1 0 0 0 OA Low-pH Stability of Influenza A Virus Sialidase Contributing to Virus Replication and Pandemic
- 著者
- Tadanobu Takahashi Takashi Suzuki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.38, no.6, pp.817-826, 2015-06-01 (Released:2015-06-01)
- 参考文献数
- 69
- 被引用文献数
- 3 11
The spike glycoprotein neuraminidase (NA) of influenza A virus (IAV) has sialidase activity that cleaves the terminal sialic acids (viral receptors) from oligosaccharide chains of glycoconjugates. A new antigenicity of viral surface glycoproteins for humans has pandemic potential. We found “low-pH stability of sialidase activity” in NA. The low-pH stability can maintain sialidase activity under acidic conditions of pH 4–5. For human IAVs, NAs of all pandemic viruses were low-pH-stable, whereas those of almost all human seasonal viruses were not. The low-pH stability was dependent on amino acid residues near the active site, the calcium ion-binding site, and the subunit interfaces of the NA homotetramer, suggesting effects of the active site and the homotetramer on structural stability. IAVs with the low-pH-stable NA showed much higher virus replication rates than those of IAVs with low-pH-unstable NA, which was correlated with maintenance of sialidase activity under an endocytic pathway of the viral cell entry mechanism, indicating contribution of low-pH stability to high replication rates of pandemic viruses. The low-pH-stable NA of the 1968 H3N2 pandemic virus was derived from the low-pH-stable NA of H2N2 human seasonal virus, one of two types classified by both low-pH stability in N2 NA and a phylogenetic tree of N2 NA genes. The 2009 H1N1 pandemic virus acquired low-pH-stable NA by two amino acid substitutions at the early stage of the 2009 pandemic. It is thought that low-pH stability contributes to infection spread in a pandemic through enhancement of virus replication.
- 著者
- Toshiaki Makino Ryosuke Shimizu Misaki Kanemaru Yukio Suzuki Masamitsu Moriwaki Hajime Mizukami
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.12, pp.2034-2040, 2009-12-01 (Released:2009-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 31
- 被引用文献数
- 71 129
Quercetin, a flavonol contained in various vegetables and herbal medicines, has various biological activities including anti-cancer, anti-allergic and anti-oxidative activities. However, low oral bioavailability of quercetin due to insolubility in water has limited its use as a food additive or dietary supplement. Since the water solubility is enhanced by glycosyl conjugation, in the present study, we evaluated the bioavailability of several quercetin glycosides with different sugar moieties in rats. Quercetin, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside (rutin), and quercetin-3-O-glucoside (isoquercitrin, IQC) in suspension, and quercetin-3-O-maltoside (Q3M), quercetin-3-O-gentiobioside (Q3G), α-monoglucosyl rutin (αMR), α-oligoglucosyl rutin (αOR), and enzymatically modified isoquercitrin (α-oligoglucosyl isoquercitrin, EMIQ) dissolved in water, were orally administered to rats under anesthesia. Bioavailability (F value) was calculated from the concentrations of total quercetin in plasma from 0 to 12 h after the administration. F value of quercetin was 2.0%, and those of IQC, Q3M and EMIQ were 12%, 30%, and 35%, respectively. Although Q3G, αMR and αOR have high water solubility, their F values were low (3.0%, 4.1%, 1.8%, respectively). In the in vitro study, the homogenate of rat intestinal epithelium rapidly hydrolyzed IQC, Q3M and EMIQ to quercetin, and αMR and αOR to rutin. However, it could not hydrolyze Q3G or rutin to quercetin. Elongation of α-linkage of glucose moiety in IQC enhances the bioavailability of quercetin, and intestinal epithelial enzymes such as lactase-phrolizin hydrolase or mucosal maltase-glucoamylase would play important roles in the hydrolysis and absorption of these flavonol glycosides.
- 著者
- Kohei Togami Sumio Chono Kazuhiro Morimoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.9, pp.1494-1499, 2013-09-01 (Released:2013-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 45
- 被引用文献数
- 9 24
Azithromycin (AZM), a 15-membered ring macrolide antimicrobial agent, has an antibacterial spectrum that includes intracellular parasitic pathogens that survive or intracellularly multiply in alveolar macrophages (AMs). The subcellular distribution of AZM in AMs was evaluated in vitro in comparison with clarithromycin (CAM). AZM and CAM (50 µM) were applied to the NR8383 cells, used as an in vitro model of AMs, followed by incubation at 37°C or 4°C. The total amount of AZM in cells and subcellular distribution (cell fractionation) was determined after incubation. High level of AZM accumulation was observed in the NR8383 cells at 37°C, and the equilibrium intracellular to extracellular concentration ratio (I/E ratio) was approximately 680, which was remarkably higher than that of CAM (equilibrium I/E ratio=28). The intracellular accumulation of AZM and CAM was temperature dependent. In addition, AZM distributed to the granules fraction including organelles and soluble fraction including cytosol in the NR8383 cells, whereas CAM mainly distributed in soluble fraction. The amount of AZM in the granules fraction was markedly reduced in the presence of ammonium chloride for increase in intracellular pH. These results indicate that AZM is distributed in acidic compartment in AMs. This study suggests that high AZM accumulation in the NR8383 cells is due to the trapping and/or binding in acidic organelles, such as lysosomes.
- 著者
- Shuji Kaneko Takuya Nagashima
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.3, pp.362-365, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 11
- 被引用文献数
- 15
Recent pharmacological studies have been developed based on finding new disease-related genes, accompanied by the production of gene-manipulated disease model animals and high-affinity ligands for the target proteins. However, the emergence of this gene-based strategy in drug development has led to the rapid depletion of drug target molecules. To overcome this, we have attempted to utilize clinical big data to explore a novel and unexpected hypothesis of drug–drug interaction that would lead to drug repositioning. Here, we introduce our data-driven approach in which adverse event self-reports are statistically analyzed and compared in order to find and validate new drug targets. The hypotheses provided by such a data-driven approach will likely impact the style of future drug development and pharmaceutical study.
- 著者
- Fumiko Yamaki Anna Koike Hikari Kono Xiaoyue Zhang Kento Yoshioka Keisuke Obara Yoshio Tanaka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.3, pp.493-502, 2020-03-01 (Released:2020-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 14
- 被引用文献数
- 2
The β-adrenoceptor (β-AR)-mediated pharmacological effects of catecholamine (CA) metabolites are not well known. We examined the effects of seven CA metabolites on smooth muscle relaxation in mouse and guinea pig (GP) tracheas and rat thoracic aorta. Among them, metadrenaline (MA) significantly relaxed GP trachea (β2-AR dominant), even in the presence of clorgiline, a monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor. In mouse trachea (β1-AR dominant), normetadrenaline (NMA) and MA (10−4 M each) apparently did not affect isoprenaline (ISO)-induced relaxation, but significantly inhibited it in the presence of clorgiline. ISO-induced relaxation was also unaffected by 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol (DHPG) (10−4 M), but significant suppression was observed with the addition of 3,5-dinitrocatechol, a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor. In GP trachea, NMA, MA, 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid (DOMA), and DHPG (10−4 M each) significantly augmented ISO-induced relaxation. However, in the presence of clorgiline plus 3,5-dinitrocatechol, both NMA and MA (10−4 M) significantly suppressed ISO-induced relaxation. DHPG (10−4 M) also significantly suppressed ISO-induced relaxation in the presence of 3,5-dinitrocatechol. In rat thoracic aorta, DHPG (10−4 M) significantly suppressed relaxation induced by CGP-12177 A (a β3-AR partial agonist) in the presence of 3,5-dinitrocatechol plus propranolol. Our findings indicate that 1) MA may possess β2-AR agonistic action; 2) NMA and MA augment β2-AR-mediated tracheal relaxation in the absence of CA metabolic inhibitors, though themselves possessing β1-, β2-AR antagonistic action (β2 > β1); 3) DHPG exhibits β1-, β2-, β3-AR antagonistic action, and this is particularly marked for β3-AR. Our observations may help explain some of the pathologies associated with pheochromocytoma, which is characterized by increased CA metabolite levels.
- 著者
- Naohiro Oshima Honoka Kume Takayoshi Umeda Haruki Takito Mitsutoshi Tsukimoto Noriyasu Hada
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.1, pp.91-95, 2020-01-01 (Released:2020-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Magnolia Flower is a crude drug used for the treatment of headaches, toothaches, and nasal congestion. Here, we focused on Magnolia kobus, one of the botanical origins of Magnolia Flower, and collected the flower parts at different growth stages to compare chemical compositions and investigate potential inhibitory activities against interleukin-2 (IL-2) production in murine splenic T cells. After determining the structures, we examined the inhibitory effects of the constituents of the bud, the medicinal part of the crude drug, against IL-2 production. We first extracted the flower parts of M. kobus from the bud to fallen bloom stages and analysed the chemical compositions to identify the constituents characteristic to the buds. We found that the inhibitory activity of the buds against IL-2 production was more potent than that of the blooms. We isolated two known compounds, tiliroside (1) and syringin (2), characteristic to the buds from the methanol (MeOH) extract of Magnolia Flower. Moreover, we examined the inhibitory activities of both compounds against IL-2 production and found that tiliroside (1) but not syringin (2), showed strong inhibitory activity against IL-2 production and inhibited its mRNA expression. Thus, our strategy to examine the relationship between chemical compositions and biological activities during plant maturation could not only contribute to the scientific evaluation of medicinal parts of crude drugs but also assist in identifying biologically active constituents that have not yet been reported.
- 著者
- Keigo Ueno Nao Yanagihara Kiminori Shimizu Yoshitsugu Miyazaki
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.2, pp.230-239, 2020-02-01 (Released:2020-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 102
- 被引用文献数
- 24
Cryptococcosis is a potentially lethal disease caused by fungal pathogens including Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii species complex. These fungal pathogens live in the environment and are associated with certain tree species and bird droppings. This infectious disease is not contagious, and healthy individuals may contract cryptococcal infections by inhaling the airborne pathogens from the environment. Although cleaning a contaminated environment is a feasible approach to control environmental fungal pathogens, prophylactic immunization is also considered a promising method to regulate cryptococcal infections. We review the history of the development of cryptococcal vaccines, vaccine components, and the various forms of immune memory induced by cryptococcal vaccines.
- 著者
- Javier Pizarro-Bauerle Hiroki Ando
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.2, pp.240-249, 2020-02-01 (Released:2020-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 97
- 被引用文献数
- 15
The diversity of advanced genetic engineering techniques that have become available in recent years has enabled a more precise manipulation of genes and genomes. Among these, bacteriophage genomes stand out as an interesting target due to their dependence on a host for replication, which previously complicated their manipulation, and due as well to the many possible fields in which they can be used. In this review, we highlight recent applications for which genetically modified bacteriophages are being employed: as phage therapy in medicine, animal industries and agricultural settings; as a source of new antimicrobials; as biosensors for research, health and environmental purposes; and as genetic engineering tools themselves.
- 著者
- Hiromitsu Takayama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.68, no.2, pp.103-116, 2020-02-01 (Released:2020-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 67
- 被引用文献数
- 8
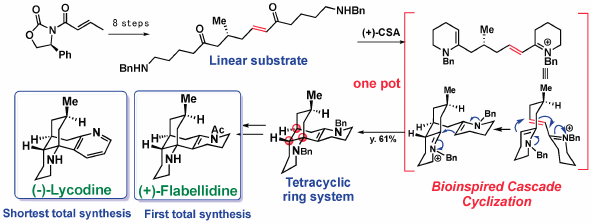
The merits of biogenetic considerations in the chemical syntheses of natural products have been emphasized by describing the total syntheses of Lycopodium alkaloids; lycodine, flabellidine, lycopodine, and flabelliformine, as well as monoterpenoid indole alkaloids; C-mavacurine, kopsiyunnanine K, koumine, and 11-methoxy-19R-hydroxygelselegine.
1 0 0 0 OA Notice of Withdrawal
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1957, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 著者
- Shinichi Harada Wataru Matsuura Masaoki Takano Shogo Tokuyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.2, pp.230-238, 2016-02-01 (Released:2016-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 80
- 被引用文献数
- 7 9
This article has been deleted at the request of the authors from this journal. The Editorial Committee of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (September 17, 2019)
- 著者
- Shinichi Harada Wakako Hamabe Kohei Kamiya Toshiko Satake Junichiro Yamamoto Shogo Tokuyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.32, no.3, pp.405-409, 2009-03-01 (Released:2009-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 20
- 被引用文献数
- 30 35
This article has been deleted at the request of the authors from this journal. The Editorial Committee of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (September 17, 2019)
- 著者
- Tomoya Tachi Yoshihiro Noguchi Hitomi Teramachi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.43, no.1, pp.77-86, 2020-01-01 (Released:2020-01-01)
- 参考文献数
- 38
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Utilization of community pharmacies/pharmacists is important for promoting appropriate self-medication; however, appropriate self-medication via pharmacies/pharmacists has not been well-implemented in Japan. Based on the transtheoretical model of health behavior change, we constructed an Educational Program for Promoting Appropriate Self-medication via Pharmacies and Pharmacists to inform the public about the assistive services of pharmacies/pharmacists regarding self-medication and the use of medication notebooks for self-medications. We then tested the efficacy of the program through a randomized controlled trial. The subjects were residents living around Gifu City, aged 20 years and above, and recruited through posters and pamphlets. The subjects were randomly allocated to a group that received only a medication/health class (control group) or one that received the medication/health class, as well as the educational program (intervention group). A questionnaire was administered immediately before the medication/health class (T1) and 2 months afterwards (T2), which allowed us to evaluate and compare the changes in the two groups’ behavior regarding performing appropriate self-medication via pharmacies/pharmacists. The percentage of people who began consulting with pharmacists concerning self-medication was significantly higher among the intervention group (38.2%, 13/34) than the control group (14.3%, 4/28) (p = 0.047). The percentage of people who began recording details of self-medication in their medication notebooks was significantly higher among the intervention group (38.2%, 13/34) than the control group (10.7%, 3/28) (p = 0.019). The educational program effectively encouraged the public to adopt appropriate self-medication practices to avail the services provided by pharmacies/pharmacists.
- 著者
- Noriaki Shima Akihiro Miki Tooru Kamata Munehiro Katagi Hitoshi Tsuchihashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Health Science (ISSN:13449702)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.51, no.2, pp.147-154, 2005 (Released:2005-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 21 26
The endogenous level of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and the in vitro production of GHB in blood from healthy humans have been investigated. The endogenous GHB concentrations in aseptically collected whole blood samples ranged from 5 to 10 ng/ml, which were far below the previously-reported “endogenous” levels . Also, the levels of in vitro GHB production during storage for 16 months at 4°C were lower than 0.4 μg/ml, which were much lower than those in postmortem samples previously reported. Based on the results of this investigation, the authors concluded that an interpretative cutoff of 1.0 μg/ml would be appropriate for differentiating exogenous from endogenous GHB, if only limited to in-life blood specimens that were collected aseptically, stored at 4°C or lower, examined within two weeks, and excludes the possibility of GHB aciduria.
- 著者
- Hiroshi Ueda
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1773-1782, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 67
- 被引用文献数
- 4 10
Currently, only a few medicines have been approved for use in the clinical treatment of chronic pain, but they are not fully satisfying due to their side effects. From the view that radical treatment, rather than simply treating symptoms, is more important in addressing life-long chronic pain, we have been investigating translational research for a mechanism-based medicine to treat pain. Through the characterization of various types of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in mice, we discovered that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) plays roles in definitive mechanisms of the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. We found LPA1 receptor- and LPA3 receptor-mediated amplification of LPA production could be a key mechanism underlying the initiation and maintenance of this pain. We have developed stress-induced fibromyalgia models, and have revealed that LPA1 receptor-signaling also plays key roles in the mechanism. Throughout these studies, we found that LPA plays a key role in pain memory, and that LPA1 receptor- and LPA3 receptor-antagonists could reverse the established pain, and thereby cure the disease source of pain.
- 著者
- Setsuo Kinoshita Tadahaya Mizuno Megumi Hori Michiaki Kohno Hiroyuki Kusuhara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.12, pp.2069-2075, 2019-12-01 (Released:2019-12-01)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Proteome profiling based on two-dimensional (2D)-DIGE might be a useful tool for investigating drug-like compounds and the mode of action of drugs. However, obtaining data for profiling requires high labor costs, and it is difficult to control the reproducibility of spot positions because 2D-DIGE usually requires large-size glass plates and spot alignments are greatly affected by the quality of DryStrips and polyacrylamide gels (PAGs). Therefore, we have developed a novel platform by employing small size DryStrips and PAGs, and an image analysis strategy based on dual correction of spot alignment and volume. Our system can automatically detect a large number of consistent spots through all images. Cytosol fractions of HeLa cells treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or bortezomib were analyzed, 1697 consistent spots were detected, and 775 of them were significantly changed with the treatment. Deviations between different days and lot sets of DryStrips and PAGs were investigated by calculating the correlation coefficients. The mean values of the correlation between days and lot sets were 0.96 and 0.94, respectively. Clustering analysis of all the treatment data clearly separated the DMSO or bortezomib treated groups beyond day deviations. Thus, we have succeeded in developing an easy-to-handle 2D-DIGE system that can be a novel proteome profiling platform.
- 著者
- Kentaro Ayada Masahiro Tsuchiya Hiroyuki Yoneda Kouji Yamaguchi Hiroyuki Kumamoto Keiichi Sasaki Takeshi Tadano Makoto Watanabe Yasuo Endo
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.8, pp.1326-1330, 2017-08-01 (Released:2017-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Recent studies suggest that histamine—a regulator of the microcirculation—may play important roles in exercise. We have shown that the histamine-forming enzyme histidine decarboxylase (HDC) is induced in skeletal muscles by prolonged muscular work (PMW). However, histological analysis of such HDC induction is lacking due to appropriate anti-HDC antibodies being unavailable. We also showed that the inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α can induce HDC, and that PMW increases both IL-1α and IL-1β in skeletal muscles. Here, we examined the effects (a) of PMW on the histological evidence of HDC induction and (b) of IL-1β and TNF-α on HDC activity in skeletal muscles. By immunostaining using a recently introduced commercial polyclonal anti-HDC antibody, we found that cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, became HDC-positive after PMW. After PMW, TNF-α, but not IL-1α or IL-1β, was detected in the blood serum. The minimum intravenous dose of IL-1β that would induce HDC activity was about 1/10 that of TNF-α, while in combination they synergistically augmented HDC activity. These results suggest that PMW induces HDC in skeletal muscles, including cells in the endomysium and around blood vessels, and also some muscle fibers themselves, and that IL-1β and TNF-α may cooperatively mediate this induction.
- 著者
- Naoki Midoh Takanori Noguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Journal of Health Science (ISSN:13449702)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.55, no.1, pp.56-61, 2009 (Released:2009-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 16
- 被引用文献数
- 3 5
Chicken soup has long been considered anecdotally healthful in Western and Southeast Asian countries. In this study, we examined the effects of a 2-week intake of chicken soup on mood states and of a single and 2-week intake on peripheral blood flow. Thirty healthy volunteers (7 men and 23 women aged 20.5±1.4 years) participated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study with 2 weeks treatment and washout periods. They were randomly assigned to two groups, and daily received either chicken soup or placebo soup. Mood states by the Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaire and peripheral blood flow by a laser-Doppler blood flow imaging system were assessed before and after each treatment period. On the first day of the treatment periods, the effect of single intake on peripheral blood flow was investigated. The 2-week intake of chicken soup significantly reduced the tension-anxiety (T-A) score compared to the placebo soup (p<0.05). The single intake of chicken soup significantly increased peripheral blood flow as compared with the base value (20 min after intake p<0.01; 25, 30 and 45 min after intake p<0.001) and that of the placebo soup (25, 30 and 60 min after intake p<0.05; 45 min after intake p<0.01). The 2-week intake of chicken soup also significantly increased peripheral blood flow over that of the placebo soup (p<0.001). Chicken soup was considered to have improved mood states such as tension and anxiety and increased peripheral blood flow.
- 著者
- Hironori Tsuchiya Maki Mizogami Takahiro Ueno Kenji Shigemi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.35, no.6, pp.988-992, 2012-06-01 (Released:2012-06-02)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 5 11
The cardiotoxic effects of local anesthetics increase in cardiac ischemia which is characterized by the tissue pH lowering to 6.5 or less. Apart from the cardiac channel blockade, the membrane interaction has been referred to as another mode of their cardiotoxic action. By using biomimetic membranes, we verified the hypothesis that bupivacaine and lidocaine may increasingly interact with cardiac mitochondrial membranes under ischemia-like acidic conditions. Biomimetic membranes were prepared with different phospholipids and cholesterol to be unilamellar vesicles suspended in buffers of pH 7.4, 6.9, 6.4 or 5.9. Bupivacaine and lidocaine were reacted with the membrane preparations at cardiotoxically relevant concentrations and their membrane interactivities were determined by measuring fluorescence polarization. Both drugs interacted with 100 mol% 1,2-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, peripheral nerve cell-mimetic and cardiomyocyte-mimetic membranes to increase membrane fluidity, although lowering the reaction pH from 7.4 to 5.9 decreased their membrane-fluidizing effects. In cardiomyocyte mitochondria-mimetic membranes containing 20 mol% cardiolipin, however, bupivacaine and lidocaine reversely increased their membrane interactivities at pH 5.9–6.4 compared with pH 7.4. Such increases were greater in anionic phospholipid membranes which consisted of substantial amounts of cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine. Positively charged bupivacaine and lidocaine would form ion-pairs with the negatively charged head-groups of anionic phospholipids under acidic conditions, thereby increasing the induced membrane fluidization. The mitochondrial membrane interactions depending on pH lowering may be, at least in part, responsible for local anesthetic cardiotoxicity enhanced in acidosis associated with cardiac ischemia.
- 著者
- Wei Peng Yan-Yan Ma Kun Zhang Ai-Yu Zhou Yu Zhang Huaqian Wang Zhiyun Du Deng-Gao Zhao
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.c16-00030, (Released:2016-03-24)
- 参考文献数
- 18
- 被引用文献数
- 6 14
Long-term use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause serious side effects such as gastric mucosal damage. Resveratrol, a naturally dietary polyphenol, exhibited anti-inflammatory activity and a protective effect against gastric mucosa damage induced by NSAIDs. In this regard, we synthesized a series of resveratrol-based NSAIDs derivatives and evaluated their anti-inflammatory activity against NO overproduction in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. We identified mono-substituted resveratrol–ibuprofen combination 21 as the most potent anti-inflammatory agent, which is more active than a physical mixture of ibuprofen and resveratrol, individual ibuprofen, or individual resveratrol. In addition, compound 21 exerted potent inhibitory effects on the LPS-induced expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. Furthermore, compound 21 significantly increased the survival rate in an LPS-induced acute inflammatory model and produced markedly less gastric damage than ibuprofen. It was found that compound 21 may be a potent anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of inflammation-related diseases.