- 著者
- Masashi Uehara Shota Ikegami Takashi Takizawa Hiroki Oba Noriaki Yokogawa Takeshi Sasagawa Kei Ando Hiroaki Nakashima Naoki Segi Toru Funayama Fumihiko Eto Akihiro Yamaji Kota Watanabe Satoshi Nori Kazuki Takeda Takeo Furuya Sumihisa Orita Hideaki Nakajima Tomohiro Yamada Tomohiko Hasegawa Yoshinori Terashima Ryosuke Hirota Hidenori Suzuki Yasuaki Imajo Hitoshi Tonomura Munehiro Sakata Ko Hashimoto Yoshito Onoda Kenichi Kawaguchi Yohei Haruta Nobuyuki Suzuki Kenji Kato Hiroshi Uei Hirokatsu Sawada Kazuo Nakanishi Kosuke Misaki Hidetomi Terai Koji Tamai Eiki Shirasawa Gen Inoue Kenichiro Kakutani Yuji Kakiuchi Katsuhito Kiyasu Hiroyuki Tominaga Hiroto Tokumoto Yoichi Iizuka Eiji Takasawa Koji Akeda Norihiko Takegami Haruki Funao Yasushi Oshima Takashi Kaito Daisuke Sakai Toshitaka Yoshii Tetsuro Ohba Bungo Otsuki Shoji Seki Masashi Miyazaki Masayuki Ishihara Seiji Okada Yasuchika Aoki Katsumi Harimaya Hideki Murakami Ken Ishii Seiji Ohtori Shiro Imagama Satoshi Kato
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2021-0183, (Released:2021-12-27)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Background: In elderly patients with cervical spinal cord injury, comorbidities such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are common, with frequent administration of antiplatelet/anticoagulant (APAC) drugs. Such patients may bleed easily or unexpectedly during surgery despite prior withdrawal of APAC medication. Few reports have examined the precise relationship between intraoperative blood loss and history of APAC use regarding surgery for cervical spine injury in the elderly.The presentmulticenter database survey aimed to answer the question of whether the use of APAC drugs affected the amount of intraoperative blood loss in elderly patients with cervical spinal cord trauma.Methods: The case histories of 1512 patients with cervical spine injury at 33 institutes were retrospectively reviewed. After excluding cases without spinal surgery or known blood loss volume, 797 patients were enrolled. Blood volume loss was the outcome of interest. We calculated propensity scores using the inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) method. As an alternative sensitivity analysis, linear mixed model analyses were conducted as well.Results: Of the 776 patients (mean age: 75.1 ± 6.4 years) eligible for IPTW calculation, 157 (20.2%) were taking APAC medications before the injury. After weighting, mean estimated blood loss was 204 mL for non-APAC patients and 215 mL for APAC patients. APAC use in elderly patients was not significantly associated with surgical blood loss according to the IPTW method with propensity scoring or linear mixed model analyses. Thus, it appeared possible to perform surgery expecting comparable blood loss in APAC and non-APAC cases.Conclusions: This multicenter study revealed no significant increase in surgical blood loss in elderly patients with cervical trauma taking APAC drugs. Surgeons may be able to prioritize patient background, complications, and preexisting conditions over APAC use before injury when examining the surgical indications for cervical spine trauma in the elderly.
- 著者
- Koji Tamai Hidetomi Terai Akinobu Suzuki Hiroaki Nakamura Masaomi Yamashita Yawara Eguchi Shiro Imagama Kei Ando Kazuyoshi Kobayashi Morio Matsumoto Ken Ishii Tomohiro Hikata Shoji Seki Masaaki Aramomi Tetsuhiro Ishikawa Atsushi Kimura Hirokazu Inoue Gen Inoue Masayuki Miyagi Wataru Saito Kei Yamada Michio Hongo Kenji Endo Hidekazu Suzuki Atsushi Nakano Kazuyuki Watanabe Junichi Ohya Hirotaka Chikuda Yasuchika Aoki Masayuki Shimizu Toshimasa Futatsugi Keijiro Mukaiyama Masaichi Hasegawa Katsuhito Kiyasu Haku Iizuka Kotaro Nishida Kenichiro Kakutani Hideaki Nakajima Hideki Murakami Satoru Demura Satoshi Kato Katsuhito Yoshioka Takashi Namikawa Kei Watanabe Kazuyoshi Nakanishi Yukihiro Nakagawa Mitsunori Yoshimoto Hiroyasu Fujiwara Norihiro Nishida Masataka Sakane Masashi Yamazaki Takashi Kaito Takeo Furuya Sumihisa Orita Seiji Ohtori
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.1, no.4, pp.179-184, 2017-10-20 (Released:2017-11-27)
- 参考文献数
- 26
- 被引用文献数
- 3 3
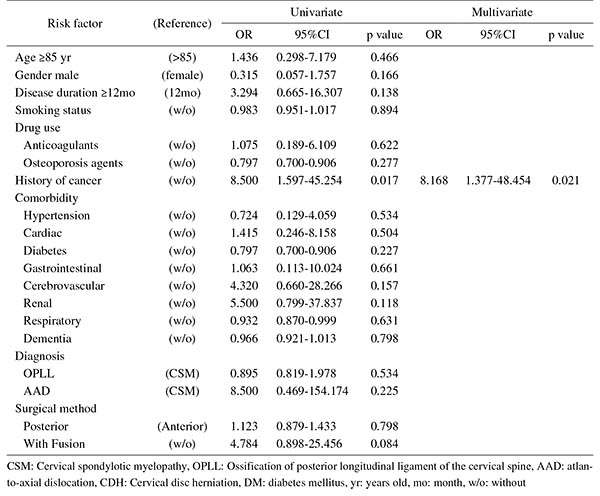
Introduction: With an aging population, the proportion of patients aged ≥80 years requiring cervical surgery is increasing. Surgeons are concerned with the high incidence of complications in this population, because "age" itself has been reported as a strong risk factor for complications. However, it is still unknown which factors represent higher risk among these elderly patients. Therefore, this study was conducted to identify the risk factors related to surgical complications specific to elderly patients by analyzing the registry data of patients aged ≥80 years who underwent cervical surgery.Methods: We retrospectively studied multicenter collected registry data using multivariate analysis. Sixty-six patients aged ≥80 years who underwent cervical surgery and were followed up for more than one year were included in this study. Preoperative patient demographic data, including comorbidities and postoperative complications, were collected from multicenter registry data. Complications were considered as major if they required invasive intervention, caused prolonged morbidity, or resulted in prolongation of hospital stay. Logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the risk factors for complications. A p-value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.Results: The total number of patients with complications was 21 (31.8%), with seven major (10.6%) and 14 minor (21.2%) complications. Multivariate logistic regression analysis, after adjusting for age, revealed two significant risk factors: preoperative cerebrovascular disorders (OR, 6.337; p=0.043) for overall complications and cancer history (OR, 8.168; p=0.021) for major complications. Age, presence of diabetes mellitus, and diagnosis were not significant predictive factors for complications in this study.Conclusions: Preoperative cerebrovascular disorders and cancer history were risk factors for complications after cervical surgery in patients over 80 years old. Surgeons should pay attention to these specific risk factors before performing cervical surgery in elderly patients.
- 著者
- Mitsuru Yagi Nobuyuki Fujita Tomohiko Hasegawa Gen Inoue Yoshihisa Kotani Seiji Ohtori Sumihisa Orita Yasushi Oshima Daisuke Sakai Toshinori Sakai Hiroshi Taneichi Daisuke Togawa Kazuo Nakanishi Hiroaki Nakashima Toshitaka Yoshii Masaya Nakamura Motoki Iwasaki Masahiko Watanabe Hirotaka Haro Tokumi Kanemura Naobumi Hosogane New Technology Assessment Committee of The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2022-0194, (Released:2022-12-12)
- 被引用文献数
- 1
IntroductionLateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF) has been introduced in Japan in 2013. Despite the effectiveness of this procedure, several considerable complications have been reported. This study reported the results of a nationwide survey performed by the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research (JSSR) on the complications associated with LLIF performed in Japan.MethodsJSSR members conducted a web-based survey following LLIF between 2015 and 2020. Any complications meeting the following criteria were included: (1) major vessel, (2) urinary tract, (3) renal, (4) visceral organ, (5) lung, (6) vertebral, (7) nerve, and (8) anterior longitudinal ligament injury; (9) weakness of psoas; (10) motor and (11) sensory deficit; (12) surgical site infection; and (13) other complications. The complications were analyzed in all LLIF patients, and the differences in incidence and type of complications between the transpsoas (TP) and prepsoas (PP) approaches were compared.ResultsAmong the 13,245 LLIF patients (TP 6,198 patients [47%] and PP 7,047 patients [53%]), 389 complications occurred in 366 (2.76%) patients. The most common complication was sensory deficit (0.5%), followed by motor deficit (0.43%) and weakness of psoas muscle (0.22%). Among the patient cohort, 100 patients (0.74%) required revision surgery during the survey period. Almost half of the complications developed in patients with spinal deformity (183 patients [47.0%]). Four patients (0.03%) died from complications. Statistically more frequent complications occurred in the TP approach than in the PP approach (TP vs. PP, 220 patients [3.55%] vs. 169 patients [2.40%]; p < 0.001).ConclusionsThe overall complication rate was 2.76%, and 0.74% of the patients required revision surgery because of complications. Four patients died from complications. LLIF may be beneficial for degenerative lumbar conditions with acceptable complications; however, the indication for spinal deformity should be carefully determined by the experience of the surgeon and the extent of the deformity.
- 著者
- Gen Inoue Takashi Kaito Yukihiro Matsuyama Toshihiko Yamashita Mamoru Kawakami Kazuhisa Takahashi Munehito Yoshida Shiro Imagama Seiji Ohtori Toshihiko Taguchi Hirotaka Haro Hiroshi Taneichi Masashi Yamazaki Kotaro Nishida Hiroshi Yamada Daijiro Kabata Ayumi Shintani Motoki Iwasaki Manabu Ito Naohisa Miyakoshi Hideki Murakami Kazuo Yonenobu Tomoyuki Takura Joji Mochida
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.2020-0083, (Released:2020-11-20)
- 被引用文献数
- 2
Introduction: Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a leading cause of disability, yet there is limited high-quality evidence to identify the most suitable pharmacological therapy. The purpose of this Japanese nationwide, multicenter, prospective study was to compare the effectiveness of four representative drug therapies—acetaminophen, celecoxib, loxoprofen, and a tramadol and acetaminophen (T+A) combination drug—to establish evidence for a drug of choice for CLBP.Methods: Patients with CLBP (N = 471) received one of the four treatments and were evaluated, prospectively and comprehensively, once every month for six months using a visual analog scale (VAS) for LBP, the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score, the JOA Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire (JOABPEQ), the Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RDQ), the EuroQol five-dimensions three-levels (EQ-5D-3L), and the Short Form-8 item health survey (SF-8). We conducted multivariable linear regression analyses of the four drugs at 1 and 6 months after drug allocation. Differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.Results: Patients who received acetaminophen showed a significant improvement from baseline in the mental health subscale of the JOABPEQ at one month (P = 0.02) and the JOA score at six months (P < 0.01). None of the other outcome measures among the four drugs differed significantly. Across groups, all outcome measures, except the mental component summary (MCS) score of the SF-8, improved equivalently, although most measurements showed no obvious cumulative effect over six months. The MCS score of the SF-8 decreased gradually over six months in all groups.Conclusions: Most of the outcome measures among the treated groups were not significantly different, indicating similar treatment effects of the four drugs for CLBP. Our study indicated the limit of each outcome measure for evaluating the patient status, suggesting that a single outcome measure is insufficient to reflect treatment effectiveness.
- 著者
- Seiji Ohtori Masayuki Miyagi Gen Inoue
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.1, pp.11-17, 2018-01-20 (Released:2018-01-27)
- 参考文献数
- 91
- 被引用文献数
- 41
Introduction: Many patients suffer from discogenic low back pain. However, the mechanisms, diagnosistic strategy, and treatment of discogenic low back pain all remain controversial. The purpose of this paper was to review the pathological mechanisms of discogenic low back pain.Methods: Many authors have investigated the pathological mechanisms of discogenic low back pain using animal models and examining human patients. Central to most investigations is understanding the innervation and instabilities of diseased intervertebral discs and the role of inflammatory mediators. We discuss three pathological mechanisms of discogenic low back pain: innervation, inflammation, and mechanical hypermobility of the intervertebral disc.Results: Sensory nerve fibers include C-fibers and A delta-fibers, which relay pain signals from the innervated outer layers of the intervertebral disc under normal conditions. However, ingrowth of these sensory nerve fibers into the inner layers of intervertebral disc occurs under disease conditions. Levels of neurotrophic factors and some cytokines are significantly higher in diseased discs than in normal discs. Stablization of the segmental hypermobility, which can be induced by intervertebral disc degeneration, suppresses inflammation and prevents sensitization of sensory nerve fibers innervating the disc.Conclusions: Pathological mechanisms of discogenic low back pain include sensory nerve ingrowth into inner layers of the intervertebral disc, upregulation of neurotrophic factors and cytokines, and instability. Inhibition of these mechanisms is important in the treatment of discogenic low back pain.
- 著者
- Shoichiro Takei Masayuki Miyagi Wataru Saito Takayuki Imura Gen Inoue Toshiyuki Nakazawa Eiki Shirasawa Kentaro Uchida Tsutomu Akazawa Naonobu Takahira Masashi Takaso
- 出版者
- The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research
- 雑誌
- Spine Surgery and Related Research (ISSN:2432261X)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.2, no.4, pp.294-298, 2018-10-26 (Released:2018-10-27)
- 参考文献数
- 22
- 被引用文献数
- 2 9
Introduction: Patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) usually have progressive scoliosis. Although fusion of the sacrum or pelvis has been recommended for correcting pelvic obliquity (PO), the procedure is invasive. This study determined as to whether performing instrumentation to the fifth lumbar vertebra (L5) is safe and effective for scoliosis in patients with SMA.Methods: Twelve patients with SMA underwent posterior spinal fusion and stopping instrumentation at the L5 level. We evaluated age at surgery, the duration of surgery, blood loss, complications, preoperative and postoperative Cobb angles, and PO.Results: The mean age at surgery was 11.4 years; the mean duration of surgery was 319 minutes, and the mean blood loss was 1170 mL. The Cobb angle improved from 97.3° to 39.1° at 1 month postoperatively (correction rate, 60.9%) and to 42.3° at the final follow-up. PO was corrected from 27.8° to 13.1° at 1 month postoperatively (correction rate, 51.7%) and to 19.8° at the final follow-up. No complications were reported. All patients showed improvement in low back pain, with reduced difficulty while sitting. However, >10% correction loss of PO was observed in 6 patients with high preoperative PO.Conclusions: The correction rate of scoliosis in SMA patients with posterior spinal fusion and instrumentation to the L5 level was acceptable, and no complications occurred. Scoliosis associated with SMA was more rigid and severer than scoliosis associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Correction rates of the Cobb angle and PO in SMA patients with instrumentation to L5 were similar to those in SMA patients with instrumentation to the sacrum or pelvis. Correction loss of PO was greater in patients with high preoperative PO than in those with low preoperative PO. Instrumentation and fusion to L5 for scoliosis in patients with SMA seems safe and effective, except in cases of high preoperative PO.