 0 OA クランク軸用ラバーダンパ
- 著者
- 煙山 英夫
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.64, no.5, pp.279-286, 1991 (Released:2007-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 2
- 被引用文献数
- 2
8 0 0 0 OA ブルーム (粉ふき) 現象について
- 著者
- 占部 誠亮
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.26, no.8, pp.495-497, 1953 (Released:2008-04-16)
- 参考文献数
- 19
- 被引用文献数
- 1
7 0 0 0 OA ゴム製品のむかしばなししりいず (10)
- 著者
- 戸原 春彦
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.7, pp.416-422, 1982 (Released:2008-04-16)
- 参考文献数
- 1
5 0 0 0 OA 耐アルカリ•耐酸•耐熱•耐油性ゴムの研究 (第6報) 各種合成ゴムに就ての試驗
- 著者
- 柿元 義秀
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.17, no.6, pp.351-365, 1944 (Released:2008-04-16)
5 0 0 0 OA 汽罐の腐蝕及スケール防止對策
- 著者
- 大谷 資利
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本護謨協會誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.9, no.10, pp.471-486, 1936 (Released:2008-04-15)
4 0 0 0 OA 第10講 混練りの物理
- 著者
- 編集委員会
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.82, no.11, pp.483-491, 2009 (Released:2010-08-25)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 2 1
4 0 0 0 OA 太平洋戦争とゴム研究について
- 著者
- 村上 謙吉
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.81, no.2, pp.65-69, 2008-02-15 (Released:2010-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 3
4 0 0 0 OA コロナ処理による表面改質
- 著者
- 斉藤 伸二
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.70, no.6, pp.333-339, 1997 (Released:2007-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 20
4 0 0 0 OA タイヤの摩擦と転がり抵抗
- 著者
- 網野 直也
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.2, pp.37-42, 2015 (Released:2015-05-22)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Rolling resistance of tires is a highly important property for tire development as well as tire traction. The rolling resistance is mainly generated by energy loss of tire components during tire deformation, because tires transform their shape from round to flat at their contact patch. It is known that to reduce the rolling resistance, tanδ of rubber around 10 Hz should be decreased. In general, silica filled rubber shows lower tanδ around 10 Hz compared to carbon black filled rubber. On the other hand, frictional force of rubber consists of two main terms. One is hysteresis term and the other is adhesion term. It is reported that silica filled rubber shows higher frictional force in comparison with carbon black filled rubber, because of higher adhesion component of friction. Therefore, silica filled rubber can improve not only rolling resistance but also traction of tires. X-ray and Neutron scattering results show that dispersed structure of silica agglomerates in rubber is different from that of carbon black agglomerates. It is considered that the good performance of silica filled rubber in rolling resistance and traction correlates to the silica dispersed structure in rubber.
4 0 0 0 OA 高分子物質の人と環境に対する安全性評価
- 著者
- 北野 大
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.66, no.7, pp.454-472, 1993 (Released:2007-07-09)
- 参考文献数
- 4
4 0 0 0 OA 第7講ゴムの劣化を理解して防止する (その1)
- 著者
- 編集委員会
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.77, no.3, pp.109-115, 2004 (Released:2007-05-28)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 2
4 0 0 0 OA 動的粘弾性とは何か
- 著者
- 五十野 善信
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.74, no.6, pp.212-217, 2001 (Released:2007-05-28)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 7 1
4 0 0 0 OA エラストマーの凝着を伴う摩擦の発生機構
- 著者
- 桃園 聡
- 出版者
- 一般社団法人 日本ゴム協会
- 雑誌
- 日本ゴム協会誌 (ISSN:0029022X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.88, no.2, pp.48-54, 2015 (Released:2015-05-22)
- 参考文献数
- 43
- 被引用文献数
- 1 3
It is well known that elastomer surfaces vary friction behavior with the sliding conditions. These frictional characteristics depend on interfacial dissipation of viscoelastic asymmetric deformation and adhesion. As adhesion plays a dominant role in such friction behavior at very low sliding velocities, adhesive friction of elastomer is focused and discussed. The one mechanism of adhesive friction force generation is macroscopic dissipation of fracture and healing of contact junction. The other one is microscopic dissipation of attachment and deformation of molecular chain of elastomer. It is shown that the combination of these two mechanisms can explain the friction characteristics at very low speed conditions.