1 0 0 0 OA Risk Factors for Severe Hyponatremia Related to Cisplatin: A Retrospective Case-Control Study
- 著者
- Shiro Hatakeyama Toshihiro Shida Hiroaki Yamaguchi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1891-1897, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Onset of severe hyponatremia following cisplatin (CDDP) administration has been previously reported. However, the risk factors associated with hyponatremia still remain unclear. We conducted a retrospective, single-center, case-control study to identify independent risk factors of severe hyponatremia in patients with various types of cancers. Adult patients who received intravenous CDDP administration between January 2012 and December 2017 met the inclusion criteria. The investigators recorded patients’ demographics and clinical information retrospectively, and assessed the lowest serum sodium level within 21 d of the first CDDP administration. Risk factors for grade ≥3 hyponatremia were examined via a logistic regression analysis. Among a total of 472 patients, fifty patients (10.6%) developed grade ≥3 hyponatremia. Univariate analysis revealed that age (≥65 years), presence of small cell lung or esophageal cancer, and lower sodium concentrations in the serum (<138 mEq/L) were significantly associated with grade 3 and 4 hyponatremia. Additionally, multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the presence of small cell lung cancer (adjusted odds ratio, 3.26; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.07–10.00) and lower sodium concentrations in the serum (<138 mEq/L) (adjusted odds ratio, 6.18; 95%CI, 3.21–11.90) were independent risk factors of grade 3 and 4 hyponatremia. Thus, serum sodium concentrations in patients with these risk factors should be closely monitored after CDDP administration.
- 著者
- Ken Konaka Takumi Sakurada Tatsuhiko Saito Sachiko Mori Masaki Imanishi Soji Kakiuchi Shuji Fushitani Keisuke Ishizawa
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.11, pp.1839-1845, 2019-11-01 (Released:2019-11-01)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 5
Uridine 5′-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), a metabolic enzyme of irinotecan active metabolite, has two genetic polymorphisms (UGT1A1*6 and UGT1A1*28). In UGT1A1 homozygous or heterozygous patients, metabolism is delayed and the risk of developing adverse effects is increased, and therefore, dose reduction of irinotecan is considered. However, the specific dose reduction rate of irinotecan for heterozygous patients is uncertain. We studied the necessity of irinotecan dose reduction and its optimal dose in UGT1A1 heterozygous patients with lung cancer. Patients with lung cancer treated with irinotecan in the Tokushima University Hospital or Tokushima Municipal Hospital were included in this study. The dose of irinotecan was evaluated based on the relative dose intensity (RDI). The time to treatment failure (TTF) was defined as the period until treatment change, death, or progressive disease based on response evaluation criteria of solid tumors. We targeted 31 patients treated with irinotecan: 12 wild types (WT), 14 heterozygotes, and 1 complex heterozygote and 4 homozygotes. There was no significant difference in the TTF, but the mean RDI during the entire treatment period was significantly different in the wild type (79%), heterozygous (62%), and complex heterozygous and homozygous groups (46%). In addition, the proportion of patients who completed treatment without dose reduction in the WT group tended to be higher than that in the other groups. For lung cancer patients with UGT1A1 heterozygote types who start irinotecan therapy, reducing the initial dose by approximately 20% might be a safer chemotherapy without decreasing the therapeutic effect.
- 著者
- Takuya Hoshino Motoshige Azuma Yuki Yamada Varin Titapiwatanakun Mika Yoshimura Fujii Yoshihisa Yamamoto Tatsuo Koide Toshiro Fukami
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.9, pp.929-934, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 3
We investigated the water contents in commercial semi-solid preparations used for pressure ulcer (PU) treatment using near-IR spectroscopy (NIRS) and compared the results with those measured using the Karl Fischer (KF) method. The aim of this study was to determine a standard method and select the appropriate topical preparation with the optimal moisture for PU treatment. The water absorption properties of bases and formulations were evaluated with a time-dependent factor using Transwell as the model membrane. KF and NIRS were applicable as measurement methods of the water content in semi-solid formulations. NIRS was shown to be a useful, simple, nondestructive tool that is more advantageous than the KF method. The water absorption characteristics tested using Transwell revealed that the rate of and capacity for water absorption are determined not only by the absorption ability of the polymer base but also by other factors, such as the osmotic pressure exerted by additives. KF and NIR measurements can be used to choose external skin preparations to control the amount of water in PU treatment.
- 著者
- Mari Hara Nakano Chihiro Udagawa Arata Shimo Yasuyuki Kojima Reiko Yoshie Hisamitsu Zaha Norie Abe Tokiwa Motonari Mikiko Unesoko Kenji Tamura Tatsunori Shimoi Masayuki Yoshida Teruhiko Yoshida Hiromi Sakamoto Ken Kato Taisei Mushiroda Koichiro Tsugawa Hitoshi Zembutsu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00527, (Released:2019-10-09)
- 参考文献数
- 42
- 被引用文献数
- 14
Trastuzumab has been administered to patients with HER2-positive cancer, however, the cardiotoxicity is identified as one of the life-threatening toxicities. Clinically useful biomarker for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity has been expected to be developed. To identify a novel genetic marker(s) determining the risk of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity, we performed a first genome-wide association study (GWAS) in Japanese population. We enrolled 481 patients who had been treated with trastuzumab and carried out a GWAS using 11 cases (with cardiotoxicity) and 257 controls (without cardiotoxicity). Top 100 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which revealed the smallest P values in GWAS (P = 7.60 x 10-7 - 2.01 x 10-4) were further examined using replication samples consisted of 14 cases and 199 controls. The combined analysis of the GWAS and replication study indicated possible association of five loci with trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity (rs9316695 on chromosome 13q14.3, rs28415722 on chromosome 15q26.3, rs7406710 on chromosome 17q25.3, rs11932853 on chromosome 4q25, and rs8032978 on chromosome 15q26.3, Pcombined = 6.00 x 10-6, 8.88 x 10-5, 1.07 x 10-4, 1.42 x 10-4, 1.60 x 10-4, respectively). Furthermore, we developed a risk prediction model for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity using the five marker SNPs. The incidence of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with risk score ≥ 5 was significantly higher (42.5%) compared to that in patients with score ≤ 4 (1.8%) (P = 7.82 x 10-15, odds ratio = 40.0). These findings suggest the potential to improve the ability of physicians to avoid the trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity for patients with HER2-positive cancer.
1 0 0 0 OA Therapeutic Application of Stem Cell Technology toward the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
- 著者
- Kaneyasu Nishimura Jun Takahashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.36, no.2, pp.171-175, 2013-02-01 (Released:2013-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 27 37
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the candidate diseases for cell transplantation therapy, since successful clinical experiments have accumulated using human fetal tissue grafting for PD patients. Although some grafted PD patients have shown drastic improvements, several issues still remain with regard to using human fetal tissue. This review highlights the recent advances in stem cell technology toward clinical applications using human pluripotent stem cells. In particular, pluripotent stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), are the focus as a source of cell transplantation therapy that can be used instead of human fetal tissues. Additionally, efficient methods for stem cell maintenance and differentiation have been developed and improved toward the clinical transition. These advances in the basic technologies have helped accelerate the realization of regenerative medicine. We also review the current topics regarding disease modeling and drug screening using iPSC technology. Finally, we also describe the future prospects of these stem cell research fields toward clinical application.
- 著者
- Hiroyuki Nojima Yasuomi Kiyota Genki Terashi Mayuko Takeda-Shitaka Hajime Matsubara
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.10, pp.1061-1071, 2019-10-01 (Released:2019-10-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
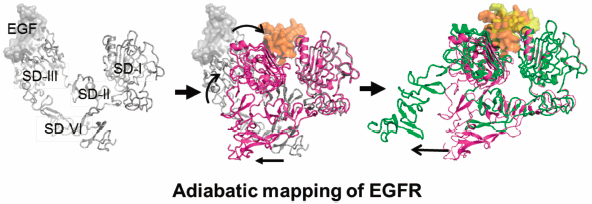
The activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) involves the geometrical conversion of the extracellular domain (ECD) from the tethered to the extended forms with the dynamic rearrangement of the relative positions of four subdomains (SDs); however, this conversion process has not yet been thoroughly understood. We compare the two different forms of the X-ray crystal structures of ECD and simulate the ECD conversion process using adiabatic mapping that combines normal mode analysis of the elastic network model (ENM-NMA) and energy optimization. A comparison of the crystal structures reveals the rigidity of the intradomain geometry of the SD-I and -III backbone regardless of the form. The forward mapping from the tethered to the extended forms retains the intradomain geometry of the SD-I and -III backbone and reveals the trends to rearrange the relative positions of SD-I and -III and to dissociate the C-terminal tail of SD-IV from the hairpin loop in SD-II. The reverse mapping from the extended to the tethered forms complements the promotion of ECD conversion in the presence of epidermal growth factor (EGF).
- 著者
- Akinori Shintani Hiroyuki Yamazaki Yukinori Yamamoto Firoj Ahmed Masami Ishibashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.57, no.8, pp.894-895, 2009-08-01 (Released:2009-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 9
- 被引用文献数
- 7 11
Chemical investigation of field-collected fruit bodies of the myxomycete Cribraria meylanii resulted in the isolation of a naphthoquinone pigment, cribrarione C, and its structure was elucidated by spectral data as 2,5,6,7-tetrahydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (1). This compound (1) had been synthesized previously, while it was isolated here for the first time as a natural product, and its NMR and MS data are described in this study.
- 著者
- Yae Ishikawa Masami Ishibashi Yukinori Yamamoto Masahiko Hayashi Kanki Komiyama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.50, no.8, pp.1126-1127, 2002 (Released:2002-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 6
- 被引用文献数
- 15 24
Lindbladione (1), 7-methoxylindbladione (2), and 6, 7-dimethoxylindbladione (3) have been isolated from a myxomycete Lindbladia tubulina and their structures were elucidated by spectral data.
1 0 0 0 OA Antibody Fragments for On-Site Testing of Cannabinoids Generated via in Vitro Affinity Maturation
- 著者
- Izumi Morita Hiroyuki Oyama Mayumi Yasuo Kazuhisa Matsuda Kengo Katagi Aya Ito Hiroka Tatsuda Hiroyuki Tanaka Satoshi Morimoto Norihiro Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.2, pp.174-181, 2017-02-01 (Released:2017-02-01)
- 参考文献数
- 40
- 被引用文献数
- 10 17
Law enforcement against illicit use of cannabis and related substances requires rapid, feasible, and reliable tools for on-site testing of cannabinoids. Notably, methods based on cannabinoid-specific antibodies enable efficient screening of multiple specimens. Antibody engineering may accelerate development of modern and robust testing systems. Here, we used in vitro affinity maturation to generate a single-chain Fv fragment (scFv) that recognizes with high affinity the psychoactive cannabinoid, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). A mouse monoclonal antibody against THC, Ab-THC#33, with Ka 6.2×107 M−1 (as Fab fragment) was established by the hybridoma technique. Then, a “wild-type” scFv (wt-scFv) with Ka, 1.1×107 M−1 was prepared by bacterial expression of a fusion gene combining the VH and VL genes for Ab-THC#33. Subsequently, random point mutations in VH and VL were generated separately, and the resulting products were assembled into mutant scFv genes, which were then phage-displayed. Repeated panning identified a mutant scFv (scFv#m1-36) with 10-fold enhanced affinity (Ka 1.1×108 M−1) for THC, in which only a single conservative substitution (Ser50Thr) was present at the N-terminus of the VH-complementarity-determining region 2 (CDR2) sequence. In competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the mutant scFv generated dose–response curves with midpoint 0.27 ng/assay THC, which was 3-fold lower than that of wt-scFv. Even higher reactivity with a major THC metabolite, 11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, indicated that the mutant scFv will be useful for testing not only THC in confiscated materials, but also the metabolite in urine. Indeed, the antibody fragment is potentially suitable for use in advanced on-site testing platforms for cannabinoids.
- 著者
- Shunsuke Nakamori Jun Takahashi Sumiko Hyuga Jinwei Yang Hiroaki Takemoto Takuro Maruyama Naohiro Oshima Nahoko Uchiyama Yoshiaki Amakura Masashi Hyuga Takashi Hakamatsuka Yukihiro Goda Hiroshi Odaguchi Toshihiko Hanawa Yoshinori Kobayashi
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1538-1544, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 34
- 被引用文献数
- 12
The analgesic effect of Ephedra Herb (EH) is believed to be derived from the anti-inflammatory action of pseudoephedrine (Pse). We recently reported that ephedrine alkaloids–free EH extract (EFE) attenuates formalin-induced pain to the same level as that achieved by EH extract (EHE), which suggests that the analgesic effect of EH may not be due to ephedrine alkaloids (EAs). To examine the contribution of EAs to the analgesic effect of EH, mice were injected with formalin to induce a biphasic pain reaction (first phase, 0–5 min; second phase, 10–45 min) at various time points after oral administration of the following test drugs: ephedrine (Eph), Pse, “authentic” EHE from Tsumura & Co. (EHE-Ts), EFE, and EHE that was used as the source of EFE (EHE-To). Biphasic pain was suppressed at 30 min after administration of Eph, EHE-Ts, and EHE-To. At 6 h after administration of EFE, EHE-To, and Pse—and at 4 to 6 h after administration of EHE-Ts—only second-phase pain was suppressed; however, the effect of Pse at 6 h was not significant. These results suggested that EHE has a biphasic analgesic effect against biphasic formalin-induced pain: in the first phase of analgesia (30 min after administration), biphasic pain is suppressed by Eph; in the second phase of analgesia (4–6 h after administration), second-phase pain is alleviated by constituents other than EAs, although Pse may partially contribute to the relief of second-phase pain.
- 著者
- Xiaoying Yu Xindi Zhang Hua Jin Zhiwei Wu Chunlu Yan Zhijun Liu Xinghua Xu Shuangfang Liu Feifei Zhu
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.9, pp.1482-1490, 2019-09-01 (Released:2019-09-01)
- 参考文献数
- 44
- 被引用文献数
- 23
Zhengganxifeng decoction (ZGXFD) is a traditional Chinese medicinal formula, from “Medical Zhong parameter West recorded” by Xichun Zhang, which has been applied to the treatment of clinical essential hypertension. Besides its effect in blood pressure reduction, ZGXFD is also known to be a radical therapy with little or no side effects. Compared with western medicines, Chinese medicinal formulas have the advantage of simultaneously attacking multiple targets. However, such a property brings trouble to the pharmacological studies of Chinese medicines. This study investigated the composition of gut microbiota in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) treated with ZGXFD. ZGXFD was shown to cause similar effects in the treatment group as benazepril: both were able to reduce in SHR the microbial diversity, Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio and coccus to bacillus (C/B) ratio. Meanwhile, ZGXFD can maintain the integrity of intestinal mechanistic barrier and elevate the percentage of bacteria producing short chain fatty acids (SCFA). By investigating renin–angiotensin system (RAS) system, we found that ZGXFD can decrease the expression of angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) in lungs, which in turn causes a increase in AngI produces angiotensin1–7 (Ang1–7) and decrease in AngII. ZGXFD regulate blood pressure in SHR via RAS.
- 著者
- Keita Hirai Toshihiro Shirai Yuya Suzuki Tatsuki Shimomura Kunihiko Itoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00385, (Released:2019-09-03)
- 参考文献数
- 39
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Vitamin D has an immune-modulating effect, related to the pathophysiology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, few studies have focused on the difference between patients with asthma and COPD in the association of circulating vitamin D levels with clinical outcomes. We sought to investigate the associations of circulating vitamin D levels with health-related quality of life (HR-QOL), severity, and exacerbations. Subjects included 152 asthma patients and 50 COPD patients. We measured plasma concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25(OH)D3]. HR-QOL was assessed using the EuroQoL 5-Dimension (EQ-5D) and the 12-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-12) scales. Exacerbations were recorded during a one-year follow-up. Associations between plasma 25 (OH)D3 concentrations and outcome variables were evaluated using linear regression. Plasma concentrations of 25(OH)D3 were positively associated with the EQ-5D index value and the SF-12 physical component score in patients with asthma; however, such associations were not observed in patients with COPD. A significant association between severity and plasma concentrations of 25(OH)D3 was found only in patients with COPD. The hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) of plasma 25(OH)D3 concentrations (per 1 ng/mL decrease) for time to first exacerbation was 1.38 (1.10–1.75; p = 0.006) and 0.95 (0.87–1.03; p = 0.179) in patients with COPD and asthma, respectively. Lower concentrations of plasma 25(OH)D3 contributed to lower HR-QOL in patients with asthma, and were associated with severity and risk of future exacerbations in patients with COPD.
- 著者
- Keita Hirai Toshihiro Shirai Yuuka Rachi Sekiko Uehara Megumi Ueda Eiji Nakatani Kunihiko Itoh
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.b19-00476, (Released:2019-08-06)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Genetic variations in glucocorticoid-induced transcript 1 (GLCCI1) have been associated with the response to corticosteroid treatment. However, the associations of GLCCI1 polymorphisms or gene expression with the prognosis of asthma and pathophysiological factors related to steroid insensitivity remain unclear. We sought to investigate the associations of GLCCI1, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2), and histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) mRNA expression levels and the GLCCI1 rs37973 polymorphism with asthma severity and future exacerbation in patients with asthma. Subjects included 25 patients with severe asthma and 127 patients with nonsevere asthma. mRNA expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were measured and evaluated as predictors of severe asthma using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The hazard ratios of the mRNA expression levels for time to first exacerbation in the 1-year follow-up period were calculated. GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA expression levels were significantly lower in patients with severe asthma than in patients with nonsevere asthma and could predict severe asthma with an area under the ROC curve of 0.68, 0.71, and 0.65, respectively. In contrast, no relationship was found between the GLCCI1 rs37973 polymorphism and severe asthma. The hazard ratios for asthma exacerbation in patients with low GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA expression levels were 3.24 (95% confidence interval, 1.42–7.40), 3.13 (1.37–7.16), and 2.98 (1.22–7.25), respectively. Patients with severe asthma could be distinguished by lower GLCCI1, Nrf2, and HDAC2 mRNA levels in peripheral blood cells, and all of these gene signatures could predict future asthma exacerbations.
- 著者
- Takuro Yasuyama Hirofumi Matsunaga Shin Ando Tadao Ishizuka
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.65, no.4, pp.396-402, 2017-04-01 (Released:2017-04-01)
- 参考文献数
- 24
- 被引用文献数
- 1
A novel type of molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP), N-benzoyl-(S)-valine anilide-imprinted polymer (IP-2), was prepared using hydrogen-bonding interactions as a main force in the pre-polymerization step. The performance of the IP-2 was evaluated via batch procedure and compared with a (S)-valine anilide-imprinted polymer (IP-1) that was prepared using an ionic interaction that is stronger than hydrogen bonding. Although both polymers showed a preferential adsorbability for (S)-amino acid derivatives, different performances were observed in terms of adsorbability and enantioselectivity. In addition, the IP-2 was able to recognize the enantiomer of a valine-derived chiral catalyst. This phenomenon was applied to a chiral amplification reaction, and a highly selective asymmetric Mannich-type amination was achieved using the combination of a racemic catalyst and a MIP.
- 著者
- Tomoaki Ishida Michiro Iizuka Yanglan Ou Shunpei Morisawa Ayumu Hirata Yusuke Yagi Kohei Jobu Yasuyo Morita Mitsuhiko Miyamura
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:09186158)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.42, no.7, pp.1128-1133, 2019-07-01 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 7
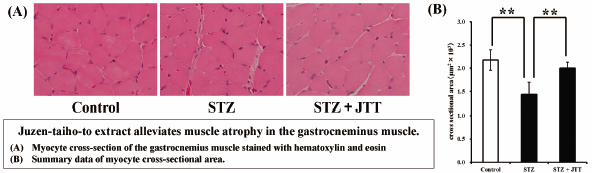
In diabetic patients, skeletal muscle atrophy occurs due to increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Skeletal muscle atrophy reduces the QOL of patients and worsens life prognosis. Therefore, development of preventive therapy for muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state is eagerly awaited. Juzentaihoto is a medicinal herb that has a function to supplement physical strength, and it is expected to prevent muscle atrophy. To determine the preventive effect of juzentaihoto on muscle atrophy in hyperglycemic state, streptozotocin (STZ) was administered to induce diabetes in mice and the preventive effect of juzentaihoto was evaluated. Mice that received juzentaihoto extract (JTT) showed that the decrease in muscle fiber cross-sectional area in the gastrocnemius muscle was reversed. Additionally, the expression level of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), an inflammatory cytokine, in serum decreased, and that of ubiquitin ligase (atrogin-1, muscle RING-finger protein-1) mRNA in skeletal muscle decreased. An anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 showed increased levels in the serum and increased levels in spleen cell culture supernatant collected from mice that received JTT. JTT had no effect on the blood glucose level. These results suggest that prophylactic administration of JTT to STZ-induced diabetic mice affects immune cells such as in spleen, causing an anti-inflammatory effect and inhibiting excessive activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, to reverse muscle atrophy.
- 著者
- Bing Leng Yuan Chao Xue Wen Zhang Tian tian Gao Gen quan Yan Hui Tang
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.3, pp.258-264, 2019-03-01 (Released:2019-03-01)
- 参考文献数
- 32
- 被引用文献数
- 1 18
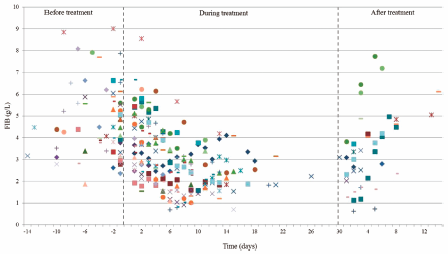
A number of clinical trials demonstrated that tigecycline was effective and well tolerated in the treatment of patients with various bacterial infections, but few literatures had shown the coagulopathy induced by tigecycline. To address this concern, we performed a retrospective analysis to assess the impact of tigecycline treatment on coagulation parameters in 50 patients with bacterial infections in our hospital (Shandong Provincial Hospital, China). These patients were treated with tigecycline at Shandong Provincial Hospital in 2015–2016 at either a recommended (50 mg q12h) or a higher dose (100 mg q12h). Coagulation parameters, including Fibrinogen (FIB) levels, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), platelet count (PLT) and D-dimer, were evaluated in order to assess the impact of tigecycline treatment in these severely infected patients. What we found was that the plasma fibrinogen (FIB) level was 4.63 ± 1.56 g/L before tigecycline treatment, and decreased to 2.92 ± 1.23 g/L during treatment, which was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The mean values of aPTT and PT were significantly increased from 39.58 ± 8.72 to 44.05 ± 10.45 s (p = 0.002), and from 15.37 ± 1.53 to 16.37 ± 2.64 s (p = 0.004), respectively. This study demonstrates that treatment of tigecycline could reduce FIB, prolong aPTT and PT. In conclusion, we advise that it is necessary for practitioners routinely monitor coagulation level in at-rick patient populations treated with tigecycline.
- 著者
- Hiromitsu Takayama
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.52, no.8, pp.916-928, 2004 (Released:2004-08-10)
- 参考文献数
- 63
- 被引用文献数
- 127 250
The leaves of a tropical plant, Mitragyna speciosa KORTH (Rubiaceae), have been traditionally used as a substitute for opium. Phytochemical studies of the constituents of the plant growing in Thailand and Malaysia have led to the isolation of several 9-methoxy-Corynanthe-type monoterpenoid indole alkaloids, including new natural products. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic and/or synthetic methods. The potent opioid agonistic activities of mitragynine, the major constituent of this plant, and its analogues were found in in vitro and in vivo experiments and the mechanisms underlying the analgesic activity were clarified. The essential structural features of mitragynines, which differ from those of morphine and are responsible for the analgesic activity, were elucidated by pharmacological evaluation of the natural and synthetic derivatives. Among the mitragynine derivatives, 7-hydroxymitragynine, a minor constituent of M. speciosa, was found to exhibit potent antinociceptive activity in mice.
- 著者
- Jiali Chen Mengxia Tan Lisi Zou Xunhong Liu Shuyu Chen Jingjing Shi Cuihua Chen Chengcheng Wang Yuqi Mei
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.8, pp.839-848, 2019-08-01 (Released:2019-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 46
- 被引用文献数
- 6
Panacis Japonici Rhizoma (PJR) contains various kinds of saponins, which possesses extensive pharmacological activities, but studies of comprehensive analysis of its saponins were limited. Thus, ultra-fast liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole-time of flight tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-Triple TOF-MS/MS) and ultra-fast liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole-linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS) methods were established for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the saponins in PJR, separately. Fifty three saponins in PJR were identified by UFLC-Triple TOF-MS/MS method, 23 saponins of which were unequivocally identified by reference substances. In addition, fragmentation pathways of different types of saponins were preliminarily deduced by fragmentation behavior of 53 saponins. Furthermore, the simultaneous determination of the contents of 13 saponins in PJR samples harvested at different times were analyzed by UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS method. Furthermore, the quality of the samples was evaluated by grey relational analysis. This study might be beneficial to the quality assessment and control of PJR. Meanwhile, it might provide the basic information for confirming its optimal harvested period.
- 著者
- Nasrul Wathoni Taofik Rusdiana Aliya Nur Hasanah Ahmad Muhtadi Elasari Dwi Pratiwi Ripa’tul Mahmudah Ahmed Fouad Abdelwahab Mohammed Maiko Okajima Tatsuo Kaneko Hidetoshi Arima
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.8, pp.849-854, 2019-08-01 (Released:2019-08-01)
- 参考文献数
- 49
- 被引用文献数
- 7
Regenerative therapy with keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is a novel therapeutic approach for treatment of chronic wounds. However, KGF cannot be used directly to the wound site due to its physicochemical instability. In previous study, sacran, a natural megamolecular polysaccharide, showed potential properties as a biomaterial for hydrogel film in wound healing. In this study, we fabricated sacran hydrogel film containing KGF (Sac/KGF-HF) and evaluated the effects of Sac/KGF-HF on fibroblasts migration and re-epithelialization process. We successfully prepared a homogenous and -amorphous Sac/KGF-HF by a casting method. In addition, Sac/KGF-HF had a high swelling ratio and flexibility. Sac/KGF-HF promoted a migration process of NIH3T3 cells and improved wound healing ability in mice with a percentage of wound closure reaching 90.4% at 9 d. Interestingly, the addition of KGF in Sac-HF considerably increased the number of epithelial cells compared to control, which is important in the re-epithelialization process. It could be concluded that KGF in Sac-HF has the potential for promoting Sac-HF abilities in wound healing process.
- 著者
- Keiko Yamamoto
- 出版者
- The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan
- 雑誌
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (ISSN:00092363)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.67, no.7, pp.609-619, 2019-07-01 (Released:2019-07-01)
- 参考文献数
- 41
- 被引用文献数
- 1 7
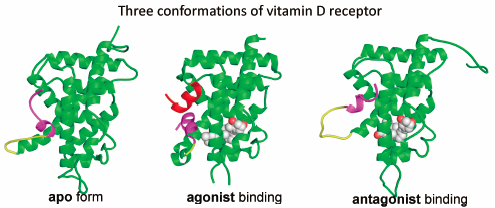
To develop potent ligands for the vitamin D receptor (VDR), we designed and synthesized a series of vitamin D analogues with and without 22-alkyl substituents. These analogues exhibited agonistic, partial agonistic, or antagonistic activity. To elucidate the mechanism of action of the analogues, we conducted crystal structure analyses of the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of VDR complexed with the analogues. The VDR-LBD/agonist complex exhibited precise interactions, which clearly explained VDR agonism. The VDR-LBD/partial agonist complex showed two conformers (agonist and antagonist binding conformers) in a single crystal, demonstrating that partial agonism could be explained by the sum of the agonistic and antagonistic activities. Antagonist binding to the VDR-LBD structure was elucidated using both crystal structure analysis and in-solution structural analyses with the small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)-molecular dynamics (MD) and hydrogen/deuterium exchange coupled with mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) methods. Several antagonist-binding structures were detected. We found that the antagonist binding structures differed depending on the structure of the antagonist itself, and those structures clearly explained the VDR antagonism. Furthermore, the apo VDR-LBD structure without the ligand in the ligand-binding pocket was revealed and found to have an entrance to accommodate the ligand. Thus we elucidated the mechanisms of action of agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists based on structural changes (differences) in the receptor protein induced by ligand binding.