- 著者
- Masashi Uehara Shota Ikegami Takashi Takizawa Hiroki Oba Noriaki Yokogawa Takeshi Sasagawa Kei Ando Hiroaki Nakashima Naoki Segi Toru Funayama Fumihiko Eto Akihiro Yamaji Kota Watanabe Satoshi Nori Kazuki Takeda Takeo Furuya Sumihisa Orita Hideaki Nakajima Tomohiro Yamada Tomohiko Hasegawa Yoshinori Terashima Ryosuke Hirota Hidenori Suzuki Yasuaki Imajo Hitoshi Tonomura Munehiro Sakata Ko Hashimoto Yoshito Onoda Kenichi Kawaguchi Yohei Haruta Nobuyuki Suzuki Kenji Kato Hiroshi Uei Hirokatsu Sawada Kazuo Nakanishi Kosuke Misaki Hidetomi Terai Koji Tamai Eiki Shirasawa Gen Inoue Kenichiro Kakutani Yuji Kakiuchi Katsuhito Kiyasu Hiroyuki Tominaga Hiroto Tokumoto Yoichi Iizuka Eiji Takasawa Koji Akeda Norihiko Takegami Haruki Funao Yasushi Oshima Takashi Kaito Daisuke Sakai Toshitaka Yoshii Tetsuro Ohba Bungo Otsuki Shoji Seki Masashi Miyazaki Masayuki Ishihara Seiji Okada Yasuchika Aoki Katsumi Harimaya Hideki Murakami Ken Ishii Seiji Ohtori Shiro Imagama Satoshi Kato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-0183, (Released:2021-12-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: In elderly patients with cervical spinal cord injury, comorbidities such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are common, with frequent administration of antiplatelet/anticoagulant (APAC) drugs. Such patients may bleed easily or unexpectedly during surgery despite prior withdrawal of APAC medication. Few reports have examined the precise relationship between intraoperative blood loss and history of APAC use regarding surgery for cervical spine injury in the elderly.The presentmulticenter database survey aimed to answer the question of whether the use of APAC drugs affected the amount of intraoperative blood loss in elderly patients with cervical spinal cord trauma.Methods: The case histories of 1512 patients with cervical spine injury at 33 institutes were retrospectively reviewed. After excluding cases without spinal surgery or known blood loss volume, 797 patients were enrolled. Blood volume loss was the outcome of interest. We calculated propensity scores using the inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) method. As an alternative sensitivity analysis, linear mixed model analyses were conducted as well.Results: Of the 776 patients (mean age: 75.1 ± 6.4 years) eligible for IPTW calculation, 157 (20.2%) were taking APAC medications before the injury. After weighting, mean estimated blood loss was 204 mL for non-APAC patients and 215 mL for APAC patients. APAC use in elderly patients was not significantly associated with surgical blood loss according to the IPTW method with propensity scoring or linear mixed model analyses. Thus, it appeared possible to perform surgery expecting comparable blood loss in APAC and non-APAC cases.Conclusions: This multicenter study revealed no significant increase in surgical blood loss in elderly patients with cervical trauma taking APAC drugs. Surgeons may be able to prioritize patient background, complications, and preexisting conditions over APAC use before injury when examining the surgical indications for cervical spine trauma in the elderly.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Yagi Nobuyuki Fujita Tomohiko Hasegawa Gen Inoue Yoshihisa Kotani Seiji Ohtori Sumihisa Orita Yasushi Oshima Daisuke Sakai Toshinori Sakai Hiroshi Taneichi Daisuke Togawa Kazuo Nakanishi Hiroaki Nakashima Toshitaka Yoshii Masaya Nakamura Motoki Iwasaki Masahiko Watanabe Hirotaka Haro Tokumi Kanemura Naobumi Hosogane New Technology Assessment Committee of The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0194, (Released:2022-12-12)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
IntroductionLateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF) has been introduced in Japan in 2013. Despite the effectiveness of this procedure, several considerable complications have been reported. This study reported the results of a nationwide survey performed by the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research (JSSR) on the complications associated with LLIF performed in Japan.MethodsJSSR members conducted a web-based survey following LLIF between 2015 and 2020. Any complications meeting the following criteria were included: (1) major vessel, (2) urinary tract, (3) renal, (4) visceral organ, (5) lung, (6) vertebral, (7) nerve, and (8) anterior longitudinal ligament injury; (9) weakness of psoas; (10) motor and (11) sensory deficit; (12) surgical site infection; and (13) other complications. The complications were analyzed in all LLIF patients, and the differences in incidence and type of complications between the transpsoas (TP) and prepsoas (PP) approaches were compared.ResultsAmong the 13,245 LLIF patients (TP 6,198 patients [47%] and PP 7,047 patients [53%]), 389 complications occurred in 366 (2.76%) patients. The most common complication was sensory deficit (0.5%), followed by motor deficit (0.43%) and weakness of psoas muscle (0.22%). Among the patient cohort, 100 patients (0.74%) required revision surgery during the survey period. Almost half of the complications developed in patients with spinal deformity (183 patients [47.0%]). Four patients (0.03%) died from complications. Statistically more frequent complications occurred in the TP approach than in the PP approach (TP vs. PP, 220 patients [3.55%] vs. 169 patients [2.40%]; p < 0.001).ConclusionsThe overall complication rate was 2.76%, and 0.74% of the patients required revision surgery because of complications. Four patients died from complications. LLIF may be beneficial for degenerative lumbar conditions with acceptable complications; however, the indication for spinal deformity should be carefully determined by the experience of the surgeon and the extent of the deformity.
- 著者
- William H. Waddell Benjamin M. Weisenthal Nicholas Golinvaux Abigail L. Henry Jacquelyn Pennings John P. Wanner Rishabh Gupta Toshitaka Yoshii Zhou Feifei Byron F. Stephens
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.5, pp.460-463, 2022-09-27 (Released:2022-09-27)
- 参考文献数
- 27
- 被引用文献数
- 2
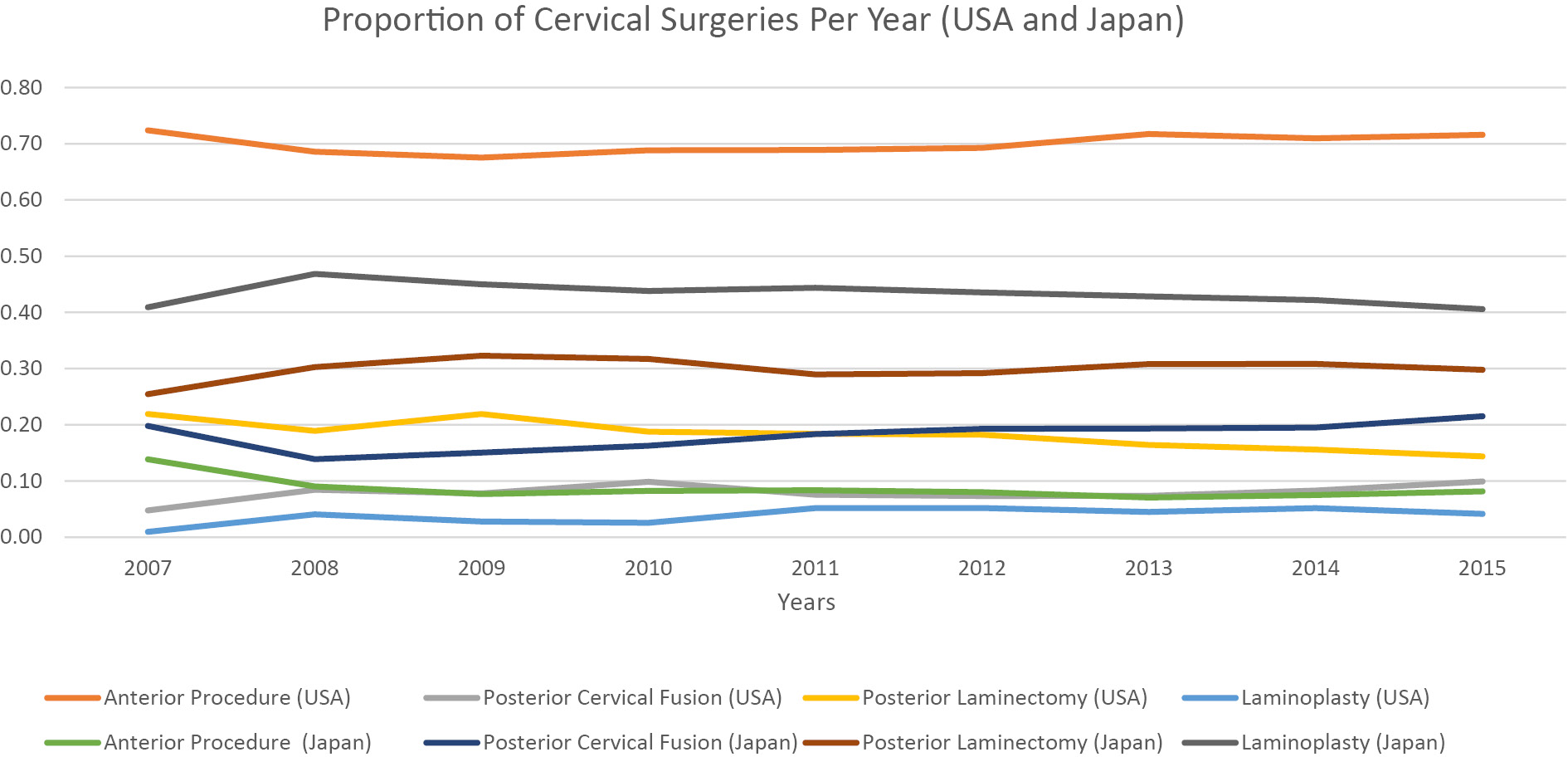
Introduction: Laminoplasty is a well-established technique used to manage cervical myelopathy (CM). Nevertheless, the degree to which United States surgeons have adopted laminoplasty from Japan to treat CM is less clear. The purpose of this study was to compare operative management strategies for CM in the United States (US) with Japan.Methods: This study used a retrospective cohort of 16,084 patients from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP) database and 389,872 patients from the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC) database from 2007 to 2015. Patients with the following diagnoses were collected: spondylosis with myelopathy (ICD-19; 721.1, ICD-10; M47.12) and disk herniation with myelopathy (ICD-9; 722.71, ICD-10; M50.00). The proportion of surgeries between Japan and the US was compared using a linear regression model controlling for year.Results: US surgeons utilized anterior procedures in 70% of cases compared to 9% in Japan (p<.001). In contrast, Japan had significantly more laminoplasties than the US (43% vs. 4%, respectively, p<.001). The percentage of laminoplasty in Japan (43%) relative to the percentage in the US (4%) was significantly different (p<.001). Accounting for increases in the number of total surgeries per year seen in the ACS-NSQIP and DPC databases, no specific surgery demonstrated a significant increase or decrease over the 8 years.Conclusions: Japanese surgeons employ laminoplasty to treat CM approximately ten times more frequently than US surgeons who prefer anterior procedures.
- 著者
- Takashi Hirai Takuya Takahashi Tomoyuki Tanaka Takayuki Motoyoshi Yu Matsukura Masato Yuasa Hiroyuki Inose Toshitaka Yoshii Atsushi Okawa
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.6, no.3, pp.252-260, 2022-05-27 (Released:2022-05-27)
- 参考文献数
- 21
- 被引用文献数
- 9
Introduction: Chemonucleolysis with condoliase (chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase) has been used to treat patients with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) in Japan since 2018. In this study, we retrospectively investigated clinical outcomes in patients who received an intradiscal condoliase injection for LDH and sought to identify significant predictors of good outcome.Methods: Indications for treatment were as follows: (1) unilateral leg pain with or without back pain, (2) nerve root compression caused by LDH confirmed on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and (3) leg pain resistant to at least 1 month of conservative treatment, including medication, nerve root block, or physical therapy. Patients with motor weakness or a history of severe allergy were excluded, as were those with the foraminal or sequestrated type of LDH. The injection was defined as effective if the numeric rating scale score for leg pain improved by ≥50% at 6 months post-treatment.Results: A total of 52 patients (mean age, 45.0 years) were enrolled and classified according to whether the injection was effective (E group, n=40, 76.9%) or less effective (L group, n=9, 17.3%). Three patients (5.8%) underwent herniotomy for residual pain within 6 months of the injection. There were no severe adverse events. Reduction of herniation was seen on MRI more often in the E group than in the L group. The effectiveness in patients with transligamentous LDH was similar to that in patients with subligamentous LDH. High-intensity signal change in the area of LDH on pretreatment T2-weighted MRI was a significant predictor of successful leg pain relief.Conclusions: An intradiscal condoliase injection was a safe and effective treatment for painful radiculopathy caused by LDH. Leg pain was more likely to improve in patients with high-intensity signal change in the area of LDH before treatment.