- 著者
- Linnan Jie Miho Sanagi Yongming Luo Haruna Maeda Yoichiro Fukao Yukako Chiba Shuichi Yanagisawa Junji Yamaguchi Junpei Takagi Takeo Sato
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.40, no.1, pp.93-98, 2023-03-25 (Released:2023-03-25)
- 参考文献数
- 48
Nitrogen (N) availability is one of the most important factors regulating plant metabolism and growth as it affects global gene expression profiles. Dynamic changes in chromatin structure, including histone modifications and nucleosome assembly/disassembly, have been extensively shown to regulate gene expression under various environmental stresses in plants. However, the involvement of chromatin related changes in plant nutrient responses has been demonstrated only in a few studies to date. In this study, we investigated the function of histone chaperone NUCLEOSOME ASSEMBLY PROTEIN1 (NAP1) proteins under N deficient conditions in Arabidopsis. In the nap1;1 nap1;2 nap1;3 triple mutant (m123-1), the expression of N-responsive marker genes and growth of lateral roots were decreased under N deficient conditions. In addition, the m123-1 plants showed a delay in N deficiency-induced leaf senescence. Taken together, these results suggest that NAP1s affect plant growth under N deficient conditions in Arabidopsis.
- 著者
- Chihaya Fukai Takanari Tanabata Tomoko Nishizawa Mikiko Koizumi Keisuke Kutsuwada Miyako Kusano
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.1107a, (Released:2023-01-23)
- 参考文献数
- 22
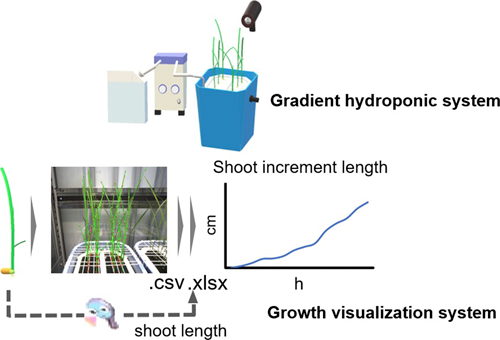
Nitrogen (N) fertilization is one of the most crucial factors that contribute to increasing food production requiring the generation of rice cultivars with improved N use efficiency (NUE) to maintain yield during low N fertilizer application. To assay NUE extent, we developed a screening system to evaluate shoot growth of each rice cultivar under gradient changes in N concentrations. This system comprises a gradient hydroponic culture and growth visualization systems. The former allows gradient changes in ammonium concentrations, while the latter records the increment in shoot length of individual rice seedlings at given time periods using a fixed-point camera. We chose 69 cultivars including two controls (Oryza sativa L. cv. Nipponbare [WRC01] and Kasalath [WRC02]) from the World Rice Core Collection to investigate shoot growth responses under ammonium-sufficient, ammonium-limited, and low ammonium concentration gradients without transplanting stress. We observed three growth patterns in response to different ammonium concentrations. Subsequently, we selected three representative cultivars (Kasalath, WRC03, and WRC05) for the characteristic responses under the different ammonium environments. Distinct expression patterns of glutamine synthetase 1;2 (OsGS1;2) but OsGS1;1 were observed in response to varying ammonium concentration regimes, indicating that the expression patterns of OsGS1;2 may be a growth marker in terms of shoot growth when transitioning from ammonium-limited to low ammonium concentrations. This system with the level of OsGS1;2 allows us to screen for candidate cultivars that return high NUE in low N environments.
- 著者
- Kazunori Kuriyama Midori Tabara Hiromitsu Moriyama Hideki Takahashi Toshiyuki Fukuhara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.405-414, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 31
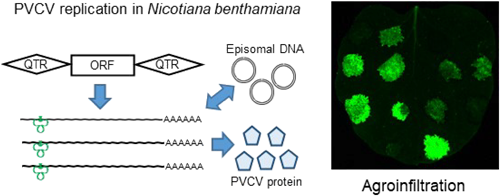
Petunia vein clearing virus (PVCV) is a type member of the genus Petuvirus within the Caulimoviridae family and is defined as one viral unit consisting of a single open reading frame (ORF) encoding a viral polyprotein and one quasi-long terminal repeat (QTR) sequence. Since some full-length PVCV sequences are found in the petunia genome and a vector for horizontal transmission of PVCV has not been identified yet, PVCV is referred to as an endogenous pararetrovirus. Molecular mechanisms of replication, gene expression and horizontal transmission of endogenous pararetroviruses in plants are elusive. In this study, agroinfiltration experiments using various PVCV infectious clones indicated that the replication (episomal DNA synthesis) and gene expression of PVCV were efficient when the QTR sequences are present on both sides of the ORF. Whereas replacement of the QTR with another promoter and/or terminator is possible for gene expression, it is essential for QTR sequences to be on both sides for viral replication. Although horizontal transmission of PVCV by grafting and biolistic inoculation was previously reported, agroinfiltration is a useful and convenient method for studying its replication and gene expression.
- 著者
- Tsubasa Shoji Kazuki Saito
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.421-425, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 15
- 被引用文献数
- 1
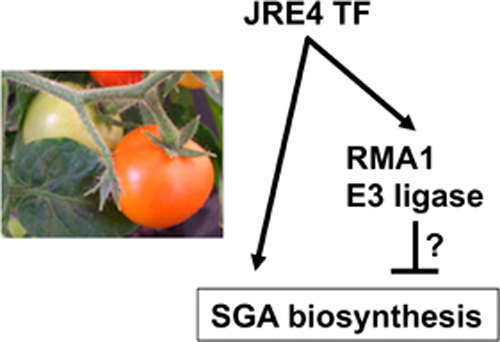
RING membrane-anchor (RMA) E3 ubiquitin ligases are involved in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein degradation, which mediates the regulated destruction of ER-resident enzymes in various organisms. We determined that the transcription factor JASMONATE-RESPONSIVE ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 4 (JRE4) co-regulates the expression of the RMA-type ligase gene SlRMA1, but not its homolog SlRMA2, with steroidal glycoalkaloid biosynthesis genes in tomato, perhaps to prevent the overaccumulation of these metabolites.
- 著者
- Lalita Jantean Kentaro Okada Yaichi Kawakatsu Ken-ichi Kurotani Michitaka Notaguchi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.415-420, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
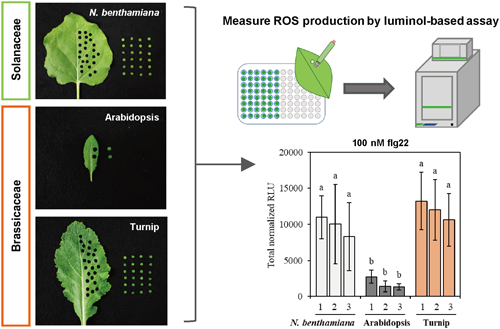
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are critical for plant biological processes. As signaling molecules, ROS regulate plant growth and development through cell expansion, elongation, and programmed cell death. Furthermore, ROS production is induced by microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) treatment and biotic stresses, and contributes to plant resistance to pathogens. Thus, MAMP-induced ROS production has been an indicator for plant early immune responses or stress responses. One of widely used methods for the measurement is a luminol-based assay to measure extracellular ROS production with a bacterial flagellin epitope (flg22) as a MAMP elicitor. Nicotiana benthamiana is susceptible to a wide variety of plant pathogenic agents and therefore commonly used for ROS measurements. On the other hand, Arabidopsis thaliana, many of genetical lines of which are available, is also conducted to ROS measurements. Tests in an asterid N. benthamiana and a rosid A. thaliana can reveal conserved molecular mechanisms in ROS production. However, the small size of A. thaliana leaves requires many seedlings for experiments. This study examined flg22-induced ROS production in another member of the Brassicaceae family, Brassica rapa ssp. rapa (turnip), which has large and flat leaves. Our experiments indicated that 10 nM and 100 nM flg22 treatments induced high ROS levels in turnip. Turnip tended to have a lower standard deviation in multiple concentrations of flg22 treatment. Therefore, these results suggested that turnip can be a good material from the rosid clade for ROS measurement.
- 著者
- Linda M. Robles Laura H. Reichenberg James H. Grissom Ⅲ Richard J. Chi Kenneth J. Piller
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.367-379, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 49
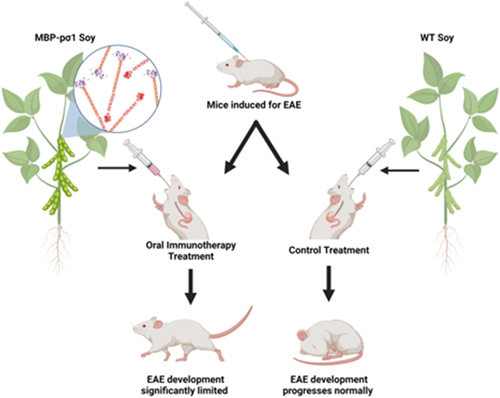
It is estimated that multiple sclerosis (MS) affects over 2.8 million people worldwide, with a prevalence that is expected to continue growing over time. Unfortunately, there is no cure for this autoimmune disease. For several decades, antigen-specific treatments have been used in animal models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) to demonstrate their potential for suppressing autoimmune responses. Successes with preventing and limiting ongoing MS disease have been documented using a wide variety of myelin proteins, peptides, autoantigen-conjugates, and mimics when administered by various routes. While those successes were not translatable in the clinic, we have learned a great deal about the roadblocks and hurdles that must be addressed if such therapies are to be useful. Reovirus sigma1 protein (pσ1) is an attachment protein that allows the virus to target M cells with high affinity. Previous studies showed that autoantigens tethered to pσ1 delivered potent tolerogenic signals and diminished autoimmunity following therapeutic intervention. In this proof-of-concept study, we expressed a model multi-epitope autoantigen (human myelin basic protein, MBP) fused to pσ1 in soybean seeds. The expression of chimeric MBP-pσ1 was stable over multiple generations and formed the necessary multimeric structures required for binding to target cells. When administered to SJL mice prophylactically as an oral therapeutic, soymilk formulations containing MBP-pσ1 delayed the onset of clinical EAE and significantly reduced developing disease. These results demonstrate the practicality of soybean as a host for producing and formulating immune-modulating therapies to treat autoimmune diseases.
- 著者
- Bin Yang Shan Sun Shengyu Li Jiali Zeng Furong Xu
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.355-365, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 65
- 被引用文献数
- 1
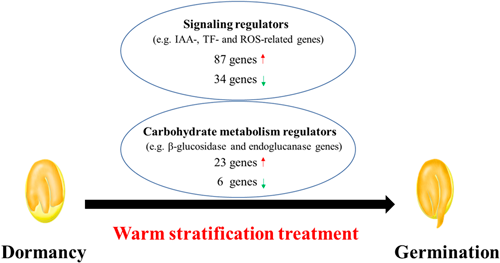
Long-term seed dormancy of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis limits its large-scale artificial cultivation. It is crucial to understand the regulatory genes involving in dormancy release for artificial cultivation in this species. In this study, seed dormancy of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis was effectively released by warm stratification (20°C) for 90 days. The freshly harvested seeds (dormant) and stratified seeds (non-dormant) were used to sequence, and approximately 147 million clean reads and 28,083 annotated unigenes were detected. In which, a total of 10,937 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified between dormant and non-dormant seeds. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) classification revealed that the majority unigenes involved in signaling transduction and carbohydrate metabolism. Of them, the signaling transduction-related DEGs were mainly hormones-, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-, and transcription factor (TF)-related genes. The largest number of signaling transduction-related DEGs were auxin-responsive genes (SAUR, AUX/IAA, and ARF) and AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor (ERF/AP2). Moreover, at least 29 DEGs such as α-amylase (AMY), β-glucosidase (Bglb/Bglu/Bglx), and endoglucanase (Glu) were identified involving in carbohydrate metabolism. These identified genes provide a valuable resource to investigate the molecular basis of dormancy release in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis.
- 著者
- Tatsushi Fukushima Yutaka Kodama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.345-354, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 36
- 被引用文献数
- 1
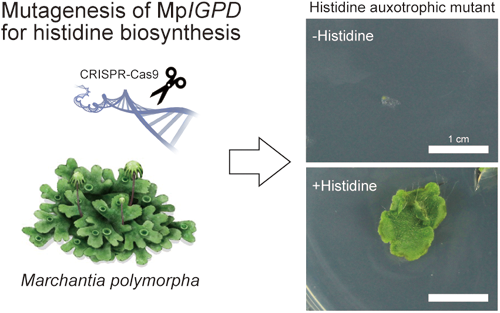
Marchantia polymorpha has emerged as a model liverwort species, with molecular tools increasingly available. In the present study, we developed an auxotrophic strain of M. polymorpha and an auxotrophic selective marker gene as new experimental tools for this valuable model system. Using CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats)/Cas9-mediated genome editing, we mutated the genomic region for IMIDAZOLEGLYCEROL-PHOSPHATE DEHYDRATASE (IGPD) in M. polymorpha to disrupt the biosynthesis of histidine (igpd). We modified an IGPD gene (IGPDm) with silent mutations, generating a histidine auxotrophic selective marker gene that was not a target of our CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. The M. polymorpha igpd mutant was a histidine auxotrophic strain, growing only on medium containing histidine. The igpd mutant could be complemented by transformation with the IGPDm gene, indicating that this gene could be used as an auxotrophic selective marker. Using the IGPDm marker in the igpd mutant background, we produced transgenic lines without the need for antibiotic selection. The histidine auxotrophic strain igpd and auxotrophic selective marker IGPDm represent new molecular tools for M. polymorpha research.
- 著者
- Xiaoxia Pan Tong Li Changmei Liao Youyong Zhu Mingzhi Yang
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.4, pp.335-343, 2022-12-25 (Released:2022-12-25)
- 参考文献数
- 47
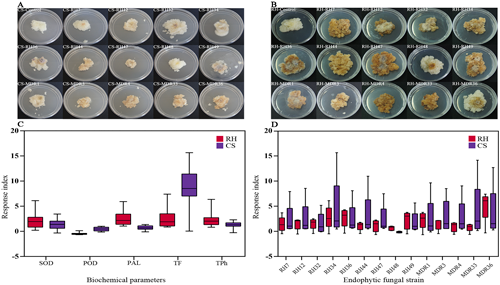
The metabolic patterns of grape cells can be specifically shaped by different strains of dual-cultured fungal endophytes. In this work, a solid co-culture system was furtherly proposed to illustrate the different impacts of endophytic fungi on the biochemical status of grape cells of different varieties. By measuring the metabolic impacts of contact fungal endophytes on grape cells of the varieties ‘Rose honey’ (RH) and ‘Cabernet sauvignon’ (CS), we observed that most of the fungal strains used had promoting effects on grape cellular biochemistry parameters. Compared with the control, inoculation with most of the fungal strains increased the superoxide dismutase (SOD) and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activities as well as the total flavonoid (TF) and total phenolics (TPh) contents in both types of grape cells. Among the tested strains, RH34, RH49 and MDR36 had relatively stronger biochemical impacts on grape cells. More interestingly, in addition to the varietal specificity, a certain degree of fungal genus specificity was also observed during the metabolic interactions between fungal endophytes and grape cells, as fungal endophytes from the same genus tended to be clustered into the same group based on the affected biochemical traits. This work revealed the differential biochemical status effects of fungal endophytes on different varietal grape cells and raised the possibility of reshaping grape qualities by applying endophytes.
- 著者
- Chikage Umeda-Hara Hidekazu Iwakawa Misato Ohtani Taku Demura Tomoko Matsumoto Jun Kikuchi Koji Murata Masaaki Umeda
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.0716a, (Released:2022-09-17)
- 参考文献数
- 28
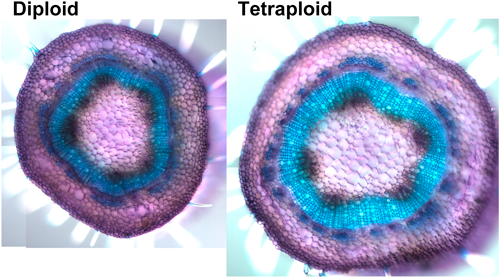
Somatic polyploidization often increases cell and organ size, thereby contributing to plant biomass production. However, as most woody plants do not undergo polyploidization, explaining the polyploidization effect on organ growth in trees remains difficult. Here we developed a new method to generate tetraploid lines in poplars through colchicine treatment of lateral buds. We found that tetraploidization induced cell enlargement in the stem, suggesting that polyploidization can increase cell size in woody plants that cannot induce polyploidization in normal development. Greenhouse growth analysis revealed that radial growth was enhanced in the basal stem of tetraploids, whereas longitudinal growth was retarded, producing the same amount of stem biomass as diploids. Woody biomass characteristics were also comparable in terms of wood substance density, saccharification efficiency, and cell wall profiling. Our results reveal tetraploidization as an effective strategy for improving woody biomass production when combined with technologies that promote longitudinal stem growth by enhancing metabolite production and/or transport.
- 著者
- Linda M. Robles Laura H. Reichenberg James H. Grissom Ⅲ Richard J. Chi Kenneth J. Piller
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- pp.22.0926a, (Released:2022-12-16)
- 参考文献数
- 49
It is estimated that multiple sclerosis (MS) affects over 2.8 million people worldwide, with a prevalence that is expected to continue growing over time. Unfortunately, there is no cure for this autoimmune disease. For several decades, antigen-specific treatments have been used in animal models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) to demonstrate their potential for suppressing autoimmune responses. Successes with preventing and limiting ongoing MS disease have been documented using a wide variety of myelin proteins, peptides, autoantigen-conjugates, and mimics when administered by various routes. While those successes were not translatable in the clinic, we have learned a great deal about the roadblocks and hurdles that must be addressed if such therapies are to be useful. Reovirus sigma1 protein (pσ1) is an attachment protein that allows the virus to target M cells with high affinity. Previous studies showed that autoantigens tethered to pσ1 delivered potent tolerogenic signals and diminished autoimmunity following therapeutic intervention. In this proof-of-concept study, we expressed a model multi-epitope autoantigen (human myelin basic protein, MBP) fused to pσ1 in soybean seeds. The expression of chimeric MBP-pσ1 was stable over multiple generations and formed the necessary multimeric structures required for binding to target cells. When administered to SJL mice prophylactically as an oral therapeutic, soymilk formulations containing MBP-pσ1 delayed the onset of clinical EAE and significantly reduced developing disease. These results demonstrate the practicality of soybean as a host for producing and formulating immune-modulating therapies to treat autoimmune diseases.
- 著者
- Natsu Takayanagi Mai Mukai Munetaka Sugiyama Misato Ohtani
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.329-333, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 18
During organ regeneration, differentiated cells acquire cell proliferation competence before the re-start of cell division. In Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), CDKA;1, a cyclin-dependent kinase, RID1, a DEAH-box RNA helicase, and SRD2, a small nuclear RNA transcription factor, are implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation competence. Here, we report phytohormonal transcriptional regulation of these cell proliferation competence-associated genes during callus initiation. We can induce the callus initiation from Arabidopsis hypocotyl explants by the culture on the auxin-containing medium. By RT-quantitative PCR analysis, we observed higher mRNA accumulation of CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 in culture on the auxin-containing medium than in culture on the auxin-free medium. Promoter-reporter analysis showed that the CDKA;1, RID1, and SRD2 expression was induced in the stele regions containing pericycle cells, where cell division would be resumed to make callus, by the culture in the medium containing auxin and/or cytokinin. However, the expression levels of these genes in cortical and epidermal cells, which would not originate callus cells, were variable by genes and phytohormonal conditions. We also found that the rid1-1 mutation greatly decreased the expression levels of CDKA;1 and SRD2 during callus initiation specifically at 28°C (restrictive temperature), while the srd2-1 mutation did not obviously decrease the expression levels of CDKA;1 and RID1 regardless of temperature conditions but rather even increased them at 22°C (permissive temperature). Together, our results implicated the phytohormonal and differential regulation of cell proliferation competence-associated genes in the multistep regulation of cell proliferation competence.
- 著者
- Takashi Nobusawa Hiroshi Yamatani Makoto Kusaba
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.317-321, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 1
Controlling the flowering time is crucial for propagating plant species and crop production. ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM1 (AMP1) in Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a putative carboxypeptidase, and an AMP1 mutant (amp1) was found to cause highly pleiotropic phenotypes including a short plastochron, an enlarged shoot apical meristem, and reduced apical dominance. Although amp1 also shows an early flowering phenotype, its mechanism has not been investigated in detail. The most important floral integrator or florigen gene, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), has a close relative, TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF). In this report, we generated a new allele of tsf using a genome-editing technique and produced ft tsf double and amp1 ft tsf triple mutants. The flowering time of amp1 ft tsf was equally as late as ft tsf under long-day conditions. In addition, the expression level of FT in amp1 was 2.4-fold higher than that in wild-type, even five days after germination under long-day conditions. These results suggest that the elevated expression level of FT is responsible for the early flowering phenotype of amp1. Furthermore, expression of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), a negative regulator of FT expression, is severely repressed in amp1, raising the possibility that low expression levels of FLC contributes to upregulation of FT expression and the early flowering phenotype of amp1.
- 著者
- Sho Takeda Taisuke Togawa Kei-ichiro Mishiba Katsuyuki T. Yamato Yuji Iwata Nozomu Koizumi
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.303-310, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 37
- 被引用文献数
- 2
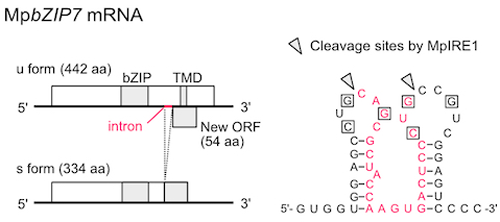
The unfolded protein response (UPR) or the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response is a homeostatic cellular response conserved in eukaryotes to alleviate the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER. In the present study, we characterized the UPR in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha to obtain insights into the conservation and divergence of the UPR in the land plants. We demonstrate that the most conserved UPR transducer in eukaryotes, IRE1, is conserved in M. polymorpha, which harbors a single gene encoding IRE1. We showed that MpIRE1 mediates cytoplasmic splicing of mRNA encoding MpbZIP7, a M. polymorpha homolog of bZIP60 in flowering plants, and upregulation of ER chaperone genes in response to the ER stress inducer tunicamycin. We further showed that MpIRE1 also mediates downregulation of genes encoding secretory and membrane proteins in response to ER stress, indicating the conservation of regulated IRE1-dependent decay of mRNA. Consistent with their roles in the UPR, Mpire1ge and Mpbzip7ge mutants exhibited higher sensitivity to ER stress. Furthermore, an Mpire1ge mutant also exhibited retarded growth even without ER stress inducers, indicating the importance of MpIRE1 for vegetative growth in addition to alleviation of ER stress. The present study provides insights into the evolution of the UPR in land plants.
- 著者
- Edjohn Aaron Macauyag Hiroyuki Kajiura Takao Ohashi Ryo Misaki Kazuhito Fujiyama
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.291-301, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 56
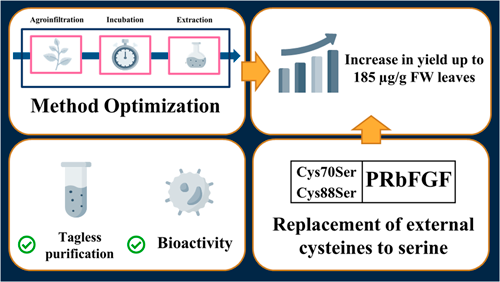
The human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is a protein that plays a pivotal role in cellular processes like cell proliferation and development. As a result, it has become an important component in cell culture systems, with applications in biomedical engineering, cosmetics, and research. Alternative production techniques, such as transient production in plants, are becoming a feasible option as the demand continues to grow. High-level bFGF production was achieved in this study employing an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression system, which yielded about a 3-fold increase in production over a conventional system. This yield was further doubled at about 185 µg g−1 FW using a mutant protease-resistant version that degraded/aggregated at a three-fold slower rate in leaf crude extracts. To achieve a pure product, a two-step purification technique was applied. The capacity of the pure protease-resistant bFGF (PRbFGF) to stimulate cell proliferation was tested and was found to be comparable to that of E. coli-produced bFGF in HepG2 and CHO-K1 cells. Overall, this study demonstrates a high-level transient production system of functional PRbFGF in N. benthamiana leaves as well as an efficient tag-less purification technique of leaf crude extracts.
- 著者
- Yoshiki Tanahara Kaho Yamanaka Kentaro Kawai Yukiko Ando Takashi Nakatsuka
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.273-280, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 28
Matthiola incana is an important floricultural plant that blooms from winter to spring, and had been desired to be established a transformation system. This study successfully obtained stable transgenic plants from M. incana. We used Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring a binary vector containing the β-glucuronidase gene (GUS) under the control of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter to evaluate the transformation frequency of M. incana. We observed that cocultivation with the A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 for 5 days effectively enhanced the infection frequency, assessed through a transient GUS expression area in the seedling. Furthermore, the addition of 100 µM acetosyringone was necessary for Agrobacterium infection. However, we could not obtain transgenic plants on a shoot formation medium supplemented with 1 mg l−1 6-benzyladenine (BA). For callus formation from the leaf sections, a medium supplemented with 1–50 µM fipexide (FPX), a novel callus induction chemical, was employed. Then, the callus formation was observed after 2 weeks, and an earlier response was detected than that in the BA medium (4–6 weeks). Results also showed that cultivation in a selection medium supplemented with 12.5 µM FPX obtained hygromycin-resistant calli. Thus, this protocol achieved a 0.7% transformation frequency. Similarly, progenies from one transgenic line were observed on the basis of GUS stains on their leaves, revealing that the transgenes were also inherited stably. Hence, FPX is considered a breakthrough for establishing the transformation protocol of M. incana, and its use is proposed in recalcitrant plants.
- 著者
- Shilian Huang Yanchun Qiao Xinmin Lv Jianguang Li Dongmei Han Dongliang Guo
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.259-272, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 61
Potassium chlorate can promote off-season flowering in longan, but the molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, four-year-old ‘Shixia’ longan trees were injected in the trunk with potassium chlorate, and terminal buds were sampled and analyzed using transcriptomics and bioinformatics tools. To generate a reference longan transcriptome, we obtained 207,734 paired-end reads covering a total of 58,514,149 bp, which we assembled into 114,445 unigenes. Using this resource, we identified 3,265 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that were regulated in longan terminal buds in response to potassium chlorate treatment for 2, 6 or 30 days, including 179 transcription factor genes. By reference to the Arabidopsis literature, we then defined 38 longan genes involved in flowering, from which we constructed the longan flowering pathway. According to RNA-seq data, at least 24 of these genes, which participate in multiple signaling pathways, are involved in potassium chlorate-stimulated floral induction, and the differential regulation in terminal buds of ten floral pathway genes (GI, CO, GID1, GA4, GA5, FLC, AP1, LFY, FT and SOC1) was confirmed by qRT-PCR. These data will contribute to an improved understanding of the functions of key genes involved in longan floral induction by potassium chlorate.
- 著者
- Zhe-Yu Liu Jiao-Jiao Ji Feng Jiang Xing-Rui Tian Jian-Kuan Li Jian-Ping Gao
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.251-257, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 33
- 被引用文献数
- 4
Codonopsis pilosula, a traditional Chinese medicinal and edible plant, contains several bioactive components. However, the biosynthetic mechanism is unclear because of the difficulties associated with functional gene analysis. Therefore, it is important to establish an efficient genetic transformation system for gene function analysis. In this study, we established a highly efficient Agrobacterium-mediated callus genetic transformation system for C. pilosula using stems as explants. After being pre-cultured for 3 days, the explants were infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 harboring pCAMBIA1381-35S::GUS at an OD600 value of 0.3 for 15 min, followed by co-cultivation on MS induction medium for 1 day and delayed cultivation on medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium for 12 days. The transformed calli were selected on screening medium supplemented with 250 mg l−1 cefotaxime sodium and 2.0 mg l−1 hygromycin and further confirmed by PCR amplification of the GUS gene and histochemical GUS assay. Based on the optimal protocol, the induction and transformation efficiency of calli reached a maximum of 91.07%. The establishment of a genetic transformation system for C. pilosula calli lays the foundation for the functional analysis of genes related to bioactive components through genetic engineering technology.
- 著者
- Elena Kurzbach Matthias Strieker Ute Wittstock
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.241-250, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 42
Glucosinolates, a group of sulfur-containing specialized metabolites of the Brassicales, have attracted a lot of interest in nutrition, medicine and agriculture due to their positive health effects and their involvement in plant defense. Their biological activities and the extensive knowledge of their biosynthesis have inspired research into development of crops with enhanced glucosinolate contents as well as their biotechnological production in homologous and heterologous systems. Here, we provide proof-of-concept for transgenic suspension cultures of carrot (Daucus carota, Apiacae) as a scalable production platform for plant specialized metabolites using benzylglucosinolate as a model. Two T-DNAs carrying in total six genes of the benzylglucosinolate biosynthesis pathway from Arabidopsis thaliana as well as NPTII and BAR as selectable markers were transferred to carrot cells by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Putative transformants selected based on their kanamycin and BASTA resistances were subjected to HPLC-MS analysis. Of 79 putative transformants, 17 produced benzylglucosinolate. T-DNA-integration was confirmed for the five best producers. Callus from these transformants was used to establish suspension cultures for quantitative analysis. When grown in 60-ml-cultures, the best transformants produced roughly 2.5 nmol (g fw)−1 benzylglucosinolate, together with up to 10 nmol (g fw)−1 desulfobenzylglucosinolate. Only one transformant produced more benzylglucosinolate than desulfobenzylglucosinolate. The concentration of sulfate in the medium was not a major limiting factor. High production seemed to be associated with poor growth and vice versa. Therefore, future research should try to optimize medium and cultivation process and to separate growth and production phase by using an inducible promoter.
- 著者
- Yusuke Shikanai Mayu Asada Takafumi Sato Yusuke Enomoto Mutsumi Yamagami Katsushi Yamaguchi Shuji Shigenobu Takehiro Kamiya Toru Fujiwara
- 出版者
- Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology
- 雑誌
- Plant Biotechnology (ISSN:13424580)
- 巻号頁・発行日
- vol.39, no.3, pp.221-227, 2022-09-25 (Released:2022-09-25)
- 参考文献数
- 25
- 被引用文献数
- 3
Calcium (Ca) deficiency affects the yields and quality of agricultural products. Susceptibility to Ca deficiency varies among crops and cultivars; however, its genetic basis remains largely unknown. Genes required for low Ca tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana have been identified. In this study, we identified a novel gene required for low Ca tolerance in A. thaliana. We isolated a mutant sensitive to low Ca concentrations and identified Glucan synthase-like (GSL) 8 as a gene responsible for low Ca tolerance. GSL8 is a paralog of the previously identified low Ca tolerance gene GSL10, which encodes β-1,3 glucan(callose) synthase. Under low Ca conditions, the shoot growth of gsl8 mutants were inhibited compared to wild-type plants. A grafting experiment indicated that the shoot, but not root, genotype was important for the shoot growth phenotype. The ectopic accumulation of callose under low Ca conditions was reduced in gsl8 mutants. We further investigated the interaction between GSL8 and GSL10 by testing the gsl8 gsl10 double mutant for sensitivity to low Ca concentrations. The double mutant exhibited a more severe phenotype than the single mutant under 0.3 mM Ca, indicating additive effects of GSL8 and GSL10 with respect to low Ca tolerance. These results establish that GSL genes are required for low Ca tolerance in A. thaliana.