- 著者
- Ryosuke Nogami Mari Nagata Risa Imada Kenji Kai Takashi Kawaguchi Shuji Tani
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.D23-038, (Released:2023-12-26)
- 参考文献数
- 43
From the 992 samples of culture extracts of microorganisms isolated from soil in Japan, we found that the extract of Streptomyces sp. no. 226 inhibited Orobanche minor seed germination without significantly affecting the seed germination of Trifolium pratense and the growth of Aspergillus oryzae and Escherichia coli. Using ESI-MS, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR, we identified the active compound as cycloheximide. Cycloheximide had half-maximum inhibitory concentrations of 2.6 ng/mL for the inhibition of seed germination of O. minor and 2.5 µg/mL for that of the conidial germination of A. oryzae. Since cycloheximide is known to inhibit translation by interacting with ribosomal protein L28 (RPL28) in yeast, we investigated whether RPL protein of O. minor plays a critical role in the inhibition of O. minor seed germination. Our data suggested that O. minor RPL27A was not sensitive to cycloheximide by comparing it to the strain expressing S. cerevisiae RPL28. These findings suggest the presence of an unidentified mechanism by which cycloheximide hinders O. minor seed germination.
- 著者
- Takamitsu Otake Keisuke Nakamura Nobuyasu Hanari
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.4, pp.137-148, 2023-11-20 (Released:2023-12-08)
- 参考文献数
- 57
A method of quantifying glyphosate (Gly) in human urine by means of MonoSpin TiO extraction and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl chloride (FMOC-Cl) derivatization with isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was investigated and optimized. The method’s quantification limit under optimized conditions was 0.3 µg/kg for FMOC-Gly, which was comparable to or lower than those described in previous studies. When a spike test using human urine samples was carried out with optimized analytical conditions, the trueness for FMOC-Gly was as follows: 101.6–104.9% for a spike level of 0.5 µg/kg and 99.2–101.0% for a spike level of 30 µg/kg. The intra-day repeatability and inter-day reproducibility were <6.5%. The spike test results for validation between the “with” and “without” derivatization methods were comparable at 1 µg/kg. Our results indicate that using MonoSpin TiO extraction and FMOC-Cl derivatization with IDMS is an accurate method for analyzing Gly in human urine.
- 著者
- Navjot Singh Brar Kousik Mandal Simerjeet Kaur Amanpal Kaur Sandhu Makhan Singh Bhullar Maninder Pal Singh
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.4, pp.225-233, 2023-11-20 (Released:2023-12-08)
- 参考文献数
- 33
Use of agro-chemicals in forage crops is restricted due to the fear of direct toxicity to livestock and risk of pesticide residue accumulation in the food chain. Wheat and barley can be used as green fodder and silage, and herbicide residue estimation in green fodder and silage is important for ensuring the safety of dairy cattle. A field experiment was conducted for two years to study pendimethalin residues in the green fodder and silage of wheat and barley. In both cereal crops, pendimethalin (1.125 kg a.i./ha) was applied as pre-emergence along with an unsprayed control. Pendimethalin residues in fodder, silage, and soil were estimated using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). At harvest, pendimethalin residues in fodder and silage of wheat and barley were below the limit of quantification (<0.01 mg/kg) during both crop seasons. Pendimethalin can be safely used for weed control in winter cereals grown for fodder and silage.
1 0 0 0 OA 「植物の代謝系理解」の再構築
- 著者
- 吉川 博道
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.316-321, 2011-05-20 (Released:2012-11-30)
- 参考文献数
- 13
1 0 0 0 OA タイの農薬事情について
- 著者
- 都築 伸幸
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.31, no.3, pp.359-365, 2006-08-20 (Released:2014-02-15)
- 被引用文献数
- 1 1
- 著者
- Soichiro Ikuta Eiichiro Fukusaki Shuichi Shimma
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.48, no.2, pp.29-34, 2023-05-20 (Released:2023-06-14)
- 参考文献数
- 23
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Fungicides must penetrate the internal tissues of plants to kill pathogenic fungi. Mass spectrometers have been used to confirm this penetration, but conventional mass spectrometric methods cannot distinguish the fungicides in different internal tissues owing to the extraction steps. However, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) can detect the penetration of fungicides into leaf sections through direct analysis of the sample surfaces. Therefore, the objective of this study was to establish a method for visualizing fungicide penetration in wheat leaf cross sections using MALDI-MSI. The penetration of azoxystrobin from the epidermal to the internal tissue of the leaves was observed. Moreover, azoxystrobin accumulates in the cells around the vascular bundle. This study suggests that MSI can be useful for the evaluation of fungicide penetration in plant leaves.
1 0 0 0 OA 病害防除における抵抗性誘導剤の可能性
- 著者
- 沢田 治子
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.4, pp.326-329, 2009-11-25 (Released:2013-12-14)
- 被引用文献数
- 2 3
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Katsuta Michikazu Nomura Takeo Wakita Hidenori Daido Yumi Kobayashi Atsuko Kawahara Shinichi Banba
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.44, no.2, pp.120-128, 2019-05-20 (Released:2019-05-20)
- 参考文献数
- 17
- 被引用文献数
- 32 49
Broflanilide (1), discovered by Mitsui Chemicals Agro, Inc., has a unique chemical structure characterized as a meta-diamide and exhibits high activity against various pests, including Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, and Thysanopteran pests. Because broflanilide has a novel mode of action, the Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) categorized it as a member of a new group: Group 30. The meta-diamide structure was generated via drastic structural modification of a lead compound, flubendiamide (2), and the subsequent structural optimization of meta-diamides on each of its three benzene rings led to the discovery of broflanilide. In the present study, the details of the generation of meta-diamides from the lead compound and the structural optimization of meta-diamides are described.
1 0 0 0 OA 新規水稲用除草剤ペノキススラムDASH-001SCの開発とその特性について
- 著者
- 白石 郁雄
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.30, no.3, pp.265-268, 2005-08-20 (Released:2014-06-08)
- 被引用文献数
- 5
- 著者
- Yingchen Li Lin Liu Jun Yang Qing Yang
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.43-52, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 48
- 被引用文献数
- 4 17
Chitin deacetylase (CDA) is a key enzyme involved in the modification of chitin and plays critical roles in molting and pupation, which catalyzes the removal of acetyl groups from N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitin to form chitosan and release acetic acid. Defects in the CDA genes or their expression may lead to stunted insect development and even death. Therefore, CDA can be used as a potential pest control target. However, there are no effective pesticides known to target CDA. Although there has been some exciting research progress on bacterial or fungal CDAs, insect CDA characteristics are less understood. This review summarizes the current understanding of insect CDAs, especially very recent advances in our understanding of crystal structures and the catalytic mechanism. Progress in developing small-molecule CDA inhibitors is also summarized. We hope the information included in this review will help facilitate new pesticide development through a novel action mode, such as targeting CDA.
- 著者
- Mei-Yin Chien Chih-Min Yang Chao-Hsiang Chen
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.47, no.1, pp.30-34, 2022-02-20 (Released:2022-02-20)
- 参考文献数
- 12
- 被引用文献数
- 10
Over ten-year routine inspection results on organochlorine pesticide (OCP) residue were summarized, OCPs residues, including BHC isomers (α, β, γ, and δ-BHC), DDT analogs (p,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDE, o,p′-DDT, and p,p′-DDT), and pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) and its metabolites (pentachloroaniline and methyl pentachlorophenyl sulfide (MPCPS)), in 1,665 samples for 37 types of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) using the QuEChERS method coupled with the GC-ECD. Based on the maximal residue levels for OCPs set by Asian pharmacopeias, PCNB contamination in Ginseng radix as well as the total DDT and PCNB contamination in Panacis quinquefolii radix are of concern. OCP residues in different parts of Panax ginseng were also compared. The total BHC residue in leaf and fibrous root, as well as the total DDT and PCNB residue in all parts, exceeded MRL of 0.1 mg/kg. Overall, this study provided meaningful results about OCP residue in CHM for pharmaceutical industries and consumers.
- 著者
- Toshifumi Nakao Miyuki Kawashima Shinichi Banba
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.D19-017, (Released:2019-05-31)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 5 9
The peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae, is a serious crop pest that has developed imidacloprid resistance, mainly through overexpression of CYP6CY3. Here, we established a metabolic assay using Drosophila S2 cells that stably expressed CYP6CY3. We found that CYP6CY3 showed metabolic activity against imidacloprid, as well as acetamiprid, clothianidin, and thiacloprid, but had no activity against dinotefuran. Our study suggested that stable gene expression in Drosophila S2 cells is useful for examining which insecticide is metabolized by P450 monooxygenases.
- 著者
- Atsushi Ishihara
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.4, pp.382-392, 2021-11-20 (Released:2021-11-20)
- 参考文献数
- 79
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Plants synthesize and accumulate a wide variety of compounds called secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites serve as chemical barriers to protect plants from pathogens and herbivores. Antimicrobial secondary metabolites are accumulated to prevent pathogen infection. These metabolites are classified into phytoalexins (induced in response to pathogen attack) and phytoanticipins (present prior to pathogen infection). The antimicrobial compounds in the grass family (Poaceae) were studied from the viewpoint of evolution. The studies were performed at three hierarchies, families, genera, and species and include the following: 1) the distribution of benzoxazinoids (Bxs) in the grass family, 2) evolutionary replacement of phytoanticipins from Bxs to hydroxycinnamic acid amide dimers in the genus Hordeum, and 3) chemodiversity of flavonoid and diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. These studies demonstrated dynamic changes in secondary metabolism during evolution, indicating the adaptation of plants to their environment by repeating scrap-and-build cycles.
- 著者
- Marie-Ève Picard Michel Cusson Stephanie E. Sen Rong Shi
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.7-15, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 61
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Reducing the use of broad-spectrum insecticides is one of the many challenges currently faced by insect pest management practitioners. For this reason, efforts are being made to develop environmentally benign pest-control products through bio-rational approaches that aim at disrupting physiological processes unique to specific groups of pests. Perturbation of hormonal regulation of insect development and reproduction is one such strategy. It has long been hypothesized that some enzymes in the juvenile hormone biosynthetic pathway of moths, butterflies and caterpillars (order Lepidoptera) display unique structural features that could be targeted for the development of Lepidoptera-specific insecticides, a promising avenue given the numerous agricultural and forest pests belonging to this order. Farnesyl diphosphate synthase, FPPS, is one such enzyme, with recent work suggesting that it has structural characteristics that may enable its selective inhibition. This review synthesizes current knowledge on FPPS and summarizes recent advances in its use as a target for insecticide development.
- 著者
- Kotaro Mori Hideya Tokuoka Hisashi Miyagawa Yoshiaki Nakagawa
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.120-123, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 22
Benzoylphenylureas (BPUs) were discovered as novel type insecticides about a half century ago; many analogs have been launched as insecticides and acaricides. BPUs are known to inhibit chitin synthesis in insects and other arthropods, but they have no effect against microorganisms such as fungi. We designed new chitin synthesis inhibitors based on the hypothesis that biomolecules that play important roles in cellulose and chitin biosynthesis are similar. In the full automatic modeling system (FAMS), the cellulose synthase was selected as a template three-dimensional structure. Thus, we focused on the structure of cellulose synthase inhibitor, isoxaben, to develop new chemistry. The 1,1-diethylethyl [-C(CH3)(CH2CH3)2] group of isoxaben was changed to a 4-substituted phenyl group bearing Cl, Et, or Ph. These compounds significantly inhibited chitin synthesis in the cultured integument of the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis. The activity of the 4-ethylphenyl analog was enhanced 30-fold by adding piperonyl butoxide to the culture medium.
- 著者
- Christopher Browning Alastair G. McEwen Kotaro Mori Taiyo Yokoi Dino Moras Yoshiaki Nakagawa Isabelle M. L. Billas
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.88-100, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 58
- 被引用文献数
- 7
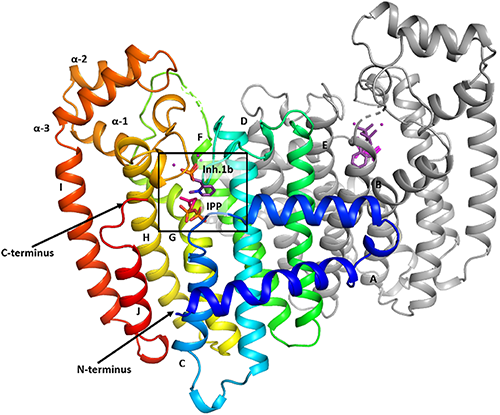
The ecdysone receptor (EcR) possesses the remarkable capacity to adapt structurally to different types of ligands. EcR binds ecdysteroids, including 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E), as well as nonsteroidal synthetic agonists such as insecticidal dibenzoylhydrazines (DBHs). Here, we report the crystal structures of the ligand-binding domains of Heliothis virescens EcR/USP bound to the DBH agonist BYI09181 and to the imidazole-type compound BYI08346. The region delineated by helices H7 and H10 opens up to tightly fit a phenyl ring of the ligands to an extent that depends on the bulkiness of ring substituent. In the structure of 20E-bound EcR, this part of the ligand-binding pocket (LBP) contains a channel filled by water molecules that form an intricate hydrogen bond network between 20E and LBP. The water channel present in the nuclear receptor bound to its natural hormone acts as a critical molecular adaptation spring used to accommodate synthetic agonists inside its binding cavity.
- 著者
- Jingbo Li Heping Han Lianyang Bai Qin Yu
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.45, no.2, pp.109-113, 2020-05-20 (Released:2020-05-20)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 1 9
Glyphosate is often tank-mixed with auxinic herbicide 2,4-D for grass and broadleaf weed control. Here we examined the possible interaction of 2,4-D and glyphosate in barnyard grass, Echinochloa colona (L.) Link. The results showed that 2,4-D antagonizes glyphosate remarkably in glyphosate-resistant populations but only marginally in susceptible populations. This antagonism is related to reduced glyphosate uptake and (to a lesser extent) translocation. As 2,4-D has multiple, unpredictable effects on other herbicides, care must be taken when tank-mixing herbicides with 2,4-D.
1 0 0 0 OA ミツバチの配偶行動
- 著者
- 吉田 忠晴
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.4, pp.497-502, 2011-11-25 (Released:2012-11-10)
- 参考文献数
- 30
- 著者
- Changmann Yoon Shin-Ho Kang Jeong-Oh Yang Doo-Jin Noh Pandiyan Indiragandhi Gil-Hah Kim
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.34, no.2, pp.77-88, 2009-05-25 (Released:2009-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 22 34
The repellent efficacy of 17 essential oils against the German cockroach, Blattella germanica was examined using a T-tube olfactometer. Five oils repelled B. germanica with good efficacy, ranging from 70.0 to 96.7%. Four of these oils, grapefruit, lemon, lime, and orange, were from the citrus family Rutaceae. These citrus essential oils showed similar repellent activity against two more cockroach species, such as Periplaneta americana and P. fuliginosa. Gas chromatography (GC) and GC-mass spectrometry analyses revealed that the major components responsible for the repellent activity of the citrus oils were limonene, β-pinene and γ-terpinene. Limonene appears to be the main component responsible for the repellent activity rather than β-pinene and γ-terpinene. The repellent efficacy of these components varied with different doses and the cockroach species tested. It is likely that minor components of the oils also contributed to the overall repellent activity of citrus essential oils, except orange oil. The activity of orange oil is almost solely attributed to the activity of limonene. Also, the repellent activity of citrus oil and that of each of the terpenoids makes little difference to the efficacy of a repellant against the three species of cockroaches.
- 著者
- Eikoh Satoh Ryota Kasahara Kosuke Fukatsu Takao Aoki Hiroto Harayama Tetsuya Murata
- 出版者
- Pesticide Science Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Pesticide Science (ISSN:1348589X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.46, no.1, pp.109-114, 2021-02-20 (Released:2021-02-26)
- 参考文献数
- 8
- 被引用文献数
- 5
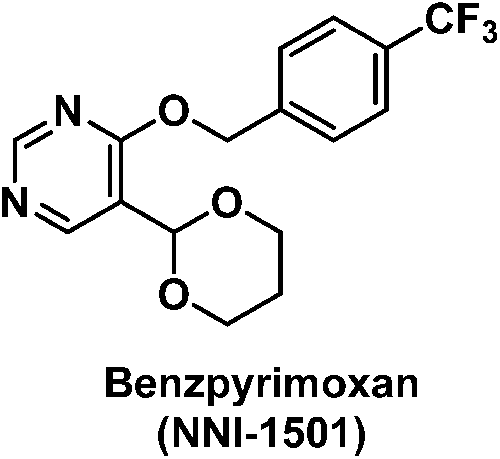
Benzpyrimoxan (5-(1,3-dioxan-2-yl)-4-{[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy}pyrimidine, NNI-1501) was discovered as a novel insecticide structurally characterized by a pyrimidine derivative substituted with 1,3-dioxanyl and 4-trifluoromethylbenzyloxy groups. The compound showed remarkable activity against nymphs of rice planthoppers, including strains resistant to existing insecticides. Furthermore, benzpyrimoxan had low adverse effects on pollinators and beneficial arthropods. Because of these features, benzpyrimoxan is expected to be a suitable part of an integrated pest management strategy. In this report, the history of the discovery to reach benzpyrimoxan and details of the structure–activity relationships are described.